What is CTR?
CTR (Click-Through Rate) is a metric that measures the ratio of users who clicked on the hyperlink to the total number of people who saw the hyperlink.
In SEO, it is used to see how many people clicked on the snippet of your page in the SERP.
How to calculate CTR?
CTR is calculated as the total number of clicks on the link divided by the total number of times the link was displayed (so-called impressions). The result is then multiplied by 100 to obtain a percentage number.
Here’s how the CTR formula looks like:
CTR = (Number of clicks ÷ Impressions) × 100
So for example, if the link was displayed to 1000 users and 200 of them clicked on it, the CTR of this hyperlink would be calculated like this:
CTR = (200 ÷ 1000) × 100 = 20%
Why is CTR important in SEO?
CTR informs you about the performance of your pages that are ranking in the SERPs.
The purpose of SEO is to bring as much relevant organic traffic to your website as possible – not only to rank high with your pages in Google Search.
By measuring the CTR of your ranking pages, you can determine how many people visited them from the overall number of users in the SERP.
Or as Matt Cutts explained:
“So many people think about rankings and then stop right there. And that’s not the right way to think about things. You want to think about rankings and then you want to think about maximizing your click-through…”
Note: CTR as a performance metric is also used in other branches of digital marketing:
- Paid ads – the performance (and the price) of ads in Google Search is measured by CTR for various keywords.
- Email marketing – you can measure how many people clicked on the link in your email from the overall number of people who opened it.
- Social media advertising – the CTR metric can show you how many people viewed your advertisements and how many of them actually clicked on it or made an action.
Besides the advertisement, CTR is also used for measuring the performance of internal links within the website, CTA (call-to-action) elements, etc.
Is CTR a ranking signal?
Click-through rate is not a ranking signal in Google’s algorithm.
The purpose of CTR is to tell the website owners how their pages are performing in Google Search – not to improve their rankings in SERPs.
CTR is a controversial topic in the SEO community – In 2014, the test done by Rand Fishkin indicated that CTR might be a ranking factor. This created a buzz in SEO and led to experiments with click volumes and manipulation of search results.
