While search engine optimization (SEO) is essential for your content and offerings to reach your target readers, it is also essential to stay up to date with the latest digital trends.
One of the emerging technologies is generative engine optimization (GEO), which refers to content optimized for the purpose of appearing in AI-generated responses.
Staying relevant today requires content that is optimized both for search and generative engines.
But the question is: How to do it properly?
Keep reading to learn:
- What is generative engine optimization?
- The difference between GEO and SEO
- How do generative AI engines work?
- Pros and cons of GEO
- How to optimize for GEO and SEO
- Optimization tips for the most popular LLMs
- How to measure GEO and SEO performance
- Frequently asked questions
What is generative engine optimization?
Generative engine optimization (GEO) is the process of optimizing content on web pages with the goal of ensuring it is properly displayed in AI-driven search engines such as ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Copilot, and others—including tools like an AI image generator.
The purpose of generative engine optimization is to improve the visibility of a website within popular large language models (LLMs), enhance brand awareness online, increase organic traffic, and improve user experience and satisfaction across AI-driven platforms.
Here’s an example of how an optimized website can appear within a generative AI engine such as ChatGPT:
Unlike traditional search engines, which crawl, index, and rank web pages, AI-driven engines are capable of generating comprehensive answers and creative solutions based on the user’s query.
While searching a specific query in a traditional search engine (such as Google) typically results in a list of ranked pages—based on how optimized they are and how well they answer the query—AI models provide detailed responses in real time, often including sources and context from multiple data points.
GEO vs. SEO: What is the difference?
While both SEO and GEO aim to increase the visibility of content, there are key differences in terms of the platforms they target and the overall user experience.
Some of the main differences include:
1. Objective
- SEO: Focuses on improving website ranking on traditional search engines (such as Google or Bing).
- GEO: Optimizes content for inclusion in the AI-generated responses in platforms like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Bard.
2. Content display
- SEO: Displays web pages by relevance and quality of the page in relation to the search engine query.
- GEO: Provides real-time generated AI responses that summarize information from multiple sources.
3. User interaction
- SEO: Users have to click on individual links to access relevant web pages.
- GEO: Users receive responses with sources, reducing the number of clicks and effort required by the users.
4. Content structure
- SEO: Content is optimized for specific keywords, with technical and on-page SEO in mind.
- GEO: Provides users with authoritative content pulled from multiple sources, structured to answer the user’s query.
5. Performance metrics
- SEO: Measures performance based on traffic and conversion.
- GEO: Measures results by how often the content is used or referenced by AI-generated results.
How do generative AI engines work?
Generative AI models leverage advanced machine learning models (large language models, LLMs) to generate comprehensive responses to the user’s query.
Behind many of these generative AI engines are complex, custom-built systems that require scalable architecture, data pipelines, and continuous model optimization. To support this level of technical sophistication, companies often rely on nearshore software development to extend their engineering capabilities while maintaining close collaboration and faster iteration cycles.
These generative language models are trained on vast amounts of data, relying on books, articles, websites, and other available online content.
This allows generative AI models to produce human-like responses, synthesize data, and create new content that aligns with the user’s search intent.
Here is a breakdown of how the generative AI models work:
- Data training: Generative AI models are trained through large datasets. This allows the artificial intelligence to learn patterns in grammar, context, tone, and more.
- Natural language processing: Natural language processing (NLP) is at the core of generative AI. It allows these models to comprehend the context and intent of the user’s query. It also helps these models understand the nuances of the language, ensuring the responses are accurate and relevant.
- Patterns: AI models are trained to recognize patterns within the data they are trained on. Once a user asks a question, AI analyzes the question to identify patterns and, consequently, provide the most appropriate response to the user’s query.
- Context: Generative AI models can understand the context behind a query. Unlike traditional search engines that look for keywords, these AI models look at the user’s entire input, considering intent, tone, and context, offering a more holistic and nuanced answer to the user’s inquiry.
- Continuous learning: Generative AI platforms are consistently updated with new data, giving them the ability to evolve and provide more accurate responses. This ongoing learning ability allows them to keep up with the newest trends and developments across industries and niches.
