What is duplicate content?
Duplicate content in SEO means that a text from a different web page was copied, re-purposed, and passed off as their own by another website.
Simply put, duplicate content is considered content that can be seen on the Internet in more than one location. By Google’s definition of duplicate content, it usually does not come with malicious intent.
How do duplicate content issues occur?
Duplicate content is mostly due to technical issues from a mistake made when setting up the website or webpage. Unfortunately, these little mishaps can lower your ranking.
Aside from human errors, some parts of the content are originally from a particular website which is imitated and reused by another. This act might bring about penalties if proven to have a malicious end. Below are two categories (with some specific scenarios) that led to the occurrence of duplicate content.
Duplicate content caused by technical issues
- Badly configured web servers leading to various canonical domains: For example, you only have a www subdomain and yet your webpage can be seen in the non-www web server.
- Problems due to URL structure: URLs should be inputted precisely because they are case-sensitive. Meaning one wrongly capitalized letter is considered a different URL if another one exists in all lowercase. A mistake in forwarding slash or trailing slash as it is called can also be an issue.
- Access through different index pages is available: You might not know it, but with a misconfigured web server, your home page might be accessible through different index versions.
- Taxonomy: In content management systems, sometimes posts are available in more than one category. If you fail to use appoint a primary one, then all will be considered duplicates.
- Pages solely for images: Some websites assign a web page for images in the post. Since this page only contains a single image, others like it will have the same image page. This leads to duplicate content.
- Long comments: When there are many comments in one post, it can lead to the creation of different pages. The paginated pages will show the same article but will differ in the comments found at the bottom section of the page.
- Targeting different regions with the same language: For instance, you have content intended for US users and another one for the British and Australian audience. The content is the same but the localization differs.
Duplicate content caused by copied content
- Landing pages: Dedicated landing pages are necessary for paid searches. Most of the time landing pages are very similar to the original articles. Sometimes, they only tweak some words to insert specific keywords.
- Other websites that use your content: Unfortunately, soon as you hit publish, other websites can use the information you shared with the world. The real struggle is when your website ranks lower than these websites. Because they have higher domain authority, they will be regarded as a more reputable source and will, therefore, be considered as the original author of the article.
- Using another website’s content: On the other end of the spectrum, copying content will not only pose a problem in terms of ranking but can also drive a wedge between website owners.
To be clear, translated content where you localize your content to be available in different languages to accommodate different countries is not duplicate content. However, if the websites are incorrectly translated by a form of software or tool, Google or other search engines might think of the contents as spammy duplicates.
Another example of non-duplicate content is exhibiting the same content on your mobile as your web version. Google has a different set of search bots for mobile sites, so it will not affect your SEO ranking in this case.
If it so happens that you encountered having an unresponsive website and you want it to have a native app version, you can visit Median.co to create an app of your own.
Duplicate content checkers
To avoid any SEO curses associated with duplicate content, it is best to perform precautionary measures within your website and across all websites. There are many duplicate content checkers that can help you do the job:
Copyscape – a paid tool that can help you identify if there are parts of your content that are similar to blog articles already available on the internet. It is fast and efficient. It quickly points out any duplicate content by highlighting them and providing you an overview of how your content measures up to published content. It also provides a percentage of how original your article is.
Grammarly – is a free writing assistant that readily detects improper use of grammar, punctuation, spelling, or word choice. The premium account provides suggestions on how to improve writing style, and it also has a feature that detects plagiarism from billions of web pages.
Duplichecker – a tool that quickly investigates the article’s originality. There is a limit of 50 searches a day per registered user.
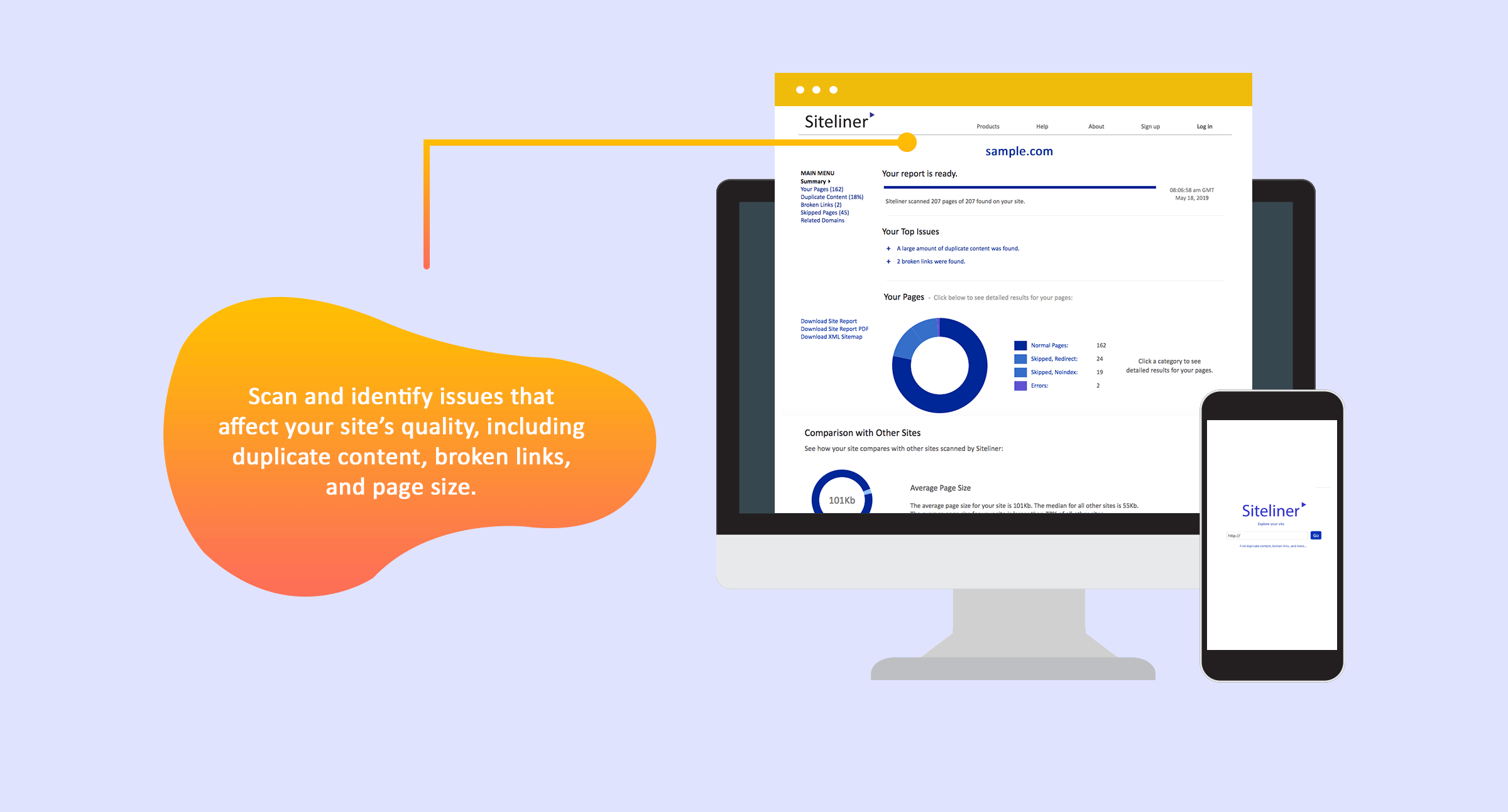
Siteliner – allows you to do monthly check-ups for duplicate content on your website. Added perks of Siteliner are it helps identify broken links and pages that are doing well in terms of ranking.
How much duplicate content is acceptable?
This is one tough case to crack because the algorithm of the leading search engine Google keeps on changing. According to Matt Cutts of Google, about 25 to 35 % of web content is considered duplicate content. And get this *cue in the drumroll, please* Google does not penalize websites with duplicate content.
However, if your whole site consists of republished content without any additional value, Google will not permit you to rise above other websites. There is no exact percentage that Google considers allowable for duplicate content, but as a general principle:
You should not expect your website to rank well in Google if it contains content that is available on more reputable and established websites. Furthermore, if you are only generating content automatically and putting zero effort on adding value to it, do not expect to earn a rank at all.
