SEO and SEM are two fundamentals in the wild world of online marketing and Google Search.
However, the distinction between the two often causes confusion. SEO focuses on improving a website’s visibility organically, while SEM includes paid strategies to appear in search results.
Today we’ll be demystifying these online marketing strategies, explaining their differences, benefits, and how to effectively use both to boost and refine your online presence.
What is the difference between SEM and SEO?
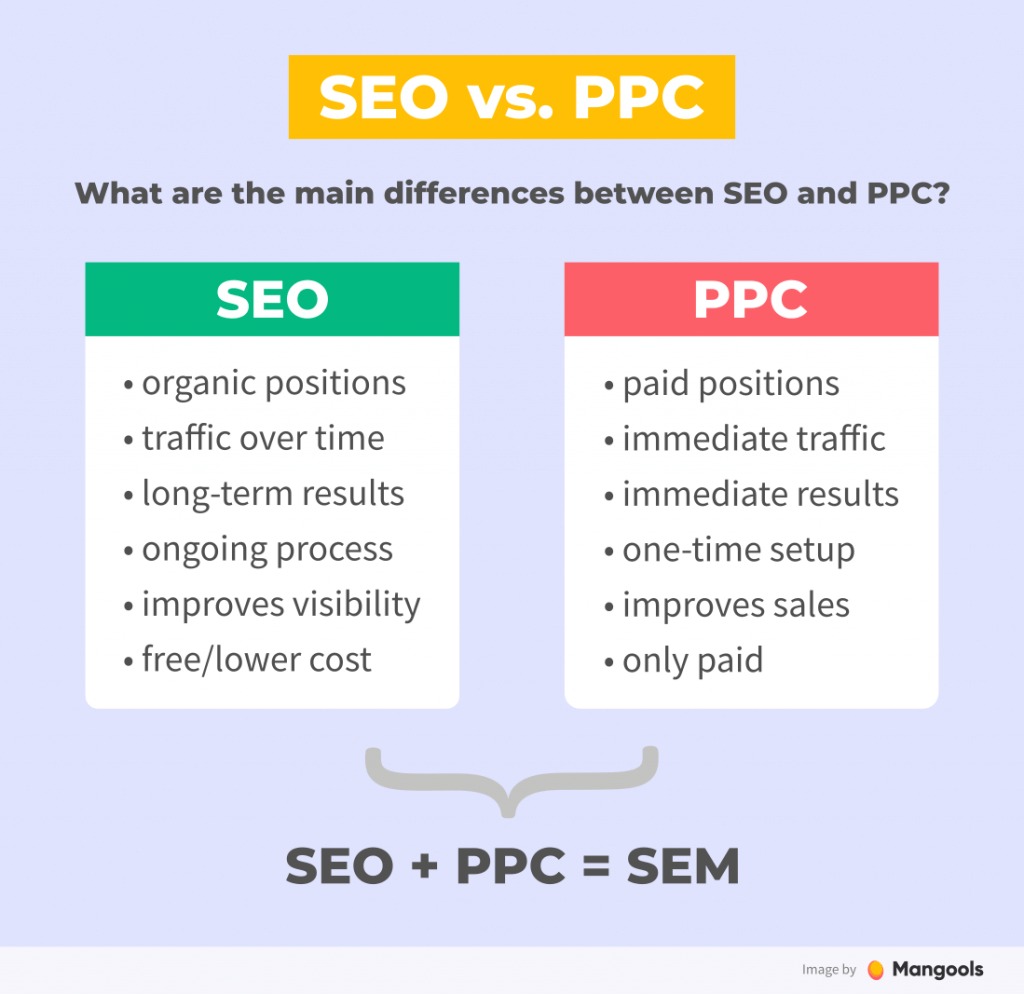
Search Engine Marketing (SEM) involves paying for advertisements on Google Search to ensure immediate top placement in the search engine results pages (SERPs) for important keywords.
In contrast, Search Engine Optimization (SEO) focuses on achieving organic rankings by gradually improving and optimizing the content on a website.
| SEO | SEM |
|---|---|
| Results appear organically, based on relevance and quality of content. | Results appear as ads at the top or bottom of search engine results pages (SERPs). |
| Takes time to build and maintain. | Provides immediate visibility and traffic. |
| Cost-effective in the long run. | Involves ongoing costs based on ad budget and bidding strategies. |
| Increases credibility and trust with users. | Allows precise targeting and quick adjustments based on performance. |
What is SEO?