Some of the most popular generative engines right now include:
- ChatGPT
- Claude
- Bard
- Gemini
- DALL-E 2
- Google AI Overviews
Benefits & drawbacks of GEO
Much like with any emerging technology, generative engine optimization presents itself with a particular set of benefits and drawbacks.
Benefits of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
- Enhanced user experience: GEO delivers comprehensive and immediate responses to users. This removes the need to go through multiple pages, streamlining the process of acquiring information and improving user experience.
- Improved content visibility: Businesses that optimize their content for generative AI models increase their chances of being featured in generated responses, consequently increasing the visibility of their brand.
- Adapting to the evolving search trends: As more and more users turn to generative AI models for their queries, businesses that implement GEO strategies will position themselves ahead of competitors who failed to do so.
Drawbacks of Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)
- Unclear metrics: While it is possible to track and measure the metrics for traditional SEO (click-through rates, traffic, etc.) the metrics for GEO are still harder to quantify. This means that it is more difficult to determine their effectiveness and ROI.
- Dependence on AI platforms: Conducting GEO means relying on the AI platforms and the changes the platforms incorporate.
- Content quality and saturation: As more companies start optimizing their content for generative engines, there’s a chance of oversaturation in the market. This heightened competition could result in a decline in quality, as many brands might end up using the same keywords and content structures.
How to optimize for GEO and SEO?
If businesses wish to stay competitive in today’s market, they have to optimize for both – search engines and generative engines.
Below are the steps you can take to stay ahead of the competition.
1. Perform holistic research
Holistic research refers to fully understanding your market, users, and competitors.
It involves careful consideration and analysis of various types of content to inform content creation and strategies.
Things to consider:
- Long-tail keywords and questions: Identify and utilize long-tail keywords. These types of keywords often lead to higher conversion rates and help in targeting specific queries that generative AI models pull from.
- Analyze your competitors: Review what your competitors are doing and what content they are ranking for. Assess their topics, keyword usage, and content strategies to identify areas of opportunity for your own content.
- Evaluate your brand in AI platforms: Regularly check how your brand is represented across various AI platforms. Ensure that your content is accurately indexed and linked to your brand’s authority.
- Thorough content research: Conduct extensive content research. This will allow you to create content that is rich, nuanced, and comprehensive, which is generally preferred by AI models.
2. Create high-quality & relevant content
High-quality content is essential for you to rank in both traditional search engines and generative AI platforms. This enhances the user experience and increases your chances of being featured in AI-generated responses.
Follow the below steps to produce content that will help you rank higher than the competition:
- Implement structured data: Utilizing structured data markup can help search engines and AI models grasp the context of your content better. This can enhance how your content appears in search results and AI-generated responses.
- Content distribution across various platforms: Share your content across various platforms to boost its visibility. This means using social media, blogs, newsletters, and forums to make sure it reaches a broader audience. When creating training and educational content, using an interactive learning platform can significantly improve content quality and user engagement.
- E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness): Build credibility by highlighting your experience and expertise in your content. Adding author bios, references, and citations can help boost trust and reliability.
- Brand authority: Establish your brand’s authority by becoming a thought leader. Sharing valuable insights in industry conversations can make your brand a trusted source of information, which increases the likelihood of being featured in AI-generated responses.
3. Focus on technical SEO
Technical SEO is essential for a successful optimization strategy, particularly when it comes to generative engine optimization (GEO). It helps ensure that your website is set up so that search engines and AI models can easily crawl and index your content.
This involves optimizing site speed, making sure your site is mobile-friendly, implementing SSL security, and keeping a clear site structure.
Effective technical SEO strategies:
- Optimize page speed and mobile friendliness: Make sure your website loads quickly and is mobile-friendly. These elements are vital for both SEO rankings and user experience, influencing how AI models interact with your site.
- Utilize clear URL structures: Create straightforward, descriptive URLs that accurately reflect the content of each page. This helps both users and AI understand what to expect from your content.
- Implement internal linking: Use internal links to help guide users through related content on your site. This not only improves the user experience but also assists AI models in grasping the connections between different pieces of content.