Unfortunately, there is no clear evidence that the CTR plays a role in Google’s ranking algorithm – Google representatives officially stated several times that it is not a ranking signal.
Even Gary Illyes, the Webmaster Trends Analyst clearly stated:
@philpearce we must have had some serious misunderstanding. These metrics are way too noisy for search in general @dejanseo
— Gary 鯨理/경리 Illyes (so official, trust me) (@methode) November 27, 2015
However, CTR can be sometimes used in the personalization of the search results.
If the typed search query has more than 1 meaning, Google will take into account the CTR as a signal that the user prefers a certain type of results.
For example, if you type “apple” into Google Search, it can mean either fruit or the Apple Company – the search engine will therefore check on which type of results you clicked more and provide similar results the next time you type “apple” as a search query – but this will apply only to you, not to the rest of Google users.
What is a “good” click-through rate?
There is no universal number for CTR that would determine whether your campaigns can be considered a success or failure.
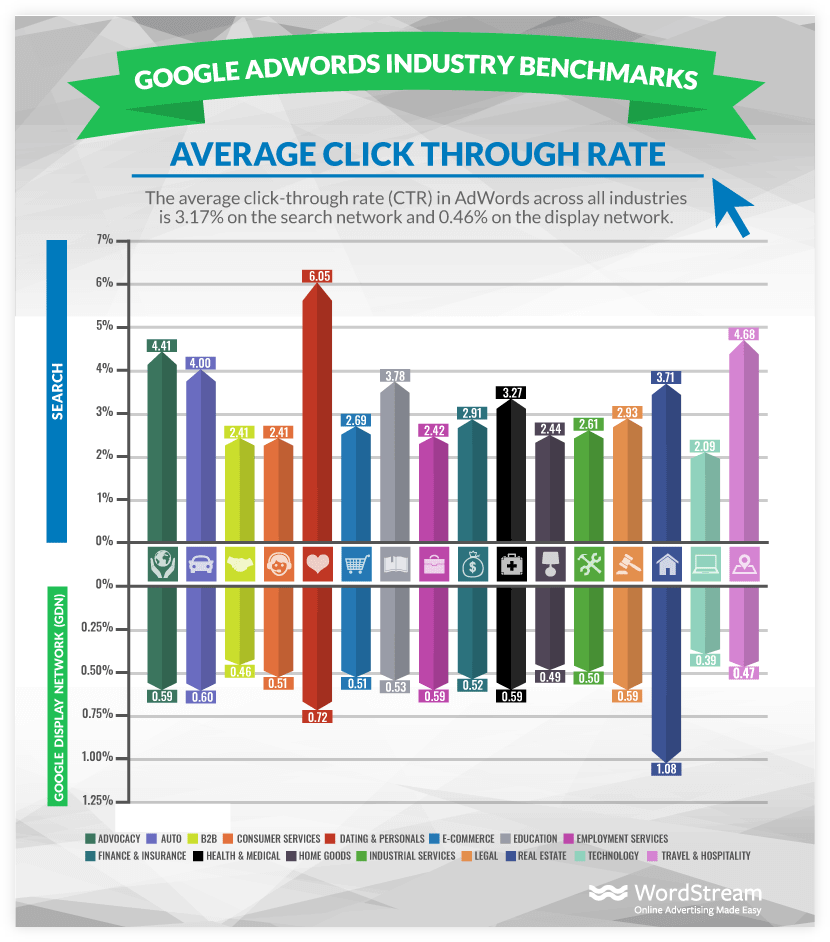
The ideal click-through rate varies from industry to industry, type of online campaign, or even from keyword to keyword.
For example, the average CTR for Google Ads can be different across various types of industries. Depending on the type of the ad, the average CTR can range from less than 1% to more than 6%:
These large differences can be also seen in other digital marketing campaigns such as organic results, email marketing, social media posts, Whatsapp marketing etc.
From the SEO perspective, it is important to understand that CTR can be completely different for every keyword that you are ranking for in the SERP – there might even be zero-click searches with a CTR of 0%.
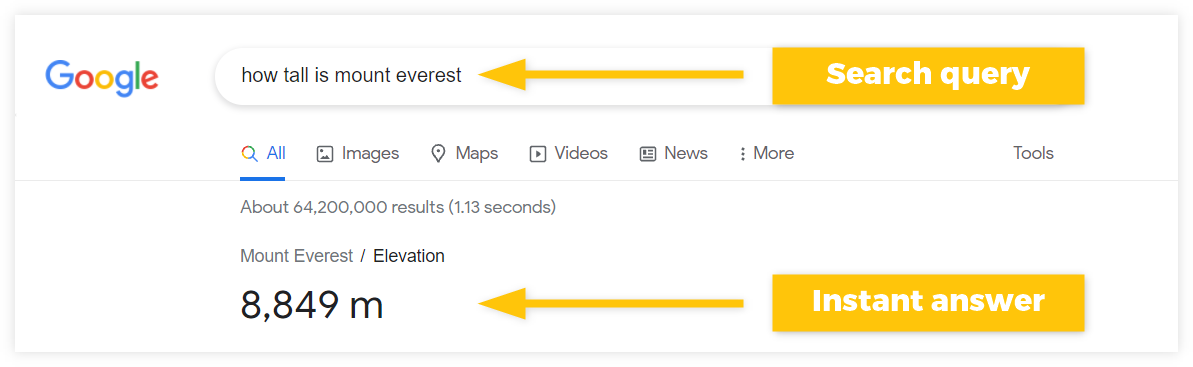
What are Zero-click searches?
Zero-click searches provide a direct answer in the SERP so the user does not need to actually click on any of the search results.
These queries are usually long-tail keywords or questions that can be answered directly in Google SERP:
How to check your CTR?
Click-through rate can be checked in Google Search Console – it is the most common and easiest way to determine the performance of your pages.