If you want to reach the top, then what you need to put out there is an original canonical version of text or content that offers significant value.
Effects of duplicate content
For search engines:
Duplicate content matter to search engines because they will not be able to identify which versions should be removed from their list. It also poses a problem regarding how SEO metrics will be associated only to a single page or to record everything across multiple versions.
Finally, it will be hard for search engines to pinpoint which version of your website is to be displayed on the search results.
For web owners:
In line with all of these, duplicate content can harm your website’s ranking and experience less traffic to your actual webpage. The traffic losses arise from two things.
First, search engines will not display all the versions that have the same content. Instead, it will choose the version that seems to have better content. In this sense, the traffic will decrease the visibility of all the duplicates. Next, link equity will also be affected.
Even other websites will have to select which is the best link to work with. Asa result, the links will be distributed among all the duplicates, instead of all of them directing it into a single webpage.
How to fix duplicate content
Practice consistency
According to the list of duplicate content causes, the majority are due to inconsistent URLs or links. Standardize your link structure to prevent such problems from occurring. Also, make use of canonical tags. It is easy to program your preferred URL by checking your Google Webmasters account and adjusting your preference.
Canonicalize your URLs
CMSes let you curate your blog content through categories and tags. When users do searches using tags and categories, the results that usually appear are the same. Because of this, bots might consider them duplicates. There are three methods to implement canonical tags:
- Set your preferred version, whether www or non-www. However, as mentioned earlier, it only addresses a certain avenue.
- Manually assign the canonical link for your pages. Identify your original source. This is the page that you want to be available to all your readers.
- Implement 301 redirects to lower the impact of duplicate content problems. Through 301 redirects, the user will be redirected from a non-preferred URL to a preferred URL. When an engine bot encounters a 301 redirect, it searches for the original resource through the duplicate content page. In this case, all non-preferred URLs become links to a preferred URL.
Use noindex
Utilize noindex meta tag to prevent search engines from forming indices of your pages that have duplicate content.
Use hreflang
Earlier it was mentioned that translated content is not considered duplicate content. However, there may be instances of it becoming so. To avoid that, add hreflang tag to facilitate engines in finding the correct content version.
How to prevent the duplicate content occurrence
The above-mentioned procedures to remedy duplicate content issues can also be done to prevent duplicate content occurrence. Furthermore, the below tips can be taken to add more preventive measures depending on the cause of duplicate content.
Tips to prevent duplicate content as a result of copied content
- Landing pages: Stop search engines from automatically indexing your landing pages by using meta robots noindex attribute. Do not include landing pages in your XML sitemap.
- Other websites that use your content: Ensure that you are given proper credit through the use of a canonical URL that leads to your page. If not, take legal action or request for Google to implement the Digital Millennium Copyright Act.
- Using another website’s content: To avoid legal charges, give credit where credit is due.
Tips to prevent duplicate content as a result of copied content
- Badly configured web servers leading to various canonical domains: Use 301 redirects and select a preferred way of showcasing your content.
- Access through different index pages is available: Before implementing 301 redirects, make sure that you canonicalize your pages. Otherwise, the pages will break.
- Taxonomy: Again, through canonicalizing the main post, you can prevent having multiple copies of one post on your website.
- Pages solely for images: If it is possible, try removing the feature that provides images with their own pages. If not, then add meta robots noindex feature to the page.
- Long comments: Utilize the pagination link relationships to notify search engines about the series of paginated comments that come with a particular content.
Dozens of SEO experts will tell you to never duplicate content on purpose. Other ways to avoid troubles with duplicate content is similar to some of the most basic SEO tips that you are probably already familiar with. These strategies will need you to go back to the basics.
How can you get original content? Simply by starting a blog and focusing on making unique, rich, and engaging content that your readers will gladly share with other people.
For websites with products, incorporate user reviews is so easy and effective. This user-generated content is guaranteed to be one-of-a-kind and can double as a marketing strategy that effectively attracts potential customers. For Amazon affiliates, you should customize product descriptions on your websites and refrain from copying what can already be found on the manufacturer’s website.
It does not need to be complicated, by following these tips, you will never have to be concerned about duplicate content issues again.