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) refers to the changes and tweaks you make in order to raise your website’s rankings within a search engine at no cost.
Doing SEO is one of the primary goals whenever you’re launching or updating a website because frankly, without good optimization, Google’s bots can’t find and read your content properly.
SEO consists of these 4 main areas:
- Keyword research
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO & link building
- Technical SEO
1. Keyword research
Keyword research is the practice of identifying the words and phrases that people use in Google when they are searching for something.
This helps in understanding what content and topics will meet user needs, and how to rank higher for those searches.
To determine the topics for which you can create and optimize website content, you need to find and use keywords that are:
- Popular (they have a high search volume)
- Rankable (you will be able to rank for them)
- Relevant to your website and content

2. On-page SEO
On-page SEO refers to the optimization of individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic in search engines.
For example, optimizing a blog post would look like including target keywords in the title, H1 headings, and throughout the content, while keeping the content valuable and engaging for readers.
Here is a s simple on-page SEO checklist that you should always keep in mind when creating web pages for your site:
- Write quality content – informative, engaging, and original content that addresses the needs and interests of your audience is the ultimate goal. Quality content is more likely to be shared, linked to, and rank higher in search results.
- Choose and implement relevant keywords – incorporate keywords naturally into your content, headings, title tags, and meta descriptions. Avoid keyword stuffing, as it can harm your rankings and readability. This not only improves your click-through rates but also helps your overall SEO performance.
- Focus on internal linking – internal linking is when you create links between different pages on your website. This helps search engines crawl your site more efficiently and keeps visitors on your site longer by guiding them to related content.
- Create user-friendly URLs – A URL slug is the part of a URL that comes after the domain name, and it should be clear, short, and include the right keywords. Well-crafted slugs aid search engines and users in understanding what the page is about before even clicking on the link.
- Implement structured data – Structured data provides search engines with additional context about your page content. This can lead to boosted search listings, known as rich snippets, which can improve your visibility and click-through rates.
Implementing all of these strategies will greatly improve your site’s SEO, making it more accessible and attractive to both search engines and users.
3. Off-page SEO and link-building
Off-page SEO and link-building is anything that happens “outside” your website – from getting backlinks to improving your social media presence and gaining the overall trust and authoritativeness.
Naturally, the most important part of this process is link building – gaining links from other websites, preferably ones with a higher authority.
The real value of link building lies in the quality of the links you get and not just their number. Therefore, you should always:
- Reach out to reputable sites in your industry and ask for backlinks.
- Create good and thorough content that naturally attracts links.
- Write high-quality guest posts
- Focus on surround sound SEO
Depending on the performance and influence of these link sources you’ll also increase your brand awareness and grow your social following/bookmarking.
4. Technical SEO
Technical SEO focuses on improving the technical aspects of your website, making it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content.
This includes optimizing your website’s speed, mobile-friendliness, and overall user experience.
Focus on a mobile-friendly website
With the majority of users accessing the web via mobile devices, having a mobile-friendly website is non-negotiable.
Search engines prioritize mobile-optimized sites in their rankings.
- Use responsive design to make sure your site adjusts to different screen sizes.
- Test your site on various devices to ensure usability.
- Optimize images and other media for faster loading on mobile devices.
Create a clear XML sitemap
An XML sitemap helps search engines understand the structure of your website and find all your content. It’s a roadmap that guides search engines to all your important pages.
- Use XML sitemap tools like Yoast SEO or Google XML Sitemaps to generate a sitemap.
- Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools.
- Regularly update your sitemap to reflect any changes to your site structure.
Implement HTTPS
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts data between the user’s browser and your website, boosting security. Search engines favor HTTPS websites over HTTP.
- Obtain an SSL certificate from a trusted certificate authority (CA).
- Install the SSL certificate on your server.
- Update your website URLs to use HTTPS instead of HTTP.
Improve page speed & Core Web Vitals
Page speed is a critical factor in user experience and search engine rankings. Core Web Vitals are a set of metrics related to speed, responsiveness, and visual stability that Google considers important in a webpage’s overall user experience.
- Optimize images by compressing them and using the right formats.
- Minimize CSS, JavaScript, and HTML.
- Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to identify and fix issues.
Manage redirects and robots.txt
Properly managing redirects and the robots.txt file ensures search engines can crawl your site efficiently without running into dead ends or restricted areas.
- Use 301 redirects for permanently moved pages to preserve SEO value.
- Regularly audit your site for broken links and fix them.
- Configure your robots.txt file to allow search engines to crawl important pages and disallow access to private or irrelevant content.
What is SEM?
SEM (Search Engine Marketing) is a strategy that uses a variety of paid services to increase a website’s visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs).
This is typically done through Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising, where advertisers pay each time a user clicks on their ad.
Note: Sometimes the term SEM semantically refers to the combination of both SEO and PPC:
SEM (or PPC) includes keyword research, ad creation, and optimizing ad campaigns to achieve the best possible return on investment (ROI).
One of the most popular platforms for SEM is Google Ads. Through Google Ads, businesses can bid on keywords relevant to their products or services.
When users search for these keywords, the ads appear at the top of the search results, above the organic listings. PPC advertising lets businesses quickly gain visibility and drive traffic.
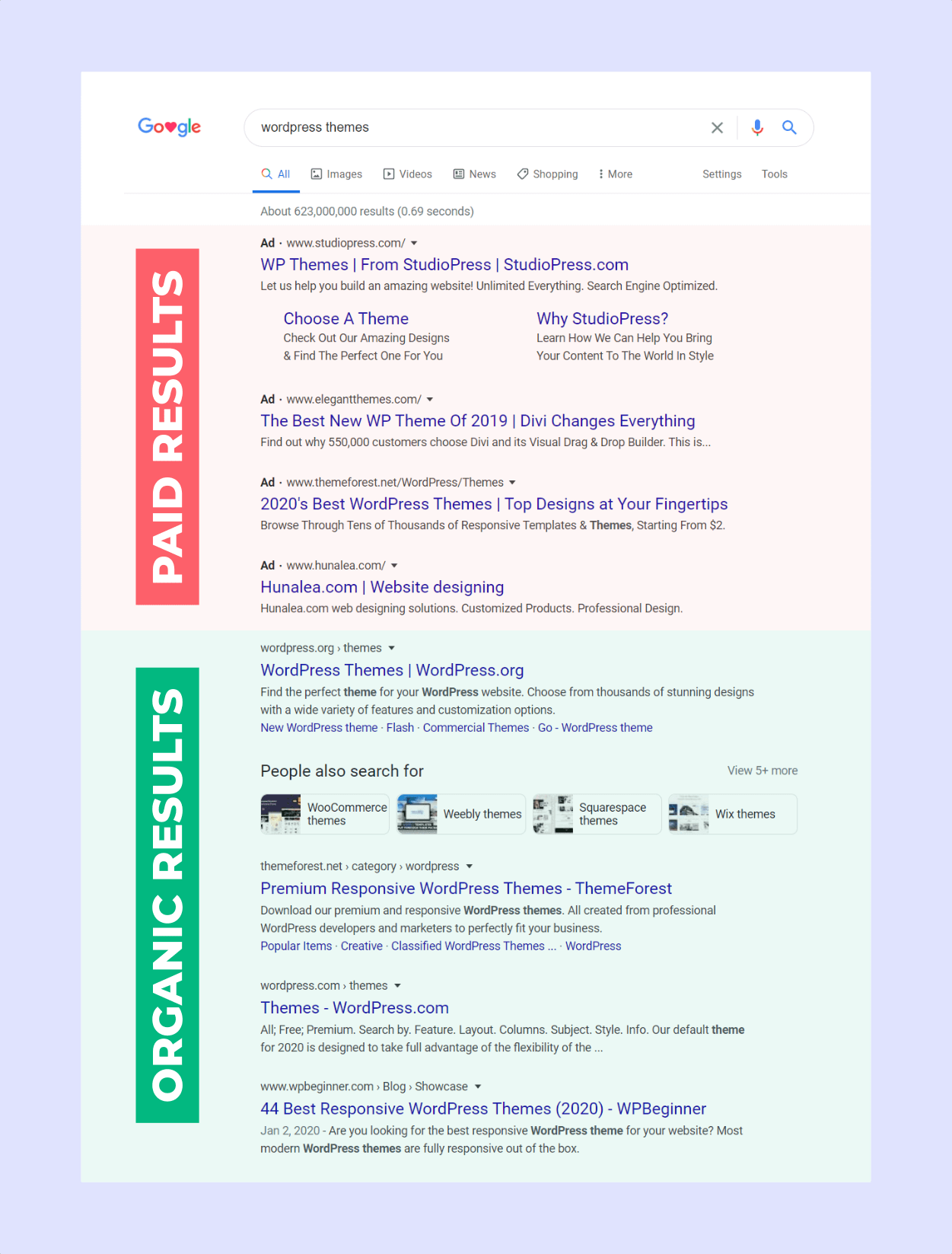
Compared to the SEO strategy, which brings in traffic for free, with PPC you’re paying for the top exposure. Depending on the keyword you want to reach for, costs can go beyond the $20/click mark and you’ll be paying every time a person clicks on your ad.