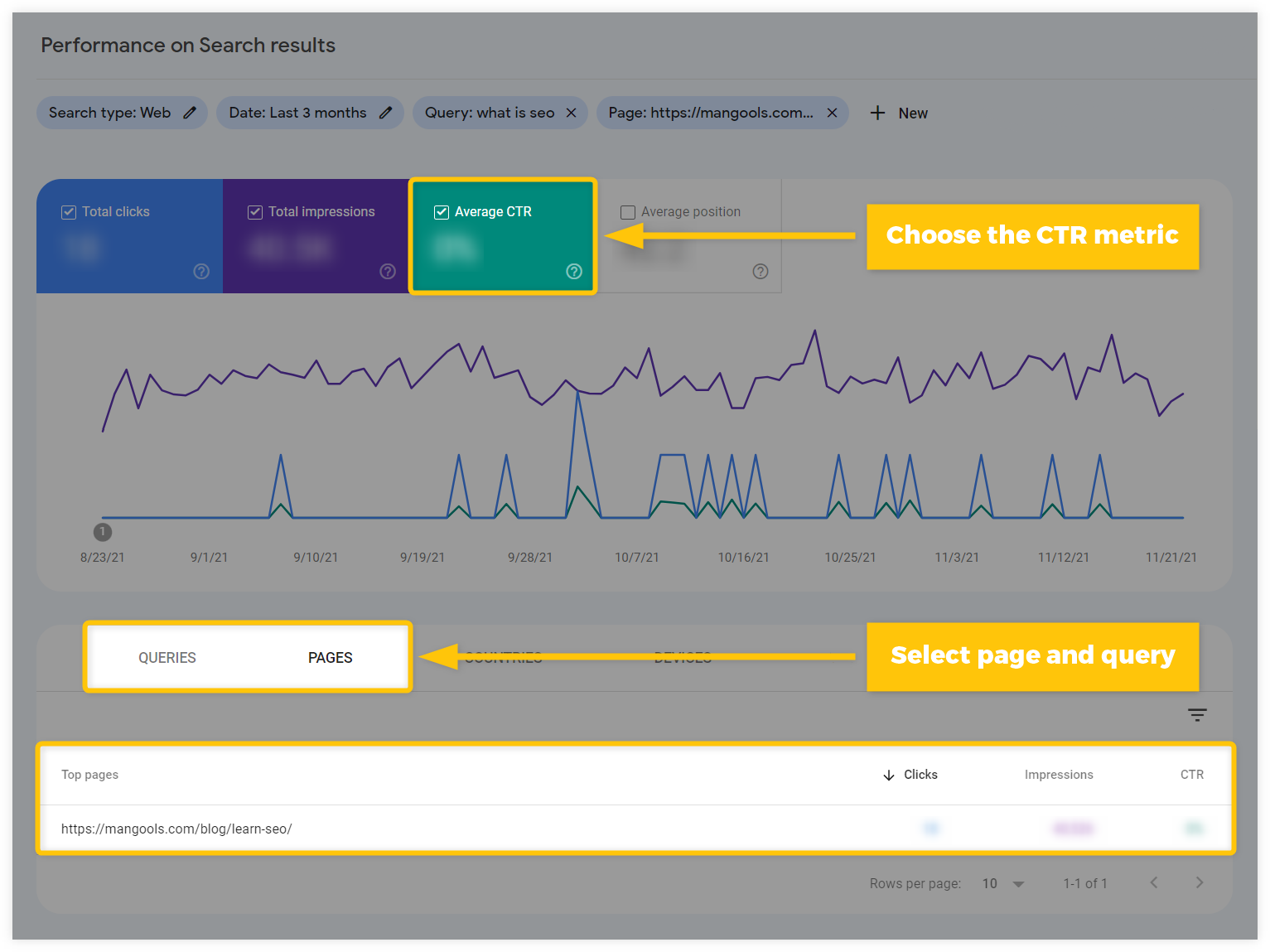
The default CTR value you see in the Performance report is an average of all the CTR values for all the pages and all the queries they rank for. To get the most relevant results for your analysis, always specify the page and the query.
To see what is the average CTR of your individual webpages in Search Console:
- Head over to the Search results section
- Choose the Average CTR metric above the Performance chart
- Define the Date range if you want to check the CTR of your pages within a specific timeline
- Select the Pages tab under the chart
- Find and check specific pages with their average CTR
- Select query
You can also use filter to display only those pages that fall under a certain CTR range.
Note: Keep in mind that Google Search Console might not be the most accurate tool for measuring CTR – it uses simplified aggregated data for clicks, impressions, and click-through rate which can lead to some discrepancies between the data from GSC and other tools (e.g. Google Analytics).
For more information about how CTR is measured in Google Search Console, check out the article about impressions, position, and clicks in Search Console Help.
What impacts CTR of organic results?
