To follow or not to follow? We’re not talking about the newest Instagram influencers – we’re talking about nofollow & dofollow links!
When it comes to SEO, understanding the distinction between nofollow and dofollow links is another aspect you’ll need to master to succeed.
In this article, we will therefore take a look at:
- What are nofollow links
- What are dofollow links
- Why are nofollow links important
- When to use nofollow links
- When to avoid nofollow links
- How to check nofollow/dofollow links
- How to manage nofollow and dofollow links
- Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s get started
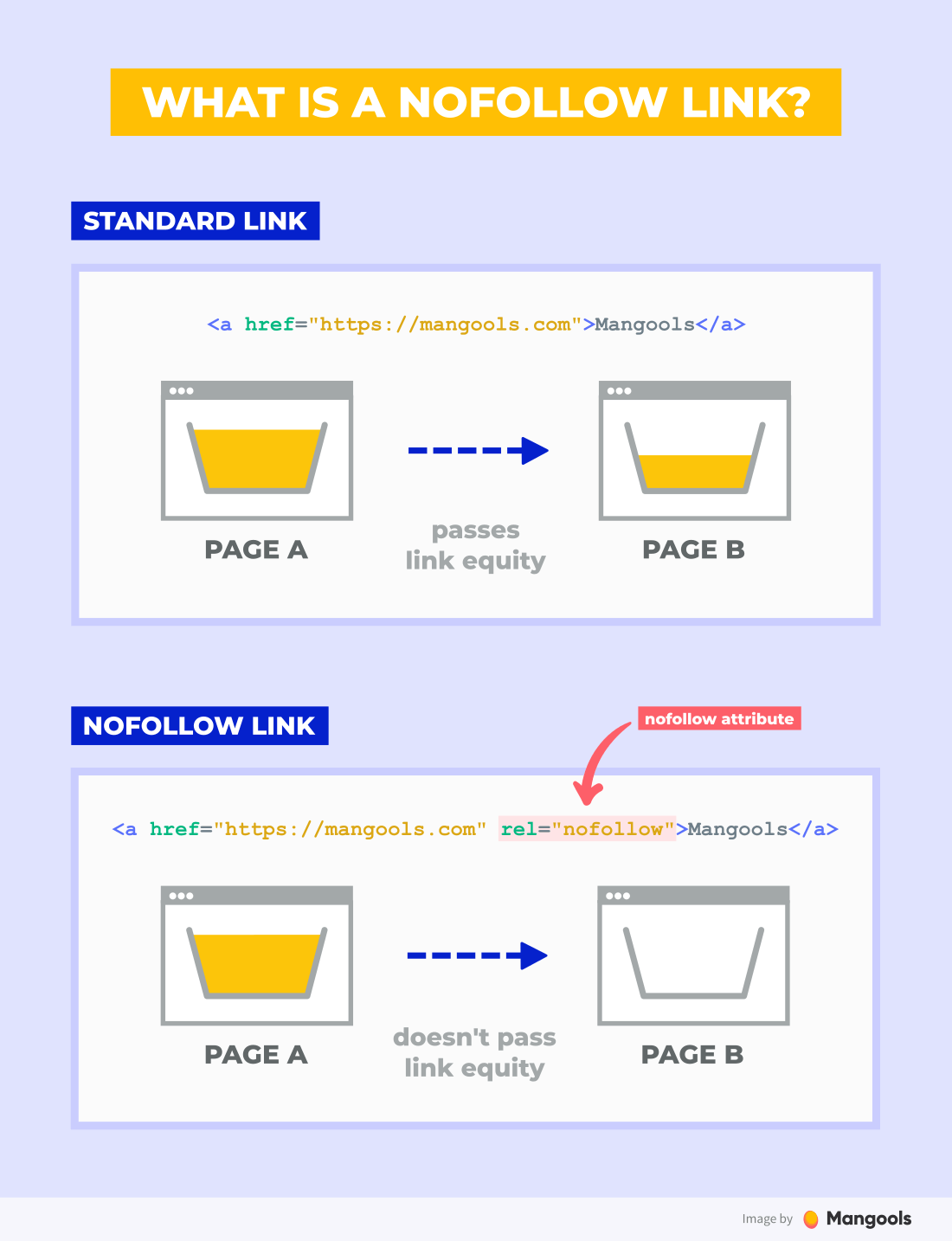
What is a nofollow link?
A nofollow link is a link that contains a rel=”nofollow” attribute in its HTML code. This attribute tells search engines not to pass authority from the linking page to the destination page.
As such, nofollow links have very little value from the SEO point of view.
Example: <a href="http://example.com" rel="nofollow">Click Here</a>
Introduced in 2005, their primary goal was to combat comment spam.
However, from 2019 onwards, Google began treating nofollow links as “hints” for crawling and indexing, rather than strict directives, allowing for more nuanced interpretation by their algorithms.
Rel=“sponsored” and rel=“ugc” link attributes
In 2019, Google introduced the rel="sponsored" and rel="ugc" attributes to provide more detailed ways to identify the nature of links.
Both can be combined with the rel="nofollow" attribute to specify that a link should not imply any endorsement or ranking influence:
a) rel="sponsored" attribute is used for links created as part of advertisements, sponsorships, or other compensation agreements.
Example: <a href="http://example.com" rel="sponsored">Example</a> Nofollow + Sponsored attributes: <a href="http://example.com" rel="sponsored nofollow">Example</a>
b) rel="ugc" attribute is intended for user-generated content, such as comments and forum posts.