- Monitor technical performance: Regularly check your website for any technical issues that might affect performance, such as broken links or incorrect redirects. Tools like Google Search Console can effectively track these metrics.
Optimization tips for the most popular LLMs
1. ChatGPT
ChatGPT, developed by OpenAI, is one of the most widely used language models. It is optimized to assist in a wide variety of tasks such as content creation, data analysis, and conversational AI.
Since ChatGPT is designed to produce coherent and contextually relevant responses, it’s vital to optimize your website content to align with its language processing capabilities.
Authority and content relevance are crucial factors, and the model can be influenced by real-time updates as future versions will handle more dynamic data.
How to optimize websites for ChatGPT:
- Brand mentions: Boost brand visibility by acquiring mentions across high-authority, relevant websites. The more often your brand is mentioned on trusted platforms, the more likely ChatGPT will recognize it.
- Relevancy and content quality: Focus on delivering content that directly addresses user queries. The more closely your content aligns with keywords in the model’s training data, the higher the chances of it being recommended.
- Age of content: Older products or companies tend to get recommended more often. If your product has been around for a while, ensure it’s documented thoroughly online.
- Domain authority: Build your domain’s authority through quality backlinks from trusted sources, particularly from authoritative, niche-specific outlets.
- Reviews: Positive reviews across trusted platforms (e.g., Amazon, TrustPilot) can help improve your ranking.
- Conversational tone: Content that is written in a conversational tone can better match the way ChatGPT interacts with users. Use engaging, user-friendly language to increase your chances of ranking well in ChatGPT-powered search results.
- Content updates: Although ChatGPT’s index is not real-time, ensure your content is consistently updated to maintain relevance when the model is retrained.
2. Perplexity
Perplexity AI is an advanced search engine powered by an LLM that provides answers directly to user queries, much like a conversational assistant.
It’s designed to provide relevant, insightful answers to questions and perform contextual searches.
Unlike traditional search engines, Perplexity leans more towards up-to-date, relevant content. This model rewards current and niche content, making it ideal for topics in rapidly evolving fields.
How to optimize websites for Perplexity:
- Leverage niche content: Content relevant to specific industries or fields (e.g., tech, SaaS) tends to rank higher. Platforms like b2bsaasreviews, thecmo, and b2bmarketing are highly regarded.
- Citations over backlinks: Focus on being cited by authoritative industry sites, as Perplexity places more value on citations than traditional backlinks.
- Regular content updates: Since Perplexity pulls from current web data, keep your content up-to-date to align with trending topics.
- PR strategy: Build relationships with industry leaders and get featured in authoritative outlets to increase visibility on Perplexity.
- Topic authority: Establish your website as an authority on specific topics. Perplexity tends to favor authoritative content, so try to generate long-form, in-depth articles that cover a subject comprehensively.
3. Claude
Claude is an LLM developed by Anthropic. Known for its safety and alignment features, Claude is designed to reduce harmful outputs while generating text in a responsible way.
Claude prioritizes long-form, reliable content. It’s trained on a large corpus that includes a variety of sources, but it emphasizes high-quality and helpful content over keyword stuffing.
How to optimize websites for Claude:
- Long-form content: Claude is great at processing extensive, well-structured content. Invest in creating comprehensive, authoritative articles or whitepapers that provide in-depth answers.
- Authoritative sources: Ensure your brand is consistently cited by reputable sources like academic journals, news outlets, and industry leaders.
- Avoid keyword stuffing: The algorithm is designed to prioritize context and coherence over excessive use of keywords.
- Clear structure: Ensure your content is organized with well-defined sections, bullet points, and concise language. This not only aids human readers but also helps Claude understand and rank the content better.
4. Llama
Meta Llama is designed to handle a variety of tasks, including information retrieval and content generation.
This model is particularly known for its versatility and efficiency in processing natural language.
While it has a public data access model, it’s less specific than proprietary models like GPT-4o. Its flexibility allows for more diverse content but may not favor highly specialized topics.
How to optimize websites for Llama:
- Broad content coverage: Create diverse, high-quality content that appeals to a wide audience. This model favors content that can cater to various topics.
- Leverage open-source platforms: Participate in open-source projects or contribute to communities where Meta Llama’s data may pull from.