The click-through rate of the search result can be influenced by many factors such as:
- Ranking position
- Presence of the ads
- SERP features
- Type of the query
- The appearance of the snippet
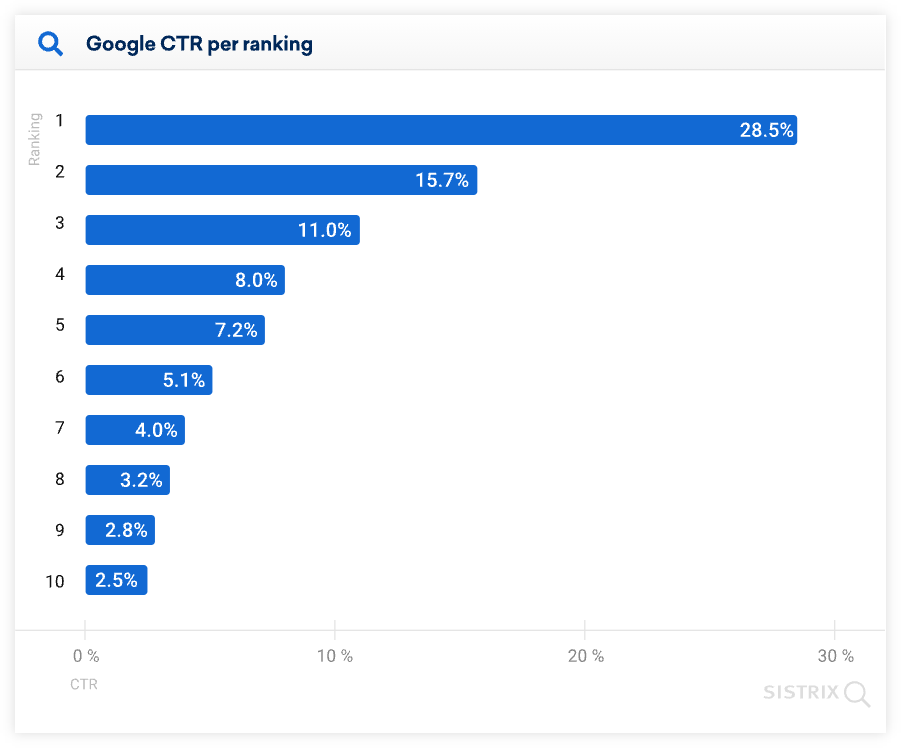
The main factor that influences the CTR of the organic search result is its position in the SERP.
Generally speaking, the top results are the most clicked on by the users.
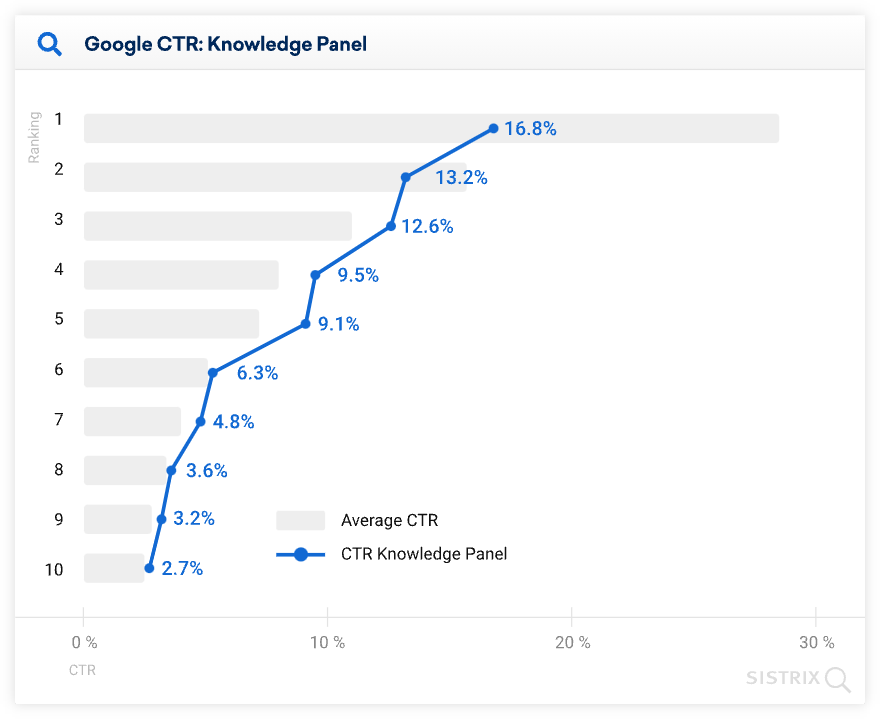
According to a study done by Sistrix, the first 3 search results have the highest CTR from the top 10 ranking pages – therefore they get the most of the organic traffic from the SERP:
But there are also other factors that may influence the CTR of the organic results.