Example: <a href="http://example.com" rel="ugc">Example</a> Nofollow + UGC attributes: <a href="http://example.com" rel="ugc nofollow">Example</a>
To be clear, you don’t have to change your existing nofollow links. The rel="nofollow" attribute still works as a catchall for all the links that do not pass authority. Moreover, you can combine more values in one attribute.
What is a dofollow link?
The term “dofollow link” is used to describe a link that passes the authority as opposed to one that doesn’t.
Unlike its rel="nofollow" cousin Google perceives dofollow links as endorsements, counting them in the calculation of the linked page’s PageRank, thus directly affecting SEO.
For example, <a href="http://example.com">Example</a> is considered a dofollow link.
Notice something about this link?
There’s no actual ‘dofollow’ attribute! Keep in mind that there is no such thing as the rel="dofollow" attribute. Some SEOs are quite strict about this, so make sure to avoid adding it:
There is no such thing as "DOfollow"
— nick Ξubanks (@nick_eubanks) July 29, 2019
This is the hill that I will die on.
What is the difference between dofollow and nofollow links?
The main difference between dofollow and nofollow links lies in PageRank passing and crawling/indexing.
- Dofollow links pass on PageRank and contribute to the ranking of the linked page, encouraging Google to crawl and index the link.
- Nofollow links do not pass on PageRank and are typically not followed for crawling and indexing purposes.
In other words, if you get a nofollow backlink, the linking page doesn’t pass the authority to your page. It won’t improve your rankings and transfer any PageRank.
Why are nofollow links important?
You may be thinking that nofollow links have no purpose because they don’t matter much for SEO, but this line of thinking is a lot like judging a fish on its ability to ride a bicycle.
There are plenty of reasons to love nofollow links:
- Extra brand exposure and referral traffic
- Healthy backlink profile diversity
- Better outbound link control
- Improved crawling and indexing
Let’s break them down a little bit more.
a) Extra brand exposure and referral traffic
Nofollow links, despite not influencing PageRank, are great for driving traffic and increasing the overall share of search for your brand.
A practical example is when a popular YouTube channel mentions your product in its video description with a nofollow link.
Even though this link won’t directly boost your site’s SEO rankings, the sheer volume of potential traffic from interested viewers provides significant exposure and can lead to increased site visits and conversions.
b) Healthy backlink profile diversity
Having a balanced mix of dofollow and nofollow backlinks is perceived by Google as a sign of a natural and authentic SEO strategy, steering clear of aggressive or deceptive techniques often associated with black hat SEO.
This diversity in backlink types suggests that your site is earning its links through genuine interest and engagement rather than through manipulative schemes, which can bolster your site’s credibility and trustworthiness in the eyes of both users and search engines.
c) Better outbound link control
When linking to external sites, it’s not-so-wise to use dofollow links indiscriminately, especially if the site’s content is just for demonstrating purposes, or if its credibility is dubious (might be spammy, for example).
Using nofollow attributes allows for referencing these sites without implying endorsement or contributing to their SEO strength, maintaining the integrity of your site’s link profile.
d) Improved crawling and indexing
By using nofollow links for certain internal content, you guide search engines toward the most valuable parts of your site.
This tactic de-emphasizes less important pages, such as those with duplicate content, making sure search engines focus on crawling and indexing pages that truly matter.
When to use nofollow links?
So we know why nofollow links have their own place in the SEO world, but when and where are the best circumstances to use them?
Endorsed external websites
When linking to external websites for endorsements, affiliations, or sponsorships, it’s good to use the rel="nofollow" or rel="sponsored" attributes, or even both, instead of dofollow links.
This practice is in compliance with search engines’ guidelines by indicating the commercial nature of the link, or preventing the passage of PageRank to the sponsored site:
“Use the sponsored attribute to identify links on your site that were created as part of advertisements, sponsorships, or other compensation agreements.” (Google Search Central)
So, for example, if you’re writing a blog post that’s being sponsored by another brand unrelated to your own, it’s better to link to the brand’s page using <a href="http://example.com" rel="sponsored nofollow">Example</a>" to maintain transparency and SEO integrity.
User-generated content
It’s crucial to apply rel="nofollow" or rel="ugc" attributes to links within user-generated content, such as blog comments or forum posts, to manage the quality of outbound links and maintain your site’s SEO health.
This approach safeguards your site from potentially harmful external links that could affect your search engine ranking.
For instance, if a user comments on your blog post and includes a link to their website, marking this link as nofollow or ugc keeps search engines from transferring PageRank or authority from your site to the linked site.
Irrelevant or spammy pages
Never use dofollow links for low-quality, irrelevant, or spammy pages to avoid passing on PageRank to them.
That’s it, no further explanation is needed.
Duplicated or auto-generated pages
To maintain your site’s SEO integrity, use nofollow links for duplicated or auto-generated content, like pages created by URL parameters from filters.
This prevents search engines from wasting resources on indexing pages that don’t contribute to your site’s value.
For example, linking to different color variants of a product through dofollow links could lead to unnecessary crawling of these near-identical pages.
Note: While nofollow links suggest to Google not to follow or index a web page, they’re not absolute guarantees.
For stricter control, consider using robots.txt or a noindex tag to prevent crawling and indexing directly.
When to avoid using nofollow links
There are only a couple of instances where it’s recommended to avoid using nofollow links, and thankfully, they’re quite easy to remember.