- Consistency: Keep publishing fresh, valuable content across different areas of your website to maintain visibility.
- Optimize for semantic search: Since Meta Llama’s algorithms rely on understanding context, ensure your content is well-structured and semantically rich.
5. DeepSeek
DeepSeek is an AI-powered search engine from China that focuses on content’s relevance, context, and user intent.
It uses deep learning and NLP techniques to rank content based on its depth and ability to provide value.
How to optimize websites for DeepSeek:
- Content quality over keywords: Prioritize detailed, informative articles that answer user queries comprehensively. DeepSeek values substance over superficial keyword use.
- Optimize for user intent: DeepSeek emphasizes understanding what the user truly needs, so structure your content to address specific questions in a clear and concise manner.
- Focus on technical SEO: Improve site speed, mobile-friendliness, and use structured data (e.g., Schema Markup) to help DeepSeek understand your content.
- Regional content for Chinese audiences: If targeting the Chinese market, create content that is relevant to regional users, incorporating cultural nuances.
6. Qwen
Qwen is a relatively newer LLM that emphasizes the novelty of information and seeks to cater to curiosity-driven content. It likely favors more innovative or cutting-edge topics.
How to optimize websites for Qwen:
- Answering specific queries: Qwen ranks well when content is highly responsive to user queries. Focus on providing clear, concise answers to frequently asked questions, and ensure you are addressing the intent behind the search.
- Innovative content: Focus on creating content around emerging technologies, innovative practices, and forward-thinking topics. Align your content with Qwen’s curiosity-driven nature.
- Structured data: Leverage structured data (such as schema markup) to help Qwen easily identify the most relevant portions of your content. Structured content, like lists and tables, can help highlight important information.
- Engage with current trends: Create content around current trends or questions being actively discussed in the industry to capture Qwen’s attention.
7. Gemma 3
Gemma 3 is an LLM that is designed for handling diverse information retrieval tasks, offering highly contextual responses. It is part of a new wave of AI models optimized for complex queries.
How to optimize websites for Gemma 3:
- Engagement-focused content: Craft content that encourages user interaction, such as discussions, comments, or feedback.
- Community-driven content: Build content that resonates with niche communities, encouraging sharing and participation.
- User-generated content: Integrate user-generated content into your website to increase its visibility in Gemma 3’s ranking system.
- Use of visuals: Gemini often enhances the user experience with integrated visual content. Make use of high-quality images, infographics, and other visuals to support your content and provide richer experiences.
8. Gemini
Gemini is closely tied to Google’s web data and indexing. It likely favors content that performs well on traditional search engines and aligns with Google’s ranking factors.
How to optimize websites for Gemini:
- Google SEO best practices: Ensure your content is optimized for Google’s algorithm, as Gemini will likely prioritize pages that already rank well on Google.
- Authoritative, current content: Focus on creating content from authoritative sources and ensure that your site’s content is regularly updated.
- Mobile and technical SEO: Gemini will likely prioritize fast-loading, mobile-optimized pages with structured data, so focus on technical SEO.
- Content relevance: Since Gemini ranks based on deep understanding of user intent, prioritize content that is highly relevant to the search query. Use clear headlines and subheadings to focus on the main theme of the query.
How to measure GEO and SEO performance?
To accurately assess how well your generative engine optimization (GEO) and search engine optimization (SEO) efforts are performing, it’s important to use a range of measurement tools.
Each tool offers unique insights into different areas of your performance, helping you refine your strategies as needed.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free site monitoring tool that helps you track your site’s performance on Google.
It provides insights into keyword rankings, click-through rates, and indexing status.
Mangools SERPWatcher
Mangools is a fantastic suite of SEO tools designed to help boost your website’s visibility online.
One of our standout products is SERPWatcher, which simplifies tracking your website’s performance in search engines for all important keywords.
It provides daily updates and a performance index to gauge the potential traffic from specific keywords.