1. Google Ads
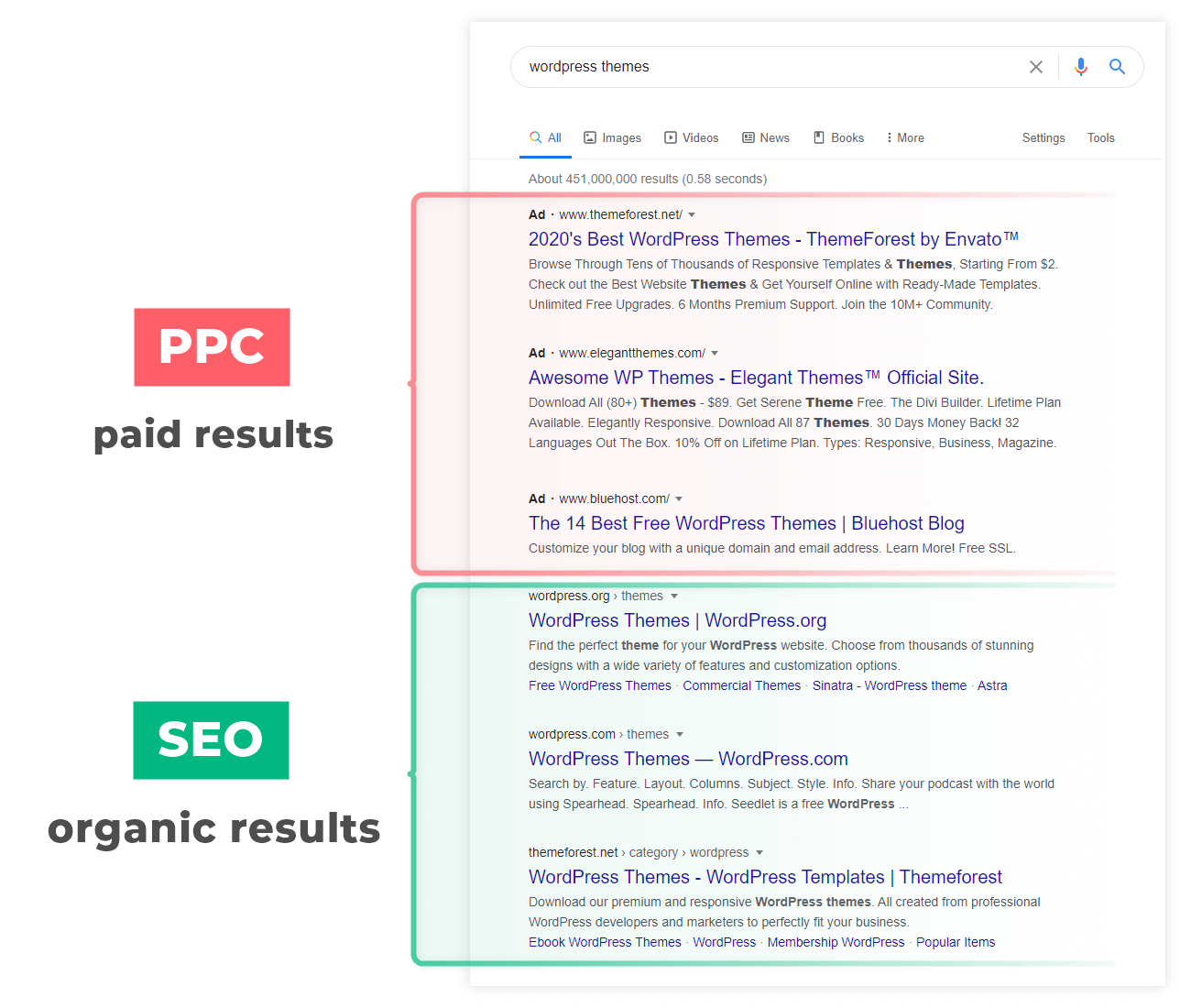
SERPs which contain paid advertisements usually have lower CTR for organic results.