For most internal links
One of the major no-fly zones is when doing internal linking for SEO, as these should typically be dofollow for proper site navigation and SEO benefits, with exceptions like duplicate pages.
Note: In the past, there was this method called “PageRank sculpting”.
The idea was that if you nofollow certain links, you’ll “redirect” more PageRank to the pages you link to with standard followed links.
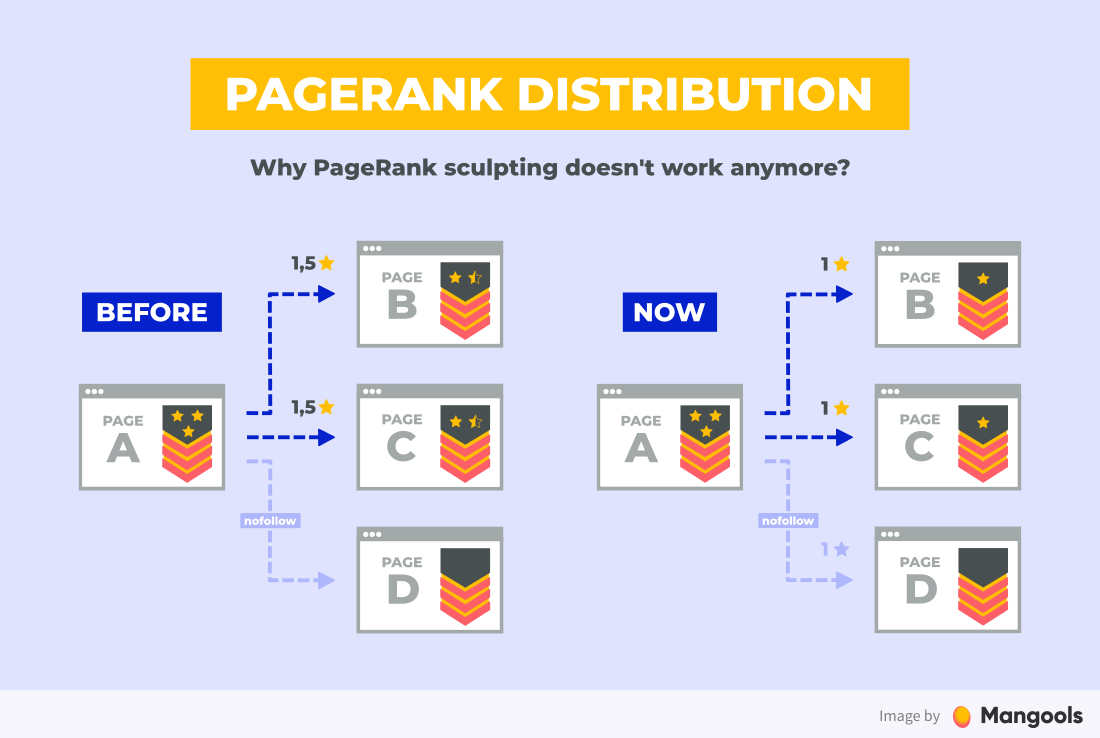
However, this blackhat SEO tactic has been ineffective since 2009. Attempting PageRank Sculpting today can lead to inefficient use of crawl budget, and potentially hinder a site’s overall SEO performance.
For relevant external websites
Avoid using the nofollow attribute for all outbound links without careful consideration.
Dofollow links to high-quality, authoritative external sites can positively impact your site’s SEO by indicating to Google that your site provides valuable resources.
Note: Remember to optimize anchor texts for dofollow outbound links to increase relevance and usefulness for users!
How to check nofollow and dofollow links
There are many ways on how to check the link attributes on the webpage:
- Check the web page manually
- Use Mangools SEO extension
- Try an SEO audit tool
- Utilize LinkMiner
1. Check the page manually
To manually check for nofollow or dofollow attributes in a web page’s HTML:
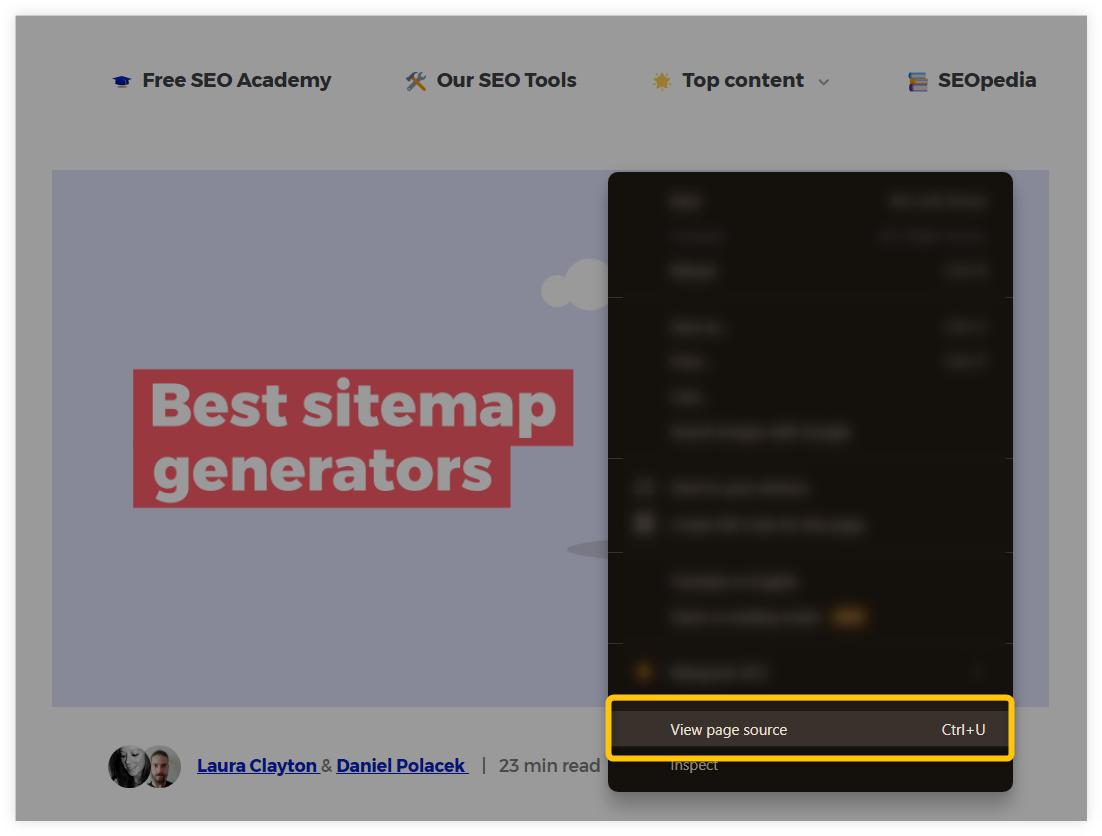
1. Open up and right-click on the web page and select “View page source” in the modal window of the browser (or press Ctrl+U).