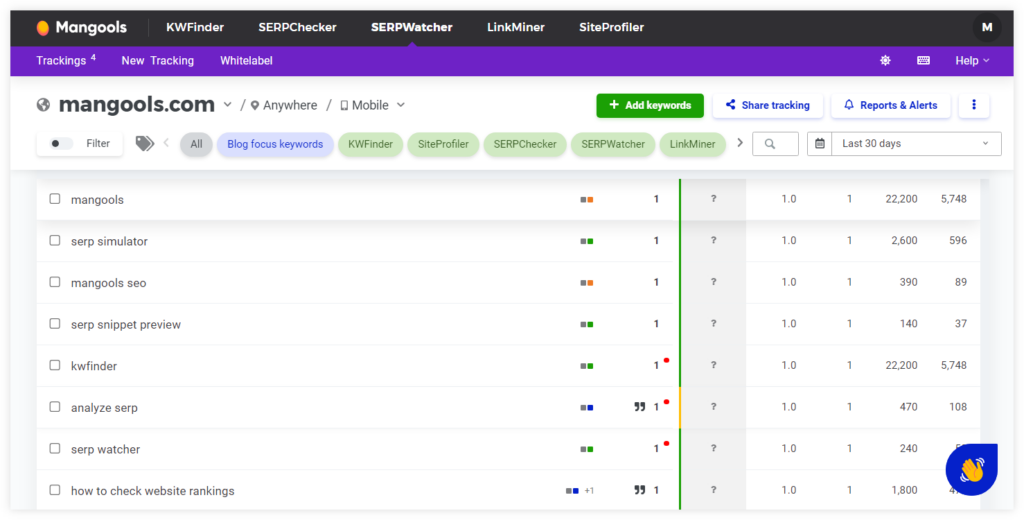
In addition to the rank-tracking tool, Mangools offers other essential SEO tools to help you rank higher in Google SERPs:
- KWFinder: A powerful keyword research tool that helps you quickly find high-volume, low-difficulty keywords.
- SERPChecker: This tool allows users to analyze search engine results pages (SERPs) for any given keyword, helping you understand the competitive landscape and identify opportunities.
- LinkMiner: A powerful backlink checker that helps you find potential external links from other websites in seconds.
- SiteProfiler: A straightforward website domain authority checker that provides you with all the essential SEO metrics for any domain.
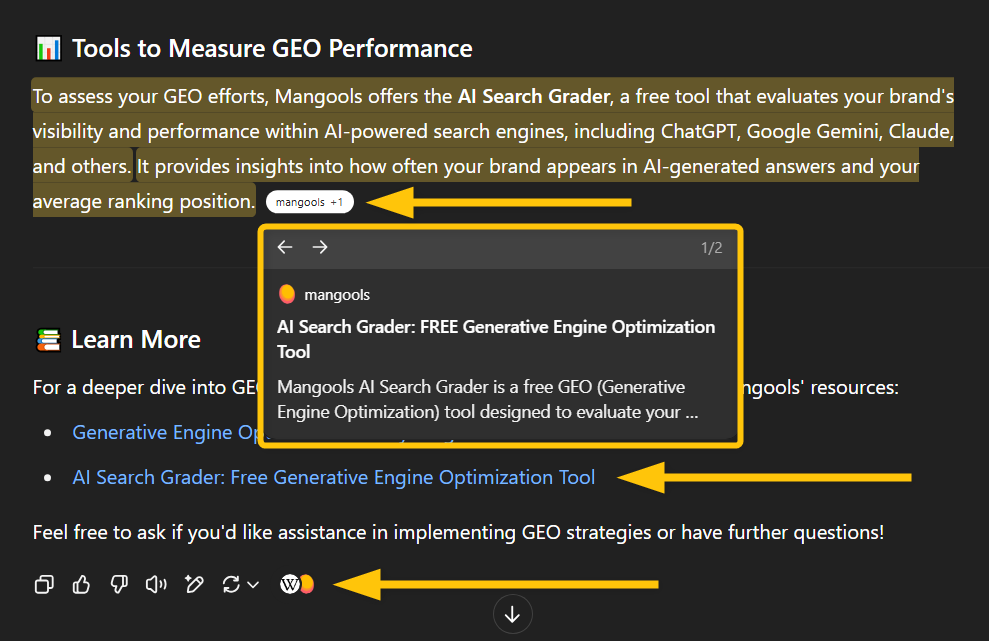
Mangools AI Search Grader
AI Search Grader is a free generative engine optimization tool designed to evaluate and grade how your brand or website performs in ChatGPT’s search results.
This tool helps you comprehend the overall visibility of your brand in your niche within the online world. It also provides insights into how your brand is perceived compared to your competitors.
Using the tool is straightforward—simply enter your brand name (or one of your competitors) and provide a description of your product or the niche in which it operates.
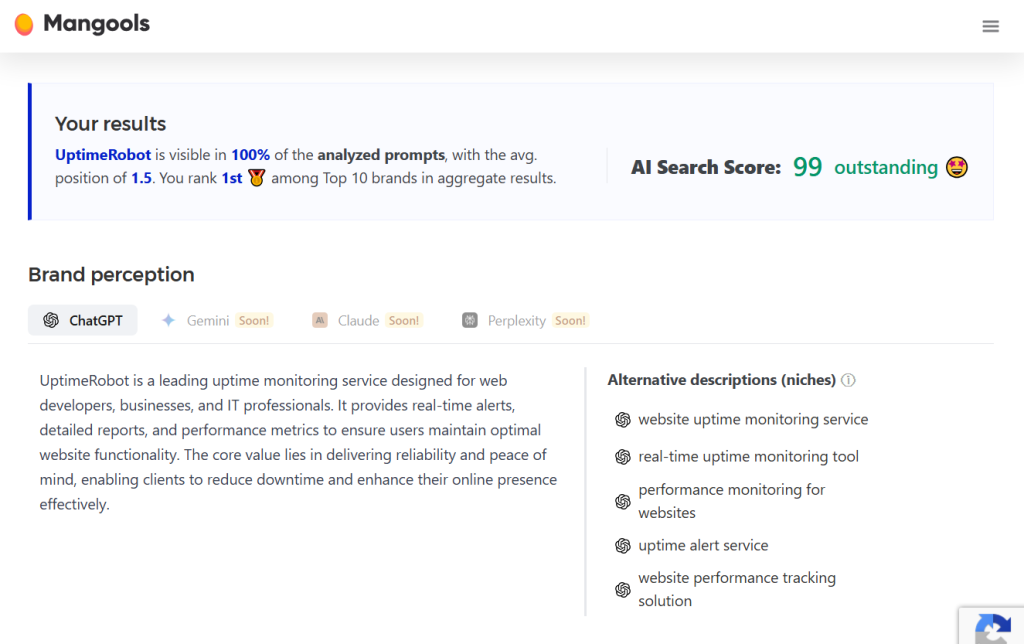
AI Search Grader will run a test by generating various relevant prompts based on the information you provided.
It will analyze multiple AI responses to check the percentage of prompts in which your brand appears and assess the average position of your brand in AI-generated recommendations.
At the end of the test, you will receive a report that calculates your brand’s importance based on ranking positions and visibility.
Google Analytics 4
Google Analytics 4 (GA4) provides a detailed look at how users interact with your website.
By examining where your traffic comes from, how users engage with your content, and your conversion rates, you can gain valuable insights into your website’s performance across various platforms.
Frequently asked questions
Is GEO replacing SEO?
GEO, or Generative Engine Optimization, is not replacing SEO; rather, it’s a new approach that complements it.
While SEO focuses on traditional search engines, GEO optimizes content for AI-driven search engines, ensuring that it meets the needs of both human users and AI algorithms.
What is the difference between generative AI and traditional AI?
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that creates new content, such as text, images, or music, based on patterns learned from existing data.
In contrast, traditional AI primarily analyzes and interprets data to make decisions or predictions.
What is the difference between SEO, SGE, and GEO?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) aims to improve visibility in traditional search engines through keyword targeting and backlinks.
SGE (Search Generative Experience) leverages AI to provide more contextual search results. GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) focuses on optimizing content specifically for AI-driven search engines to enhance its visibility in generated responses.
How do I turn on Google AI generative search?
To enable Google’s generative search features, check your Google account settings or search settings for options related to experimental features or AI enhancements. Simply toggle them on if they’re available.