1. Keyword Research for PPC
Keyword research for PPC is like normal keyword research, but instead of being used in your web pages, they’re used in ads.
- Utilize keyword research tools Mangools KWFinder to search for relevant keywords with high search volumes and manageable competition.
- Look at the keywords your competitors are targeting and consider including them in your campaigns.
- Organize keywords into groups based on their relevance and create specific ad campaigns for each group.
By bidding on well-research keywords, your ads will appear when users search for these terms, bringing a lot of targeted traffic to your site … which brings us to the next aspect of PPC.
2. PPC Bidding
PPC bidding is the process of setting the maximum amount you’re willing to pay for each click on your ad.
This amount, combined with the quality of your ad and landing page, determines your ad’s position on the SERPs.
3. Audience targeting
Audience targeting in SEM is about directing your ads to specific groups of people who are more likely to be interested in your products or services.
This can be based on demographics, interests, behaviors, or previous interactions with your website. Here’s a little more information:
- Demographic targeting: Focus on age, gender, income level, and other demographic factors.
- Interest targeting: Target users based on their interests and online behaviors.
- Retargeting: Show ads to users who have previously visited your website or interacted with your brand.
If you sell fitness equipment, you might target ads to users who have shown interest in fitness, health, and wellness websites.
Additionally, you could retarget users who visited your site but didn’t make a purchase, encouraging them to come back and complete their transaction.
4. Ad creation
Ad creation is exactly what it sounds like – designing and writing ads that attract clicks and bring traffic to your website.
Effective ads are interesting or eye-catching, relevant, and include a clear call to action (CTA).
- Choose short, enticing headlines: Write headlines that grab attention and include your primary keyword.
- Write persuasive copy: Bring out your persuasive techniques and focus on the benefits of your product or service and include a strong CTA.
- Use high-quality images: If using display ads, make sure your images are clear, well-made, and draw the eye.
5. Ad assets
Ad assets are items such as site links, callouts, and structured snippets. They provide extra information and increase the range and effectiveness of your ads.
- Add site links: Include links to different pages on your website, such as product categories or special offers.
- Use callouts: Highlight specific features or benefits of your product or service.
- Implement structured snippets: Provide additional details, like types of services offered or product specifications.
What are the costs of SEO and SEM?
Determining the true cost of SEO isn’t straightforward, as it can vary significantly depending on the services you opt for. These costs encompass tools, resources, and time.
Investment in SEO tools for keyword research, technical audits, and analytics can range from $500 to $5,000 per month. Additionally, hiring SEO experts or agencies will further increase your expenses.
On the other hand, the cost per click (CPC) in SEM campaigns depends on factors such as competition, keyword popularity, and ad quality. Advertisers pay for each click on their ads, with CPC ranging from a few cents to several dollars.
How long does it take to see results for SEO & SEM?
