The security of a website is more than a technical concern, it’s a fundamental aspect of a site’s success and its relationship with its users.
With increasing threats to online security and privacy, providing a secure browsing environment has become a priority for both internet users and website owners.
In this context, HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is one of the main components of website security … and it also serves as a ranking factor in Google’s algorithm.
In this article, we explore the importance of HTTPS in SEO, how it affects search rankings, and discuss why it is indispensable for modern site owners committed to providing secure and trustworthy platforms for their users.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) is an extension of HTTP that provides encrypted and secured communication between a user’s web browser and a website. The HTTPS can be obtained by installing an SSL (or TLS) certificate on your website.
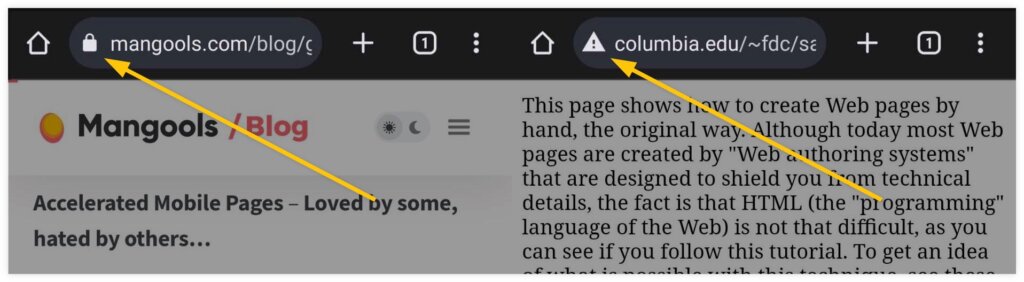
Here’s how secured (HTTPS) and unsecured URLs (HTTP) can look on a user’s browser side-by-side:
In the past, HTTPS was primarily used for securing transactions and sensitive data on various banking or e-commerce sites.
In our current digital landscape, however, HTTPS has become a standard for the majority of websites – it provides basic security for online users and serves as a sign of quality and trustworthiness.
HTTP vs. HTTPS
The HTTPS protocol can establish encrypted communication between a client and web server while HTTP cannot.
Whenever a user visits some website or types in a URL into his browser, the browser will ask the website’s server for the resources that it needs to load the page.
When it comes to HTTP however, all the information that is being exchanged between the browser and the website is sent in plain text – which can be then exploited by using various malicious techniques such as eavesdropping or MitM (man-in-the-middle) attack.
This is why HTTPS plays a crucial role in user protection since it can encrypt (and decrypt) the requests made by the user for the website, as well as information provided by the website server.
Why is HTTPS important in SEO?
a) HTTPS is a ranking factor
Back in 2014, Google made a significant announcement: HTTPS was officially identified as a ranking signal used in its search algorithms.
While HTTPS was initially described as a “lightweight” signal that affected fewer than 1% of global queries, it became a much more significant factor over the years that affected the majority of websites in Google Search.
In other words: Google will rank higher websites that use HTTPS encryption.
b) It creates a sense of trust
An encrypted connection enabled by HTTPS protects user data and creates a sense of security for site visitors – which plays a crucial role in the overall page experience ranking algorithm.
Think about it this way: Would you trust a website that pops up in your browser like this:
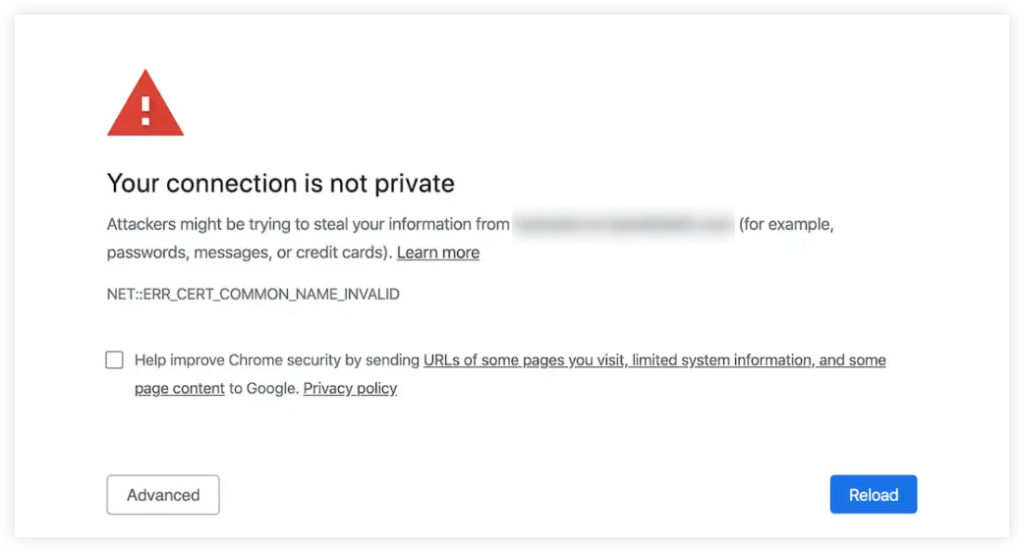
Most probably not…
c) HTTPS improves traffic reports
HTTPS improves the accuracy and reliability of traffic reports in your analytics tool.
When a site without HTTPS encryption gets a bunch of visitors, the source which they are coming from (e.g. social media, ads, organic, etc.) won’t be shown in your analytic dashboard.
As a result, in analytics tools, this traffic will be misleadingly shown as ‘direct’ and hide the true source of your visitors.
HTTPS resolves this issue since traffic that flows between HTTPS sites retains its referral data.
d) It is used in Google Search Console
Websites operating on HTTP miss out on some of the richer data sets and features that Google Search Console offers.
In 2022, Google announced a new HTTPS report in Search Console which allows webmasters to get insights about HTTPS pages that are served in Google Search.
The report can also show you various issues that prevent web pages from being served as HTTPS:
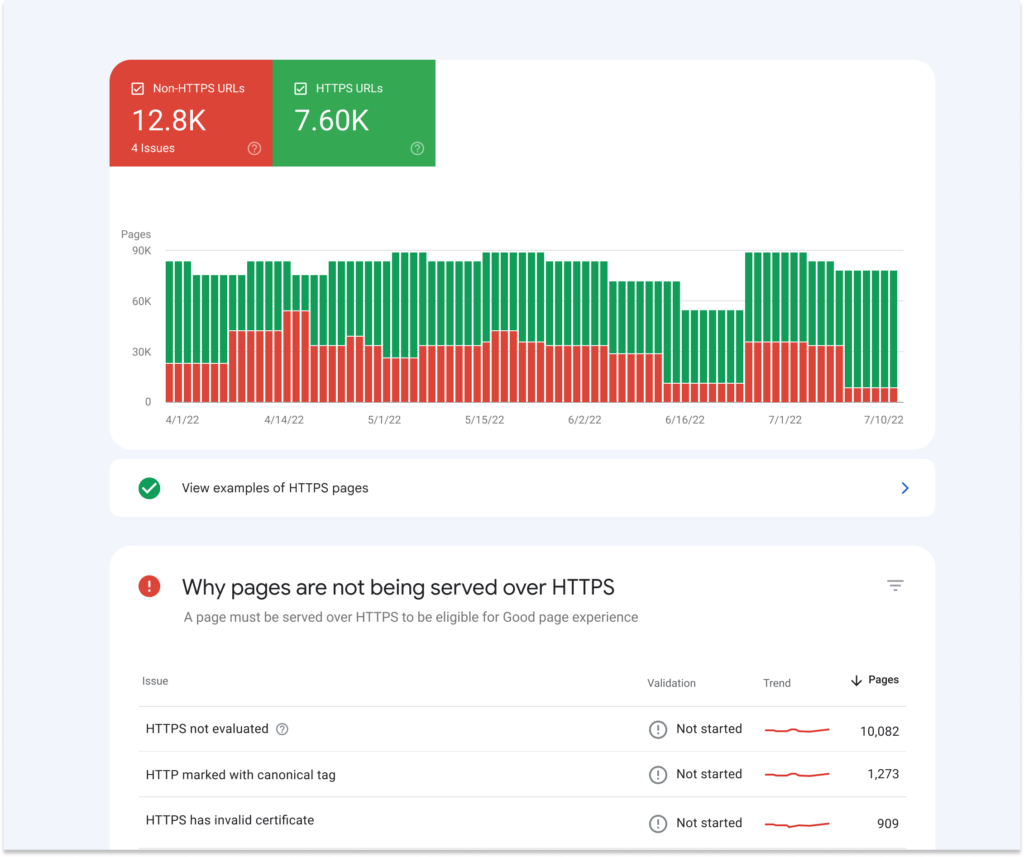
How to switch to HTTPS?
Switching to HTTPS isn’t the hardest thing you’ll ever face in the world of SEO, but it is more than just A, B, and C.
1. Acquire & install an SSL certificate
First things first, you need to obtain an SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificate for your website.
These days, you can get a free SSL certificate from a third party such as Let’s Encrypt or simply from your web host – many hosting providers offer an SSL/TLS as a part of their hosting plans.
Once you install your SSL certificate on the website server, it is time to activate it in your CMS.
2. Active your SSL certificate
Implementing and enabling HTTPS for your website is a pretty straightforward process.
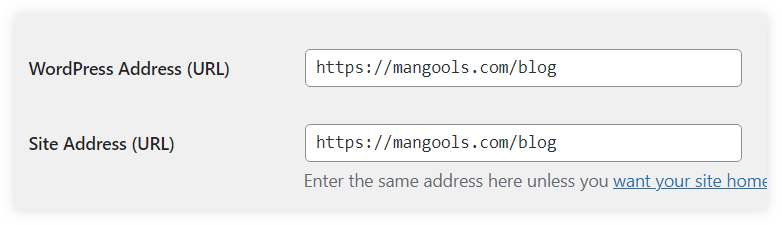
If you are using WordPress, simply go to Settings → General and enter your new HTTPS version of your URL address into the WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL) tabs and click on the Save Changes button:
Since the WordPress 5.7 version, your website can be automatically switched from HTTP to HTTPS if your SSL certificate is already set up on your hosting server.
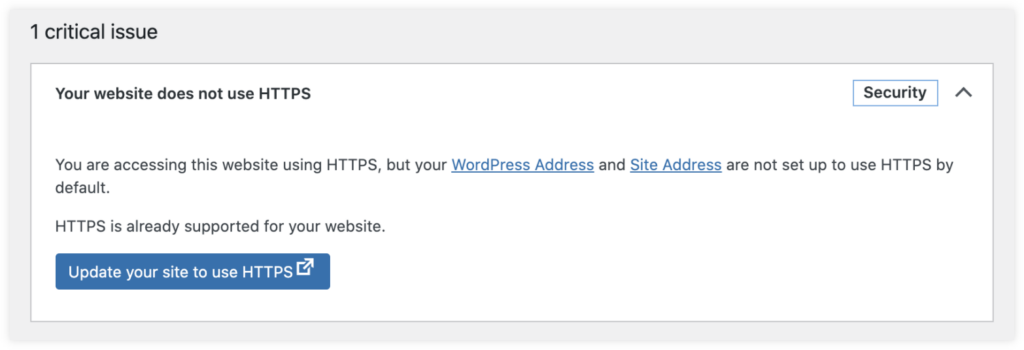
3. Redirect from HTTP to HTTPS
With enabled HTTPS on your website, it is time to redirect all traffic (and web crawlers) going into the HTTP to the HTTPS version instead.
There are multiple ways you can redirect HTTP to HTTPS – you can either use a WordPress plugin such as Really Simple SSL or set up your redirects in the .htaccess file.
For more information on how to redirect HTTPS, check out this simple guide.
4. Update your internal links
Once you enabled your HTTPS encryption, you also need to update your internal links to point them to the HTTPS versions of their linking URLs.
Large sites may find this particularly demanding due to the large number of web pages they have.
To do this, you can use tools like Screamingfrog to quickly run an SEO audit to see, which pages contain links pointing to the HTTP versions.
5. Verify the HTTPS version in GSC
If you have properly set up your HTTPS version and optimized your website for it, you need to tell Google that there is a new version of the site.
In Google Search Console, add and verify a new URL-prefix property for HTTPS protocol and declare the HTTPS version of your website as the canonical one.
After the transfer, Google Search Console should accept your HTTPS version after a few days (and use it for indexing and ranking purposes).
6. Monitor your SSL certificate
Having HTTPS encryption on your website requires constant monitoring of the SSL certificate in order to make sure that it works properly, as well as to check if (or when) the SSL certification will expire.
To do this, you can use a monitoring service such as UptimeRobot and be instantly aware of any potential SSL issues.
With UptimeRobot, you can set up SSL monitoring just in a few seconds – after that, you will get:
- Overview of any SSL certificate errors
- Notifications about an upcoming SSL expiration
- Instant alerts via a preferred type of communication (email, SMS, voice call, Slack notification, etc.).

Final thoughts
In conclusion, while migrating to HTTPS demands planning and execution, the secure user experience and potential SEO benefits make the effort worthwhile.
In an increasingly digital and security-conscious world, HTTPS is not just an optional add-on for websites anymore – it is a core component of modern SEO tactics.
As search engines, notably Google, continue to emphasize secure, high-quality user experiences, having an HTTPS website is increasingly synonymous with strong search engine rankings.
For website owners who prioritize both security and visibility, making the move to HTTPS is an essential step in the contemporary digital landscape.
It’s a commitment to maintaining a strong, secure, and SEO-optimized online presence in a world where these factors are intrinsically intertwined.
Are you ready to make the change for safety and security?