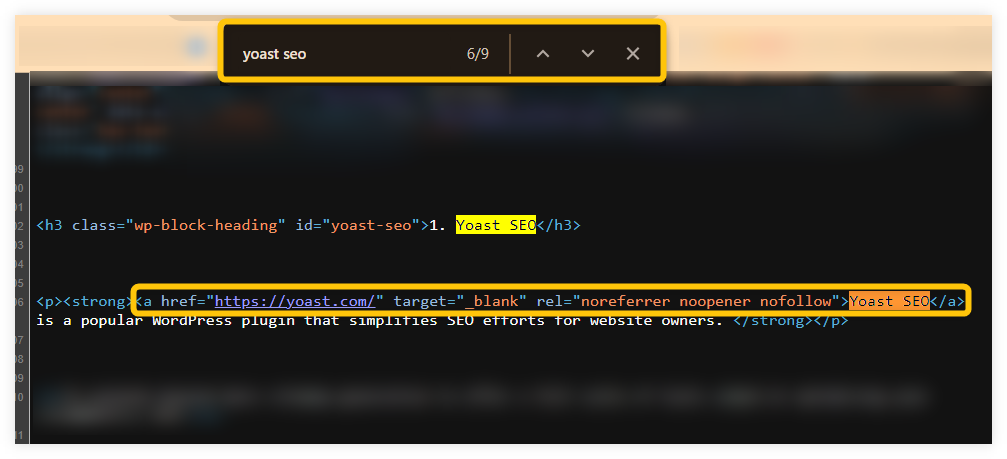
2. Scroll down to the link location in the HTML document (or try to find the link by typing its anchor in the search bar (Ctrl+F).
Alternatively, you can also check the link attribute via “Inspection mode” within your browser:
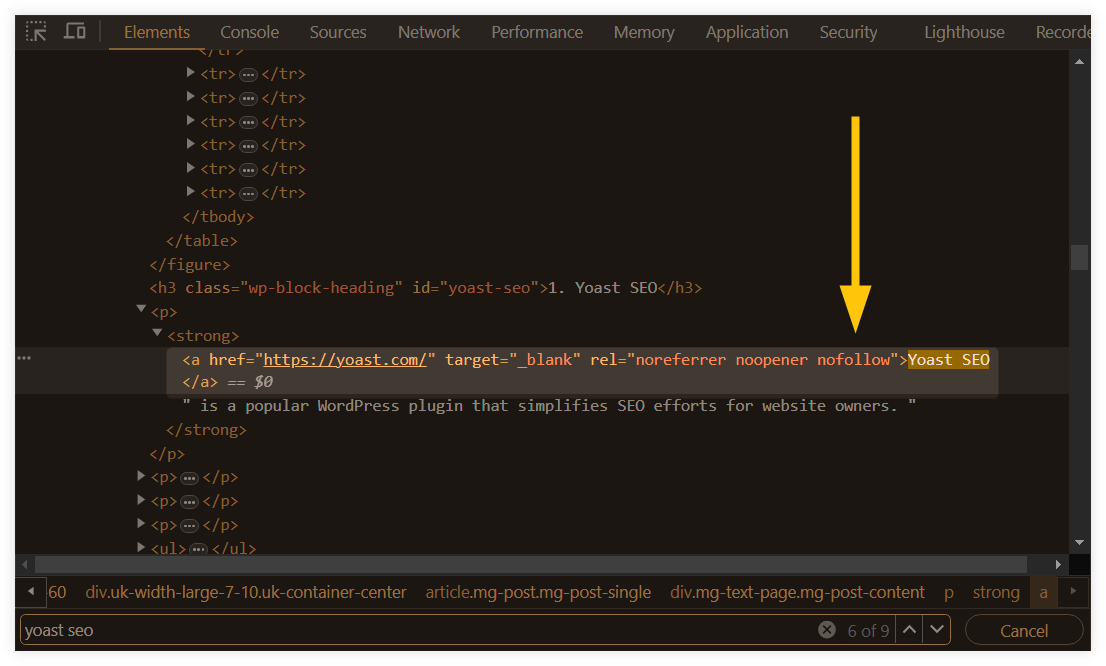
1. Right-click on the webpage and select “Inspect” or press Ctrl+Shift+I to open Developer Tools.
2. Navigate to the “Elements” tab to view the page’s HTML source.
3. Find the link (<a> tag) you want to check.
4. Look for the rel attribute within the <a> tag. If it says rel="nofollow", the link is nofollow.
2. Use Mangools SEO extension
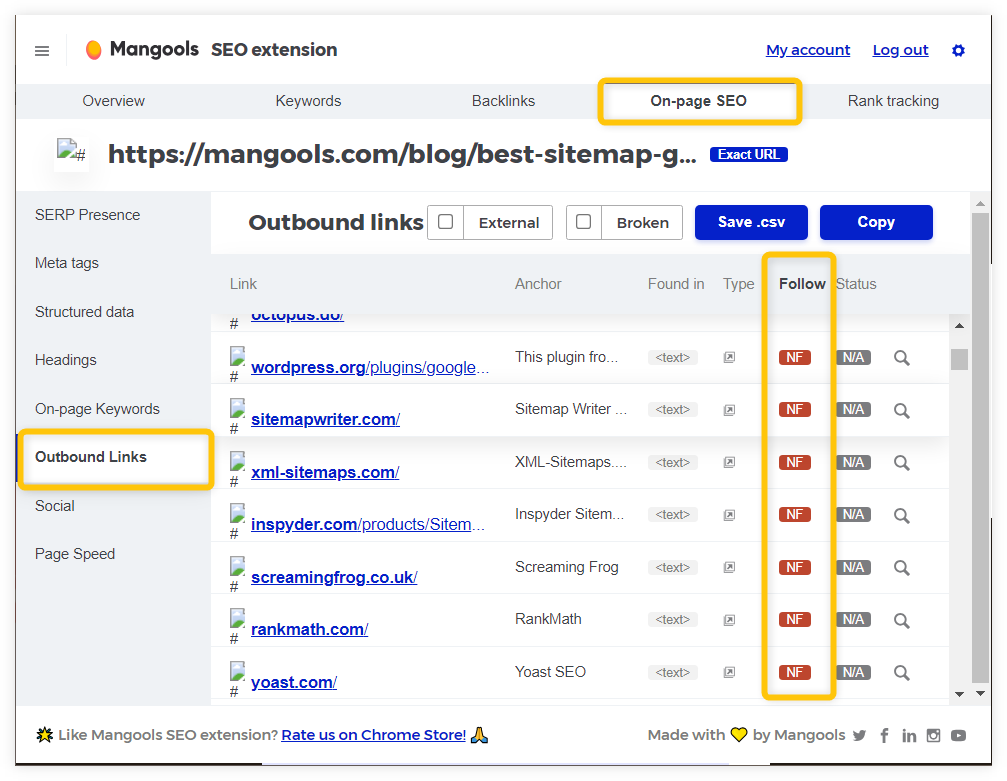
In the Mangools SEO extension, you can quickly check the status of all the outbound links:
- Go to the “On-page SEO” section within the extension
- Click on the “Outbound Links” tab on the right.
- Scroll down to the link you want to analyze and check the “Follow” column in the table.
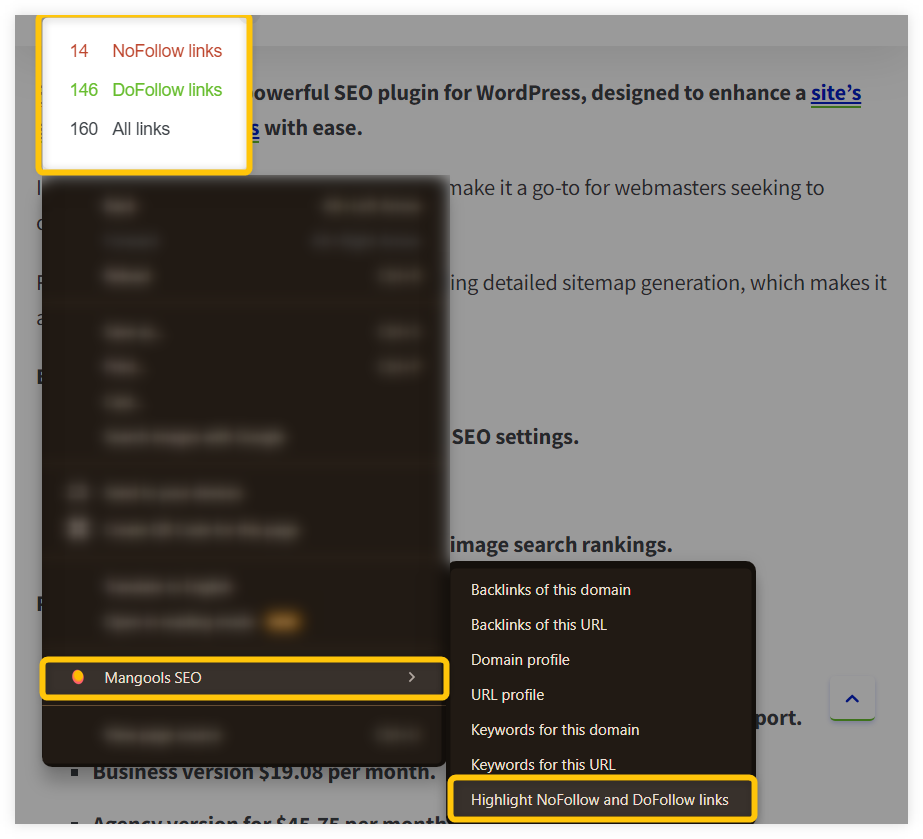
Tip: If you have installed our SEO extension to your browser, you can also check the total number of nofollow/dofollow links on the page simply by right-clicking on the web page and checking the “Mangools SEO” option in the modal window:
3. Utilize an SEO audit tool
The Screaming Frog SEO Spider tool is also a good choice. Here’s how to use it:
- Use Spider mode to select URLs individually or in bulk.