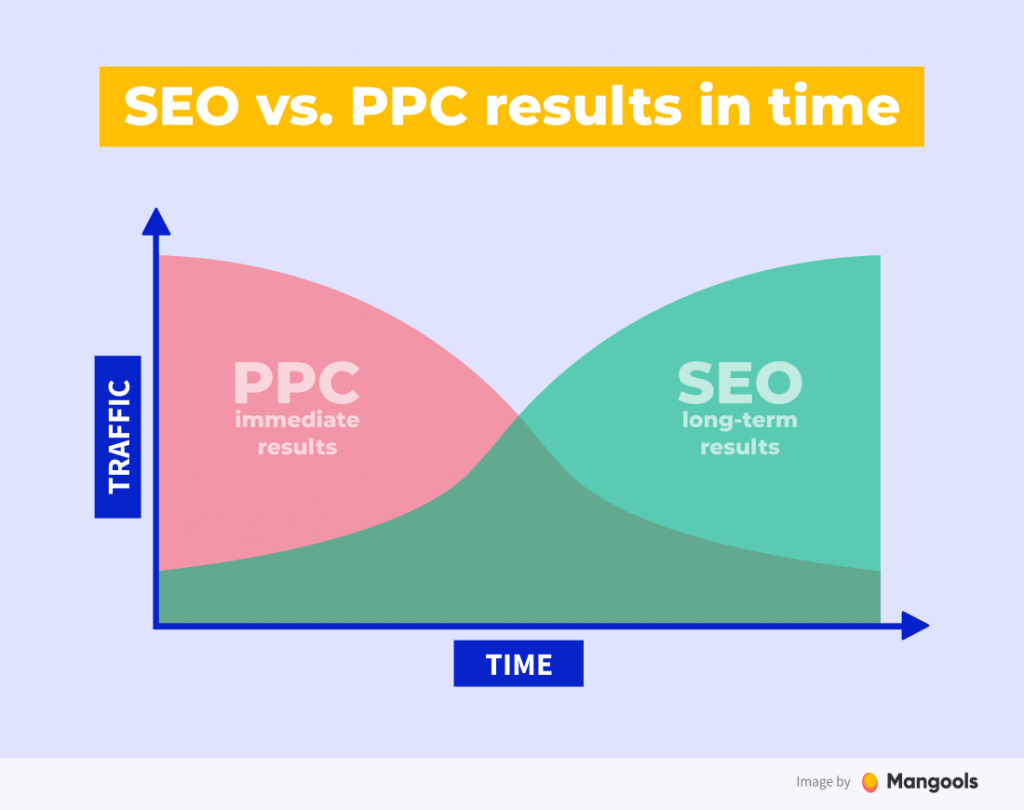
Slow and steady wins the race, and SEO is a perfect example of this old adage. SEO typically takes 3-6 months to start seeing noticeable improvements in website’s rankings and organic traffic.
Factors influencing the timeline include competition, the quality of SEO efforts, and the current state of your website.
Conversely, SEM offers much quicker results. Once a campaign is launched, ads can appear almost immediately, driving traffic to your site within hours.
Adjustments to bids and targeting can affect results in real-time, making SEM ideal for short-term goals and immediate visibility.
SEO vs. SEM: Which is better?
To build a sustainable online presence and have lasting results, SEO is your answer. It focuses on creating good, valuable content and improving your overall website structure, resulting in long-lasting organic traffic and credibility.
SEM is perfect for short-term objectives, such as promotions or product launches. It provides immediate visibility and traffic, allowing businesses to reach their target audience quickly.
As with any online ads, this can bring in lots of traffic at a certain point. However, it’s all temporary and, not to mention, costly.
Ultimately, the decision on how to balance these two strategies often comes down to high-level resource allocation. A chief marketing officer is typically responsible for determining the right mix of organic and paid efforts to align with the company’s broader revenue goals. By understanding the distinct ROI of each channel, leadership can ensure that the marketing budget delivers both immediate wins and sustainable long-term growth.
Frequently asked questions
What is the advantage of SEM over SEO?
SEM offers immediate results and precise targeting, which is ideal for short-term goals and quick traffic boosts.
Is SEO or SEM paid?
SEO relies on efforts and tools without direct costs for clicks, whereas SEM is a paid strategy that incurs costs for each click or impression.
Do you need SEO and SEM?
Yes, combining both provides full coverage, leveraging the strengths of each strategy for sustained growth and immediate impact.
How is SEO different from SEM and PPC?
SEO focuses on organic search results, while SEM encompasses both organic and paid strategies, with PPC specifically referring to paid ads.
What is the difference between SEO and SMO?
SEO optimizes websites for search engines, while Social Media Optimization (SMO) focuses on social media presence and engagement.
Should I use SEO or SEM?
Use SEO for long-term growth and SEM for immediate results. Combining both is often the most effective strategy.
How do SEM and SEO work together?
SEO builds a solid foundation for organic traffic, while SEM boosts visibility and drives immediate traffic. Together, they maximize your online presence.