Google Ads often appear together with organic results in Google Search – they can appear at the top, bottom, or somewhere in the middle of the SERP:
Because of the paid ads, the click-through rate of organic results may be significantly reduced – since Google Ads can “steal” some of the clicks in the SERP.
2. SERP features
CTR of the organic search results can be drastically changed by the presence of SERP features.
The number of clicks on the organic results can decrease (or even increase) according to the SERP features that are present in the SERP.
For example, Knowledge Panel (as a SERP feature) can significantly lower the CTR of all search results since it takes up a lot of space and provide instant answers to Google users:
On the other hand, certain SERP features such as Sitelinks or Rich Snippet may drastically improve the CTR of the search result.
3. Type of the query
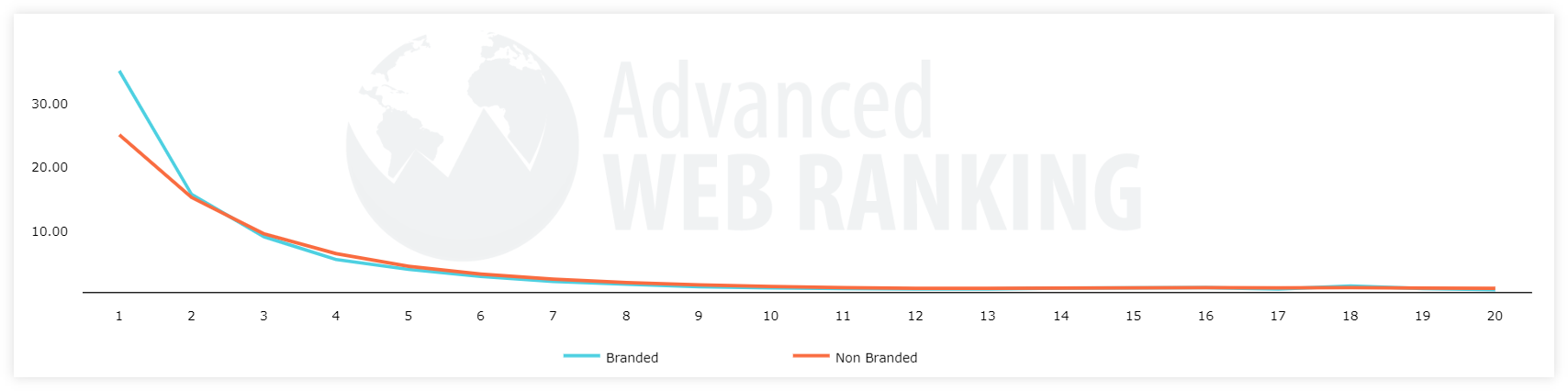
Branded search queries provide higher CTR at the top positions than the non-branded ones.
Generally speaking, branded queries usually have navigational intent – users are trying to find a specific website by using its brand name in the search.
This leads to the decrease in CTR of other search results in the SERP since the user is not looking for random websites, only for the specific brand:
Furthermore, the length of the search query may also influence the click-through rate of organic results – long-tail keywords can provide higher CTR for ranking pages as opposed to general one-word/two-word search terms.
4. Snippet optimization
A well-written and optimized snippet may significantly improve the CTR of the organic result in Google SERP.
Users who find provided snippet relevant and attractive can be much more compelled to click on the result as opposed to the generic snippets with automated descriptions and titles.
How to improve the CTR of organic results?
The click-through rate of ranking pages in the SERP can be increased by:
- Optimizing title tags
- Providing attractive meta descriptions
- Creating useful URLs
- Implementing Structured data
Let’s break down every element individually.
1. Write appealing title tags
Catchy and attractive Title Tags are the first thing that can catch the user’s attention in Google Search and therefore significantly improve the CTR of your ranking pages.
For creating a good title, you should:
- Write a concise headline
- Include relevant keyword
- Use power-words and numbers
- Utilize special symbols
2. Optimize meta descriptions
Meta descriptions might not be only informative – they can also attract users to click on the search snippets and improve their CTR.
By creating well-written descriptions, users can immediately know what your pages are about and be more inclined to click on them.
You can improve copies of your meta descriptions by:
- Writing short and accurate copy
- Providing original text for every snippet
- Including CTA (Call-To-Action) phrases
- Using special symbols and characters
3. Create descriptive URLs
Descriptive URLs and optimized slugs can give Google users a better idea about the structure of your website.