- Go to the “Inlinks” tab.
- Apply a filter in the “Inlinks” tab to sort links by the follow or nofollow status.
- For nofollow links, search if the (Follow) contains ‘False’ in the lower pane.
- Look for the rel attribute in the “Rel” column to identify specific tags like ‘ugc‘.
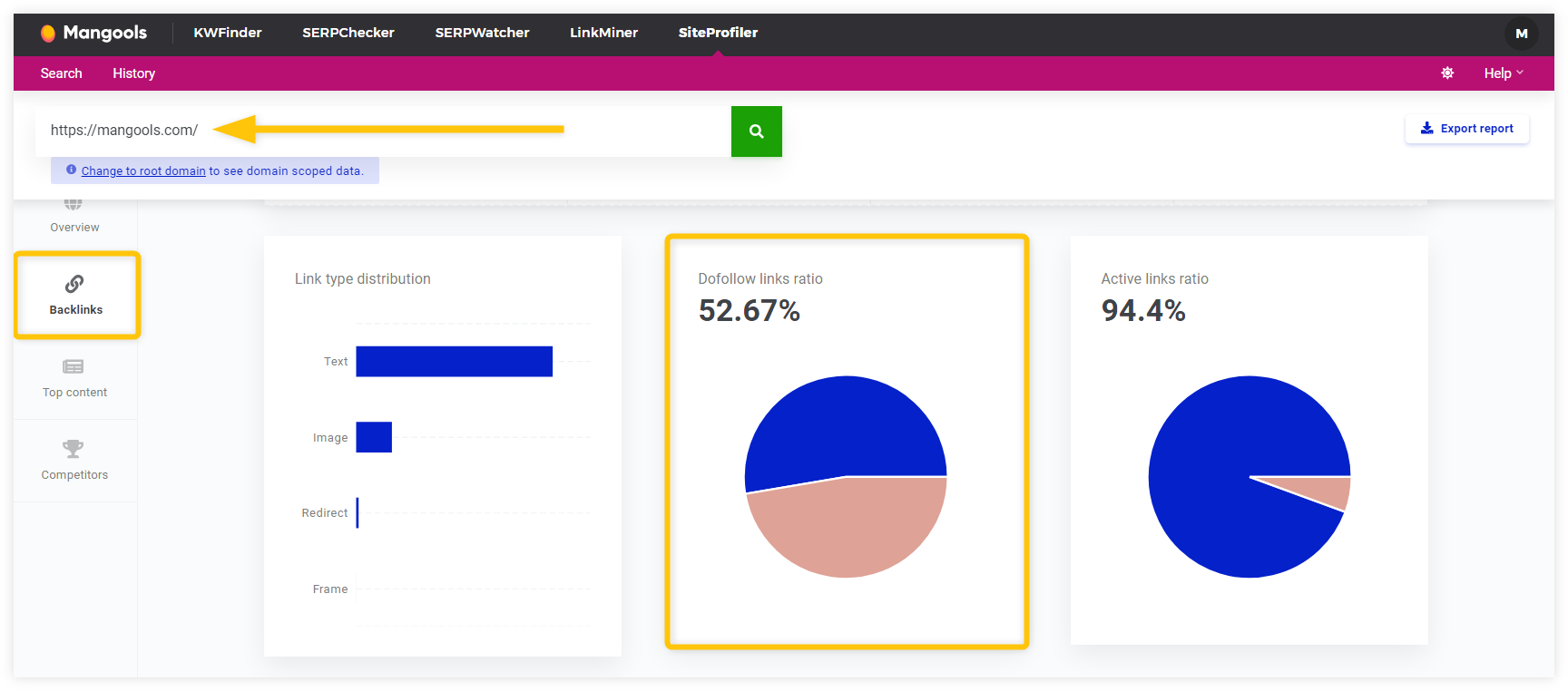
4. Use SiteProfiler
Mangools SiteProfiler is a free domain authority checker that can quickly tell you about the overall status of the dofollow backlink distribution for your site.
To check how backlinks from external websites are pointing to yours with the “dofollow” attribute, simply:
- Enter the desired domain into the search bar.
- Scroll down to the “Backlinks” sections.
- Find the pie chart labeled “Dofollow links ratio“
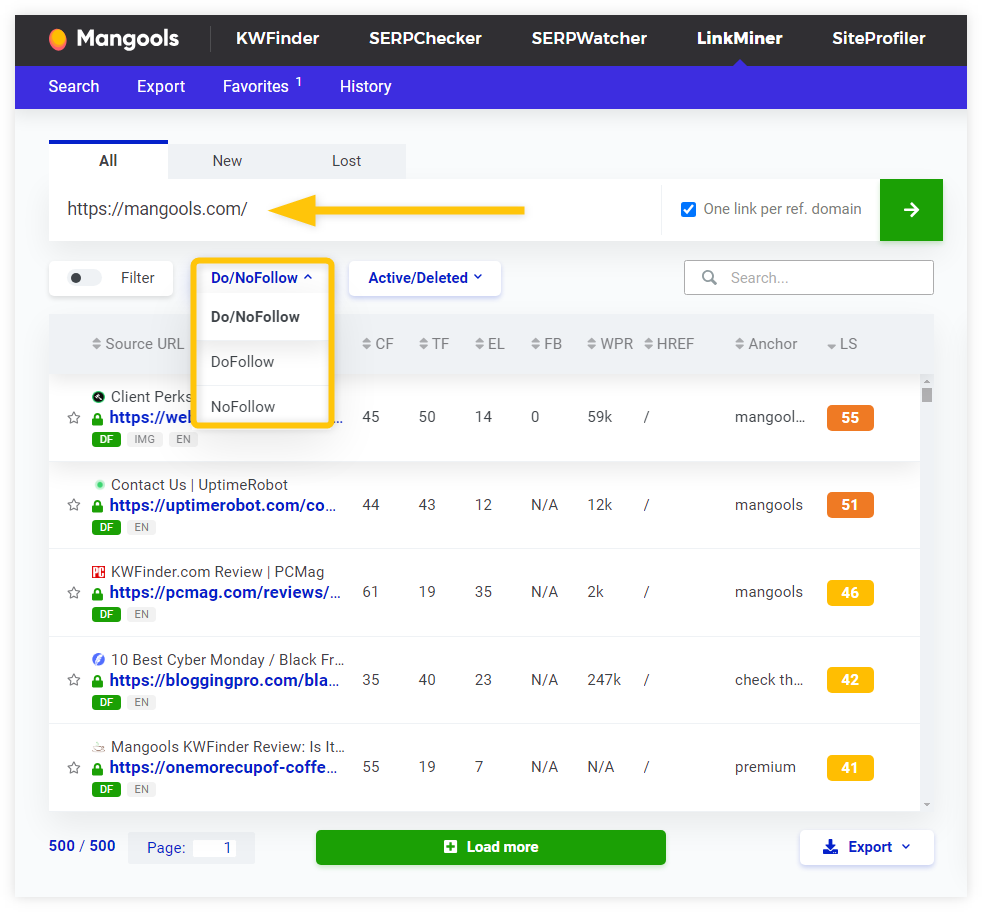
5. Check LinkMiner
In order to get a more precise overview of your dofollow/nofollow backlinks, you can also utilize the Mangools LinkMiner tool.
Our free backlink checker can help you analyze any URL and its backlink profile in a matter of seconds.
To see how many (and which) external sites are pointing to you with a dofollow backlink, you can simply:
- Enter the desired URL.
- Click on the “Do/NoFollow” filter below the search bar.
- Select one of the options (depending on your goal).
The tool will then show you a list of backlinks with either nofollow or dofollow (or both) attributes based on your preferences.
How to manage nofollow and dofollow links on the WordPress site?
Edit links manually in WordPress editor
As you likely know, there are two editor types in WordPress these days. This is how to add nofollow links in the classic editor:
- Create a new page or post.
- Insert your anchor text and create a hyperlink.
- To have the link open in a new tab, use the link options.
- After adding the link, switch to the Text view in the editor.
- Add
rel="nofollow"within the link’s HTML tag.
To learn more detailed steps, check out this post on how to add nofollow links in WordPress.
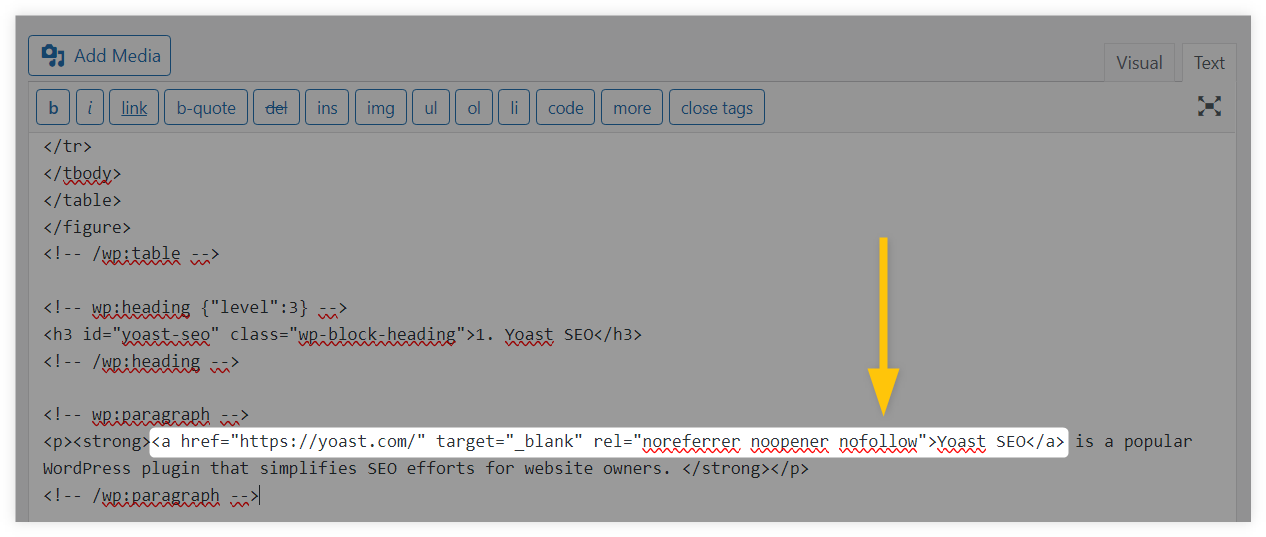
Use WordPress plugin
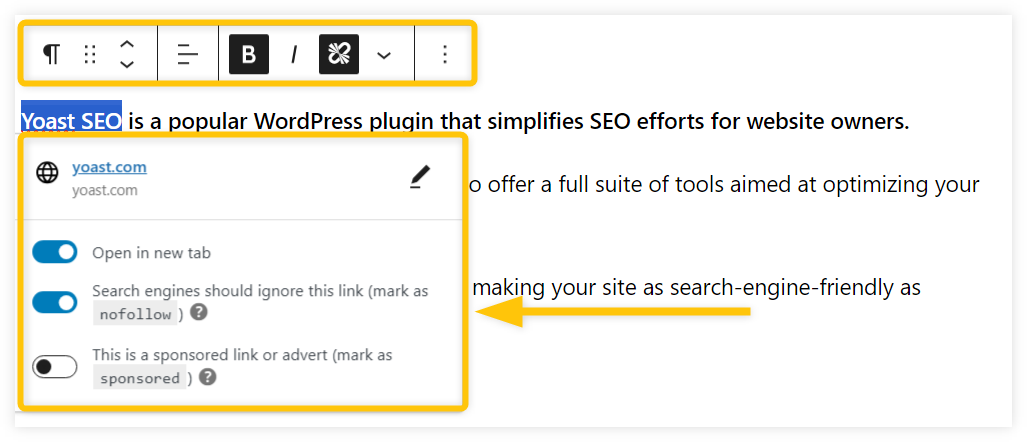
With plugins like Yoast SEO, you can add a nofollow attribute to all links on the chosen web page or just add it to individual links.
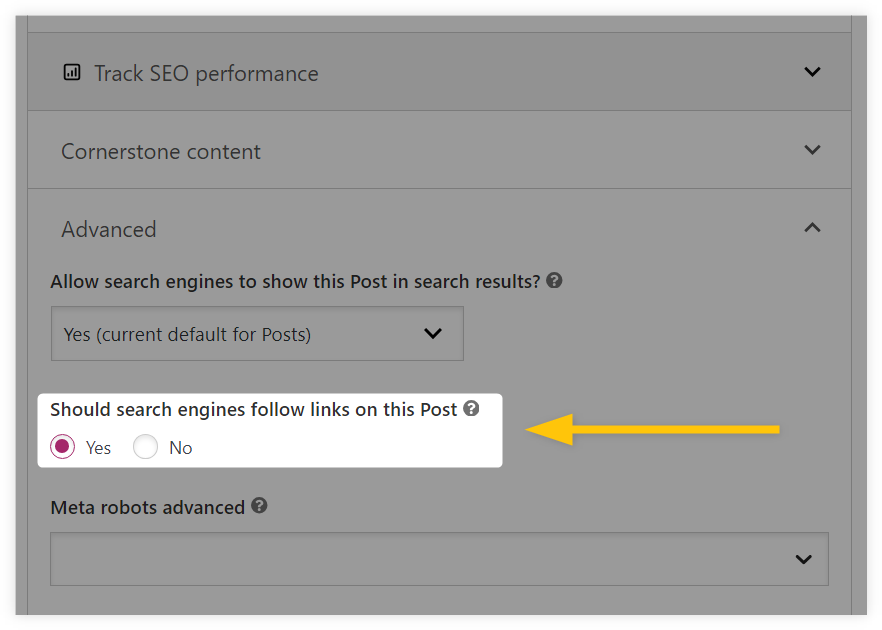
To change all links on the page from dofollow to nofollow, scroll down to the Yoast SEO plugin → click on the “Advanced” tab and check the “Yes” or “No” option in the “Should search engines follow links on this Post” section.
Changing dofollow/nofollow status for only a few links via Yoast SEO is pretty straightforward as well:
- Highlight the text that you want to use as a link in the WordPress editor.
- Click the link icon to add your URL.
- Check the “nofollow” option from the dropdown menu.
Alternatively, you can use the External Links plugin for WordPress for a complete link management system.
Tip: When linking externally, use target="_blank" to open links in a new tab. This will make it easier to return to your page and make the user experience more pleasant.
Frequently asked questions
Are nofollow backlinks bad for SEO?
No, nofollow backlinks are not inherently negative for SEO. They do not pass PageRank, which influences a website’s search engine ranking, but they can still drive referral traffic and help improve your site’s visibility.
Including both nofollow and dofollow links in your backlink profile can contribute to its natural diversity, which is great from an SEO perspective.
Can nofollow links be crawled by Google?
Google can crawl nofollow links, but it traditionally did not follow them to discover new pages or pass PageRank.
However, in 2019, Google updated its approach to treat the nofollow attribute as a hint for crawling and indexing, which means it might choose to follow a nofollow link in some cases.
How long does it take for Google to recognize a dofollow/nofollow link?
The time it takes for Google to recognize a dofollow or nofollow link can vary based on several factors, such as the site’s crawl rate and when the link was added.
Generally, it could range from a few days to a few weeks for Google to crawl and process these links.
What is the difference between a nofollow link and a nofollow meta tag?
A nofollow link is an individual link marked with a rel=”nofollow” attribute, which tells search engines not to pass PageRank.
In contrast, a nofollow meta tag is placed in the header of a webpage and instructs search engines to not pass PageRank for any outbound links on the entire page.