They can also look more attractive in the SERP as opposed to randomly generated URLs:
To create a useful URL, make sure that it is:
- Short but descriptive
- Contain focus keyword
- Separate words with hyphens (-)
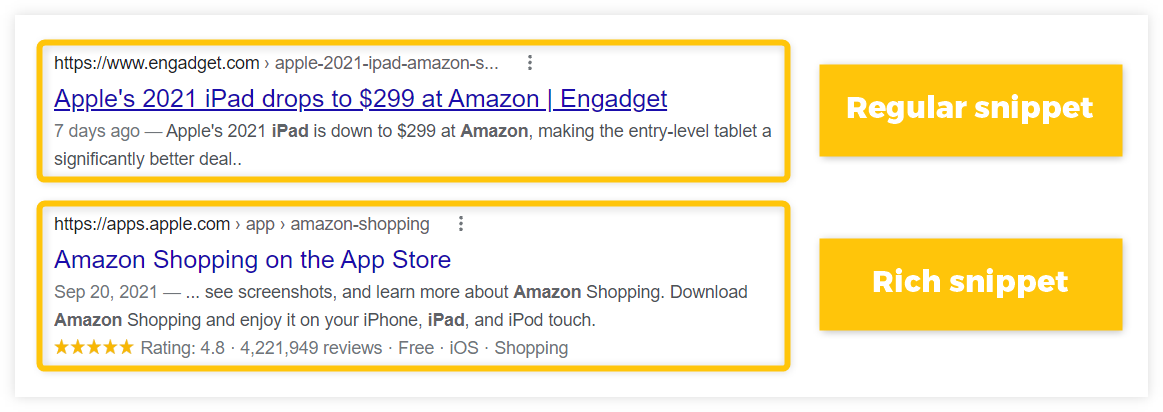
4. Use rich results
Rich results can significantly boost the CTR of the page in the SERP – they look much more attractive as opposed to regular search snippets:
By implementing structured data to your pages, you can visually enhance your pages in the SERP and boost their CTR with various features such as:
- Breadcrumbs
- Reviews
- Prices and dates
- Thumbnails
- FAQ
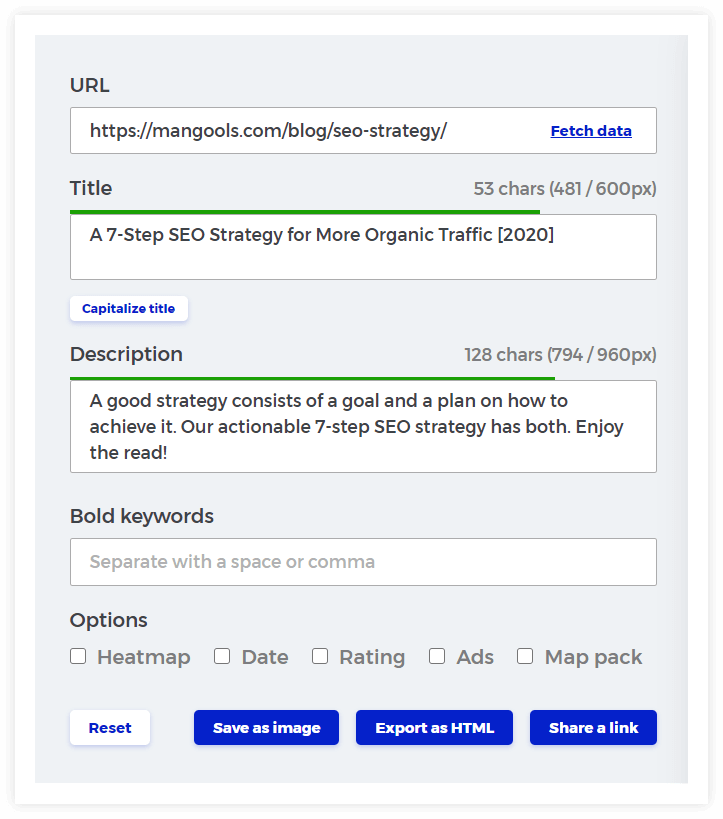
Tip: You can check and test the appearance of your pages in the SERP with our free SERP Simulator tool so you can improve their CTR in Google Search: