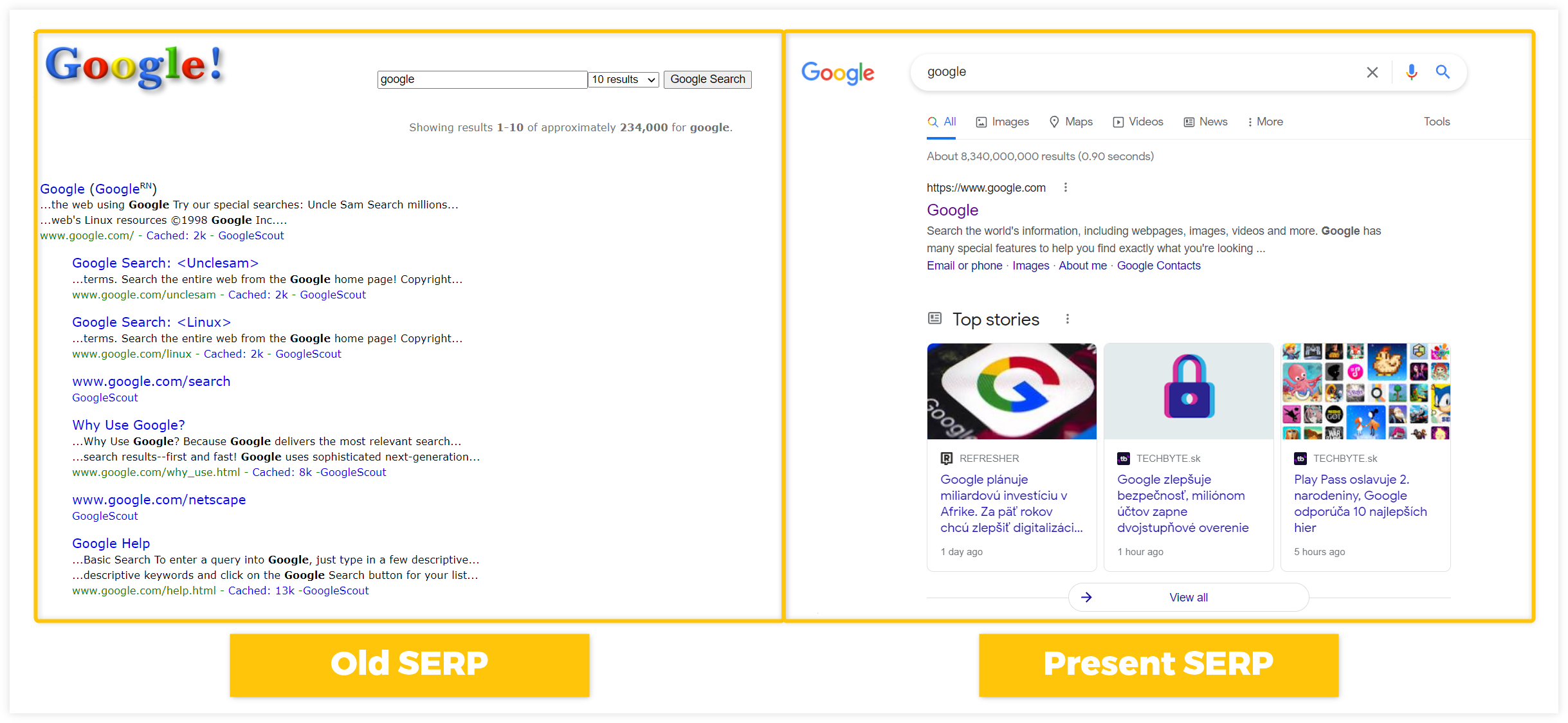
What is SERP?
SERP (Search Engine Result Page) is a page with a list of results that a search engine displays after a user submits a search query.
There are various types of results that can be displayed in SERP – Organic results, Ads, and other SERP features (e.g. Featured Snippet, Sitelinks, etc.).
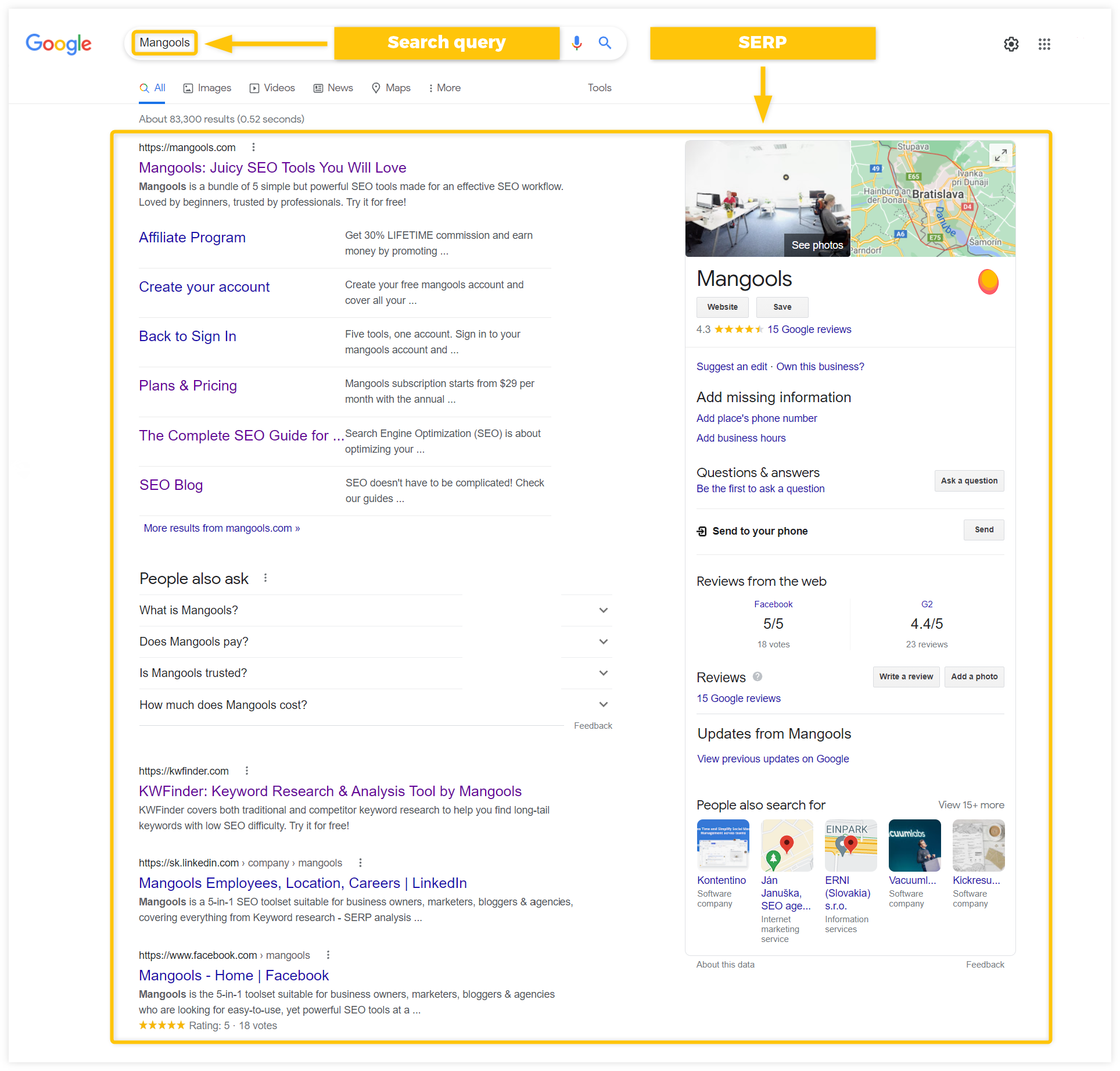
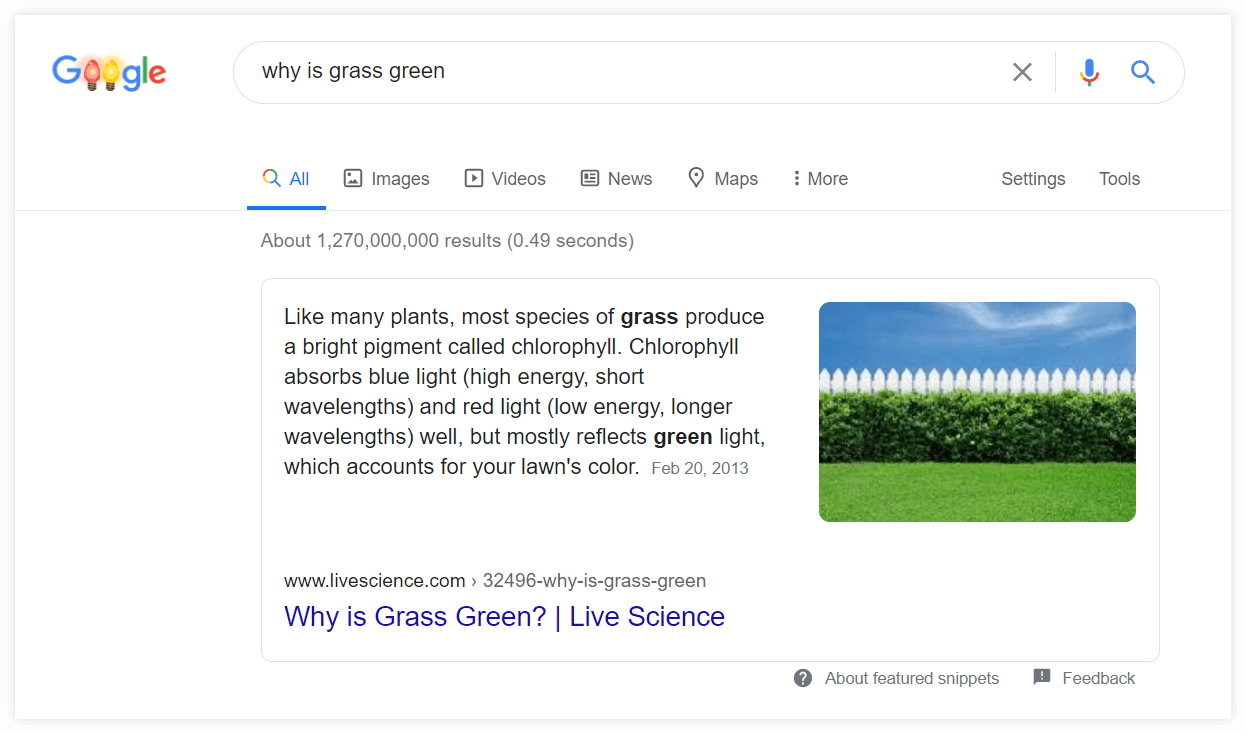
Here’s an example of what SERP can look like:
Why is SERP important in SEO?
Obtaining the top positions in a SERP is the primary purpose of Search Engine Optimization. It is a place where you can promote your brand or company and attract new users to your pages.
SERP can be seen as an “SEO battlefield” for two main reasons:
- it is a place through which organic traffic comes
- it helps you to identify and analyze your competitors
Let’s take a closer look at both of them.
1. Organic traffic
Pages that rank high in SERP get the most organic traffic from it.
Whenever users submit their search queries in Google Search, they usually scan and click on the top results that appear in the SERP. This leaves the rest of the search results without any organic traffic.
From the SEO perspective, it is important to get pages to the top of the SERP as it will bring more users to your website.
2. Competitor analysis
SERPs can show the user’s intent behind the search query as well as help you identify your competitors.
The user’s intent behind the search query can be divided into 4 types:
- Navigational query – a search term used for a specific brand or website (e.g. “Facebook“)
- Informational query – a search term used for any type of informational content (e.g. “how to make a pizza“)
- Transactional query – a search term that is used when a user wants to buy something on the internet (e.g. “buy iPhone 13“).
- Commercial query – a search term indicating that the user wants to do research before buying an actual product (e.g. “tesla car review“).
To start ranking in the SERP, you need to find out what users are looking for and what type of content would be relevant for them (e.g. educational content, product pages, etc.).
Besides the search intent, SERP can show you which websites are competing at the top and how difficult it will be to outrank them.
By performing the SERP analysis, you can identify your competitors, examine the top-ranking pages and obtain valuable information such as:
- The type of content – discover which type of content is ranking at the top of the SERP and create pages with the same (or similar) content.
- The coverage of the topic – provide high-quality content that covers the topic in a much deeper way than your competitors.
- The length of content – determine what is the average content length of the top-ranking pages so you can cover the topic in a more comprehensive way than them.
- The authority of competitors – find out what is the Page Authority of the top results so you can estimate how hard it would be to outrank them.
- Other important factors – metrics such as Domain Authority, Citation flow/Trust Flow, or the number of external links of your competitors can also help you get a better picture about the difficulty of ranking in the particular SERP.
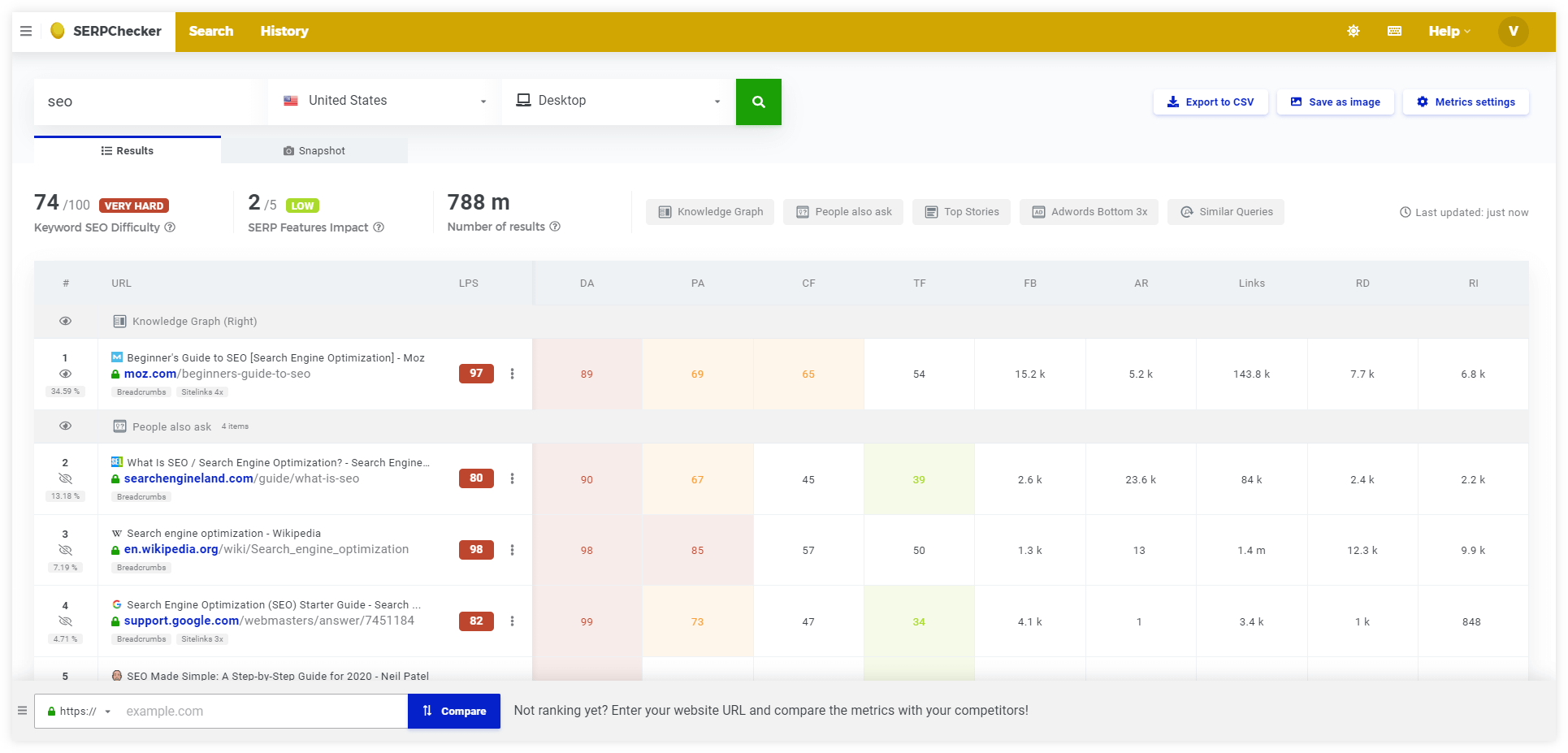
Tip: You can use our tool SERPChecker for a deeper analysis of the SERP – it will help you to:
- Compare your pages with your competitors
- Analyze SERP features that are displayed
- See the actual snapshot of the SERP
- Check over 45 SEO metrics (e.g. Link Profile Strength, Number of backlinks, Domain/Page Authority, etc.).
How is SERP generated?
The search engine generates SERP based on the search query submitted by the user and ranks results by their relevance, quality, and many other factors.
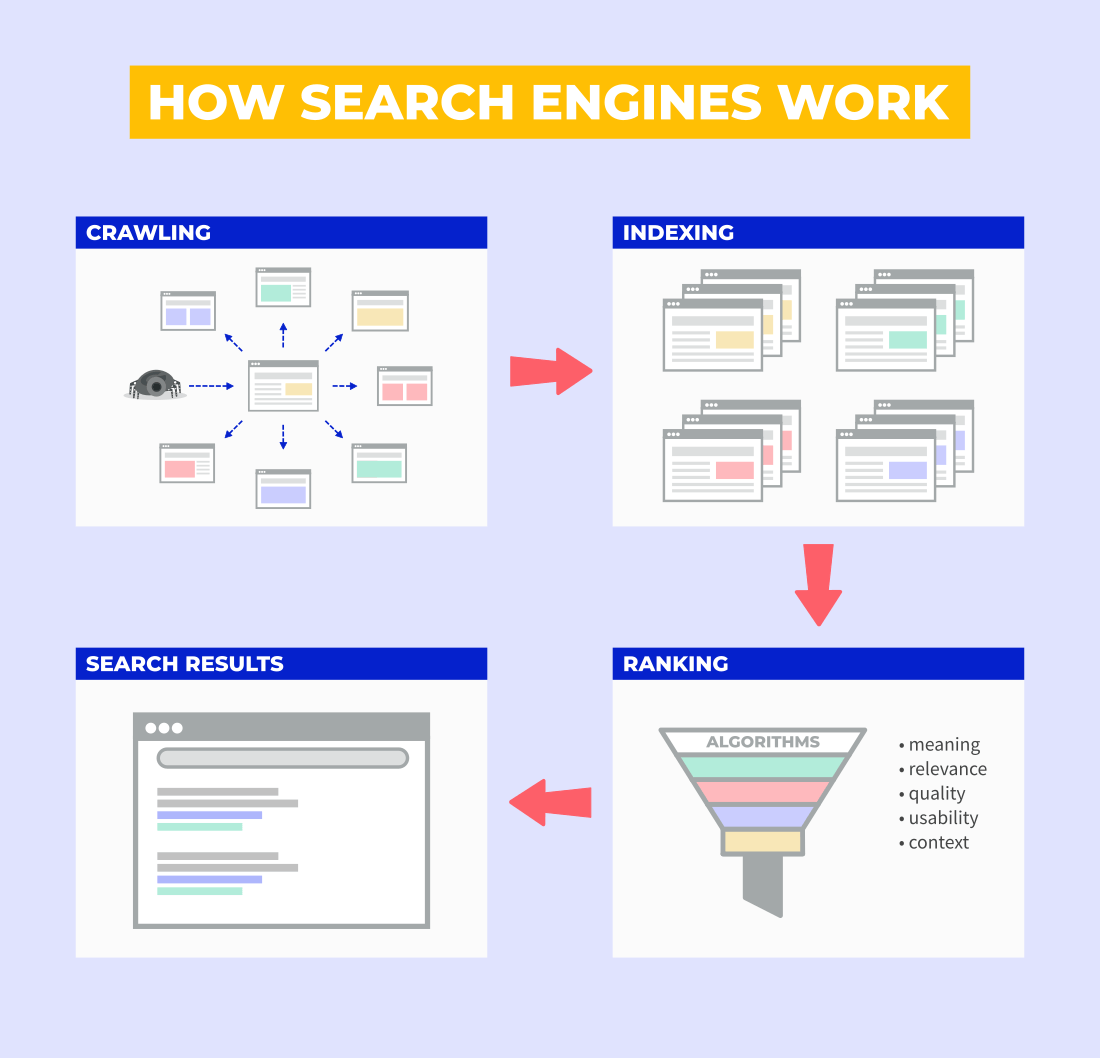
Generating results in SERP is based on 3 fundamental processes:
- Crawling – searching for pages on the web
- Indexing – storing the content from pages to search engine’s library (Index)
- Ranking – sorting and displaying the indexed pages in the SERP
When a user types a search query in Google, the search engine will browse its index to check which pages might be relevant for the user and sorts them according to its various ranking factors.
Note: It is important to understand that every generated SERP is different and unique – 2 different users can see similar but not identical SERP.
Google personalizes SERPs for every user individually based on the information from:
- Browser history
- User’s Location
- Registered Google Account
- Used device
The form, position, and other factors can significantly influence the click-through rate of the search result in the SERP.
Click-Through Rate in SERP
Organic Click-Through Rate (CTR) is the number of clicks on a search result from the overall number of impressions it receives in the SERP.
Ranking position in SERP has the biggest impact on the CTR of the search result – people usually click only on a few top results in SERP which leaves other pages without almost any organic traffic.
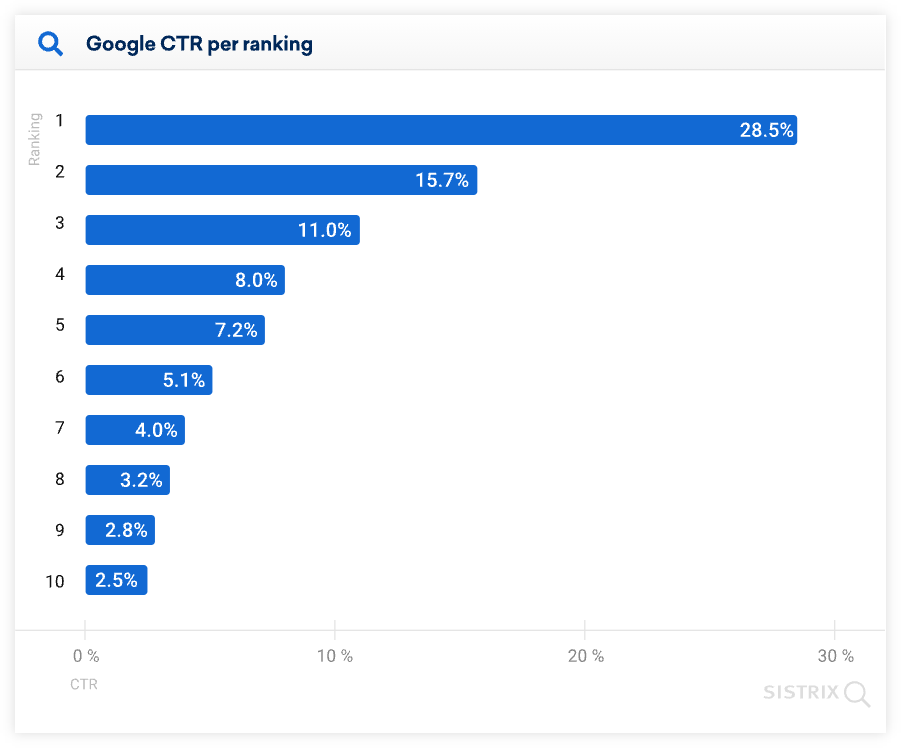
According to a study by Sistrix, the combined CTR of the top 3 pages in SERP is on average higher than the click-through rate of the other 7 ranking pages together:
Prominent spots in the SERP play an important role but there are also other factors that have an impact on the CTR:
- The presence of ads – paid advertisements in the SERP can lower the CTR of organic results.
- SERP features – SERP features tend to stand out in the SERP, leading to drastic changes in CTR for traditional search results.
- Branded vs non-branded queries – branded search queries usually provide higher CTR at the top positions than non-branded ones.
- Snippet optimization – optimized Title Tags and Meta descriptions may improve CTR of the organic search results in SERP.
Keep in mind though, that even with well-optimized snippets and high rankings, there are still many SERPs that won’t bring you any traffic to the website – so-called zero-click searches.
What are Zero-click searches?
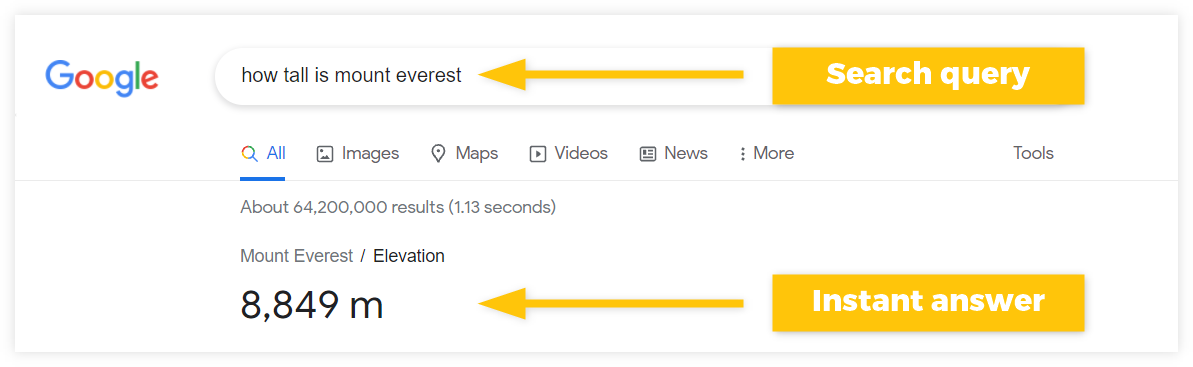
Zero-click searches are queries that provide an instant answer to the user without the need to click on any of the search results in SERP.
They usually have a form of a specific question that can be directly answered in the SERP – leading to a dramatic decrease in traffic for website owners.
For example, if you type into the Google Search query “How tall is Mount Everest“, Google will provide an instant answer:
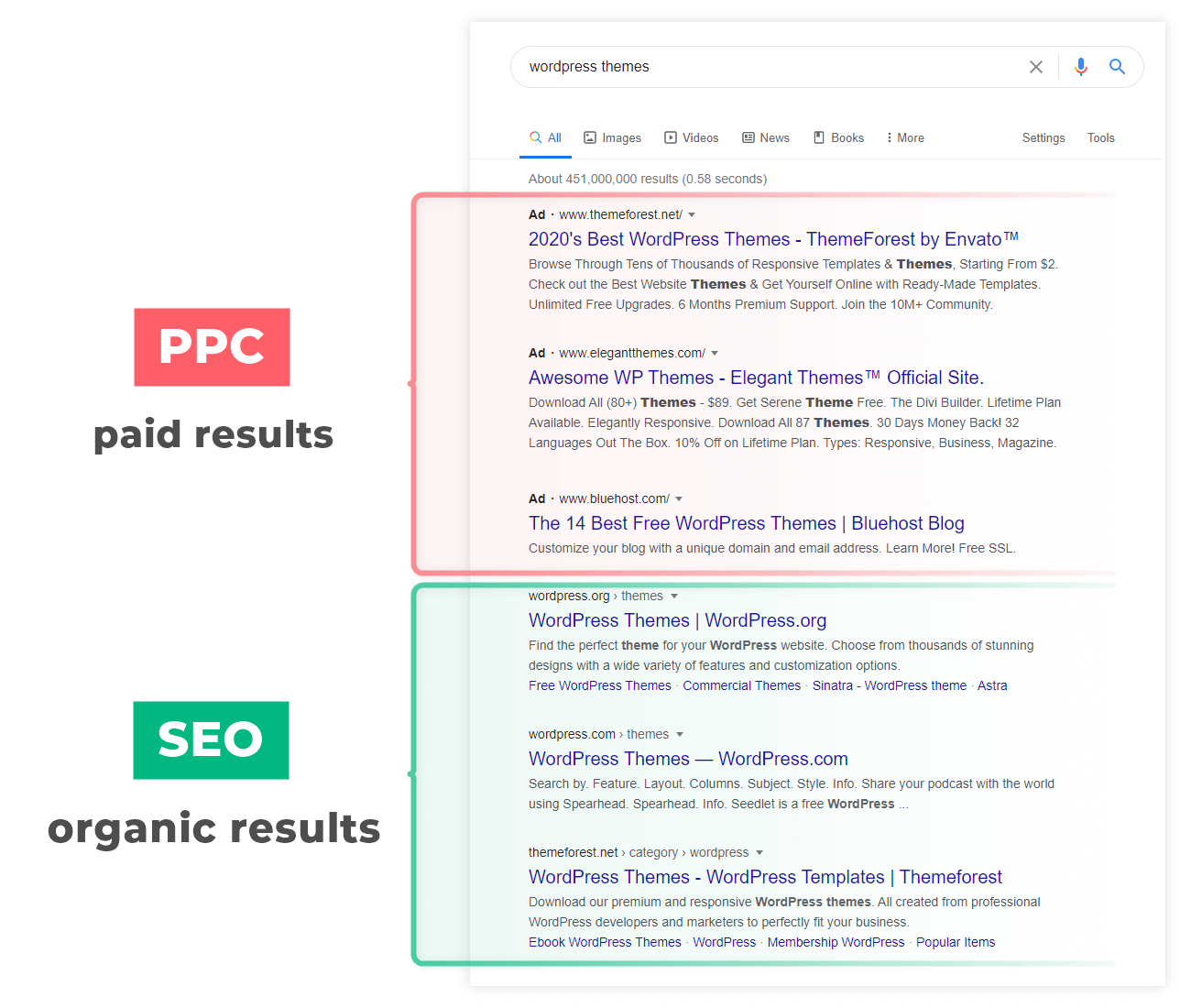
Organic vs. paid results
Google SERP consists of two main types of search results:
- Organic results – results that are displayed in the SERP thanks to the proper search engine optimization, relevancy for the search query, and Google’s ranking algorithm.
- Paid results – results that are displayed for selected search queries as paid advertisements.
Although these two types look very similar (or almost identical) in SERP, they are different in their nature.
Organic results
Organic results are pages that are displayed and sorted in the SERP by the search engine.
They can get to the top of the SERP only by proper page optimization, relevancy, and Google’s algorithm – it uses various ranking factors that determine which results should be ranked high.
Standard organic result (also called a plain blue link) appears in the SERP in the form of a short snippet. It is composed of:
- URL of the page
- Page Title
- Meta description
Ads
Ads are paid results that appear on the prominent spots in the SERP.
They are based on the principle of PPC (Pay-Per-Click). Advertisers can show their ads in SERP by bidding on keywords – the highest bid wins and will appear in the given places in SERP.
Besides the price, several other factors influence whether ads will appear such as relevance, written snippet, etc.
Organic and paid results appear in the SERP in various forms – those are called SERP Features.
What are SERP features?
SERP features are advanced search results that display more information in the SERP than the traditional organic snippets.
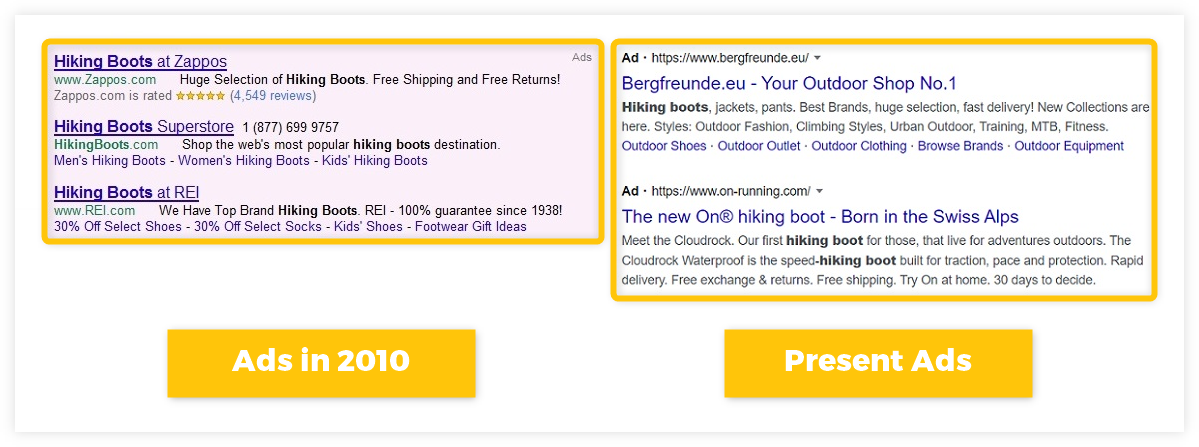
In the past, the Google SERP contained only 10 blue plain links per page sorted according to their relevance.
This changed in 2000 when Google launched its advertising program called Google AdWords – it enabled companies and brands to use ads as advanced features in the SERP.
From that point, Google has added many new SERP features over the years and is constantly changing and developing new ones to improve user experience in Google Search.
It is important to understand that there are dozens of various SERP features – some of them are very common (e.g. Featured Snippet), some of them can occur very rarely.
SERP features can be divided into 4 basic categories:
- Ads – paid advertisements that occur in the prominent spots in SERP
- Organic results – various types of results that are displayed by Google’s algorithm due to their high-quality content, relevancy, and other factors
- Local results – results that are displayed for location-based search queries
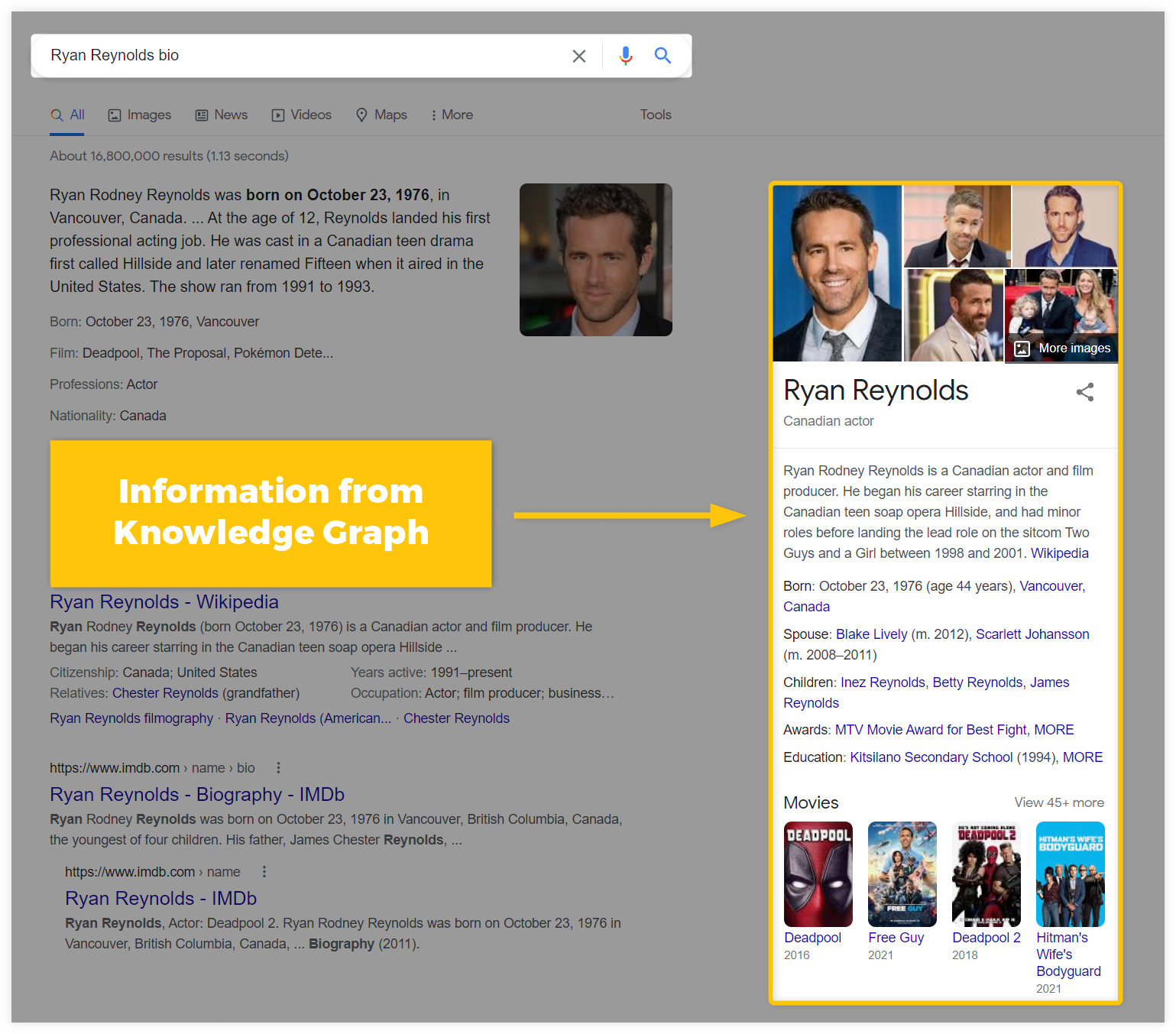
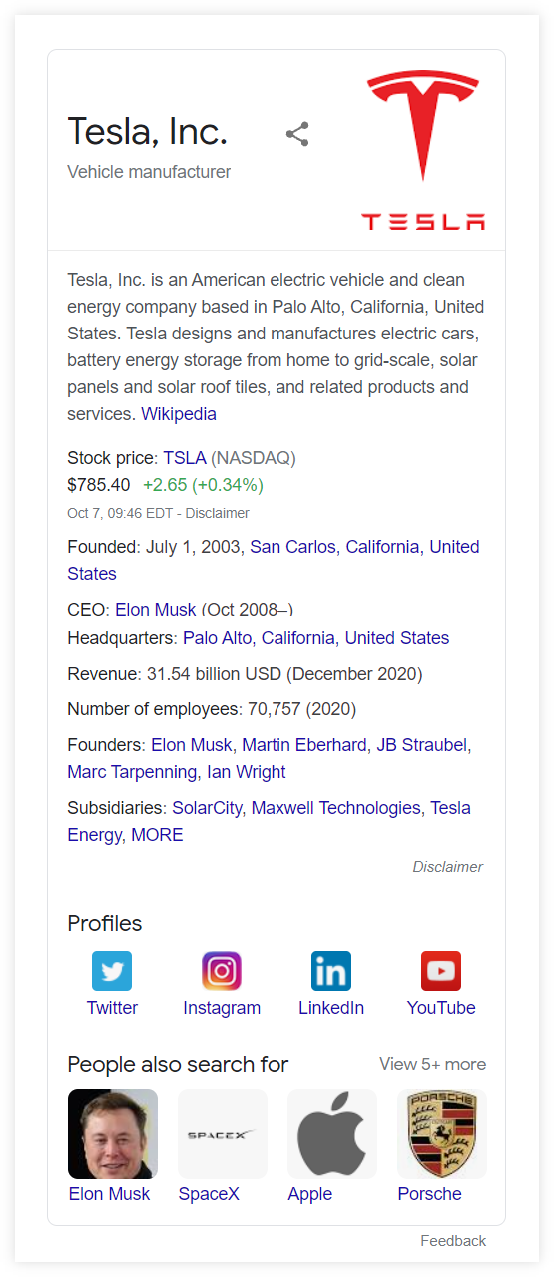
- Knowledge Graph results – provides quick answers to search queries about people, places, or companies. The displayed data in the search results come from Google’s huge database – Knowledge Graph.
What is Knowledge Graph?
Knowledge Graph is Google’s database of factual information about people, places, or things. It contains pieces of information that are interconnected together to create a reliable source for the users.
The data from this huge encyclopedia is further displayed in various SERP features in order to provide deep answers or summaries about any topic.
For example, if you type “Ryan Reynolds bio” as a search query, Google will display a comprehensive summary about the actor with a lot of information that the database collected:
Let’s now take a look at the most common SERP Features that can be found in SERPs.
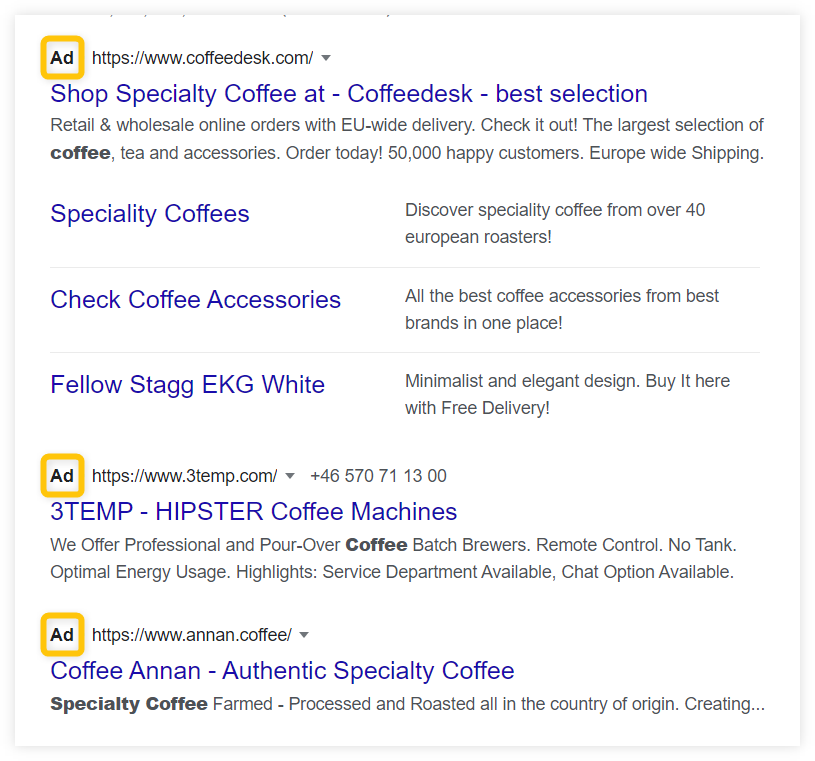
1) Ads
Ads are enriched results that usually appear at the top, bottom, or on the side of the SERP.
In the past, ads were limited only to 1 textual snippet which was displayed in limited areas of the SERP. Nowadays, Google provides several ad formats that can be used by advertisers.
Generally speaking, ads in Google can be shown by using one of the 2 main types of sponsored advertisement:
- 1. Google Ads – previously known as Google AdWords, Google Ads are based on the PPC advertisement. These ads can be enriched by additional headlines, descriptions or may contain linking keywords within their snippets. They also contain an “Ad” icon in the left corner of their snippet that distinguishes them from the organic results.
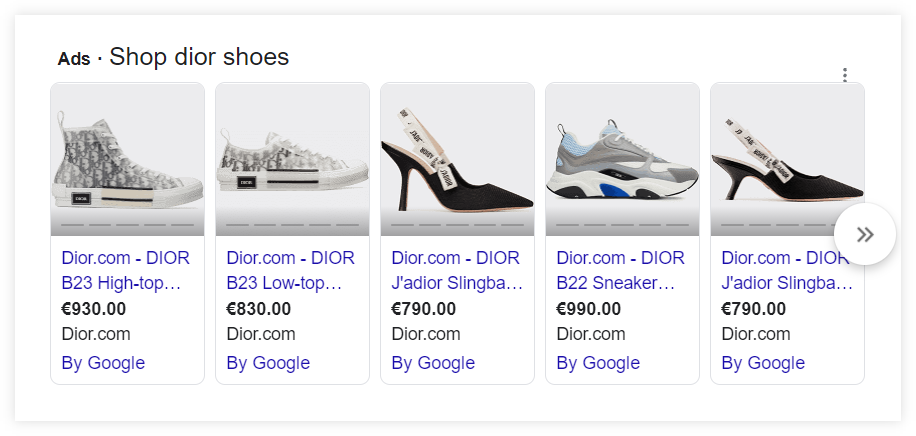
- 2. Google Shopping – previously known as Google Product Listing Ads (PLA), Google Shopping is another form of advertisement that can offer users products directly in the SERP. It usually appears as a block of products (or tab) for product queries with a small description.
Tip: If you would like to know how to display ads in the SERP, check out Google Ads Checklist.
2) Featured Snippet
A featured snippet is a small extract of content from the webpage that is displayed at the top of the SERP (also called “position zero”). It can also appear between the search results or together with the Knowledge Panel:
Featured Snippet can display several formats of content:
- Paragraph – a small block of text that usually provides an answer to question queries (e.g. “What is …” or “Why is …“).
- Bulleted/Numbered list – sorted pieces of content for search queries such as “the best of …“, or “How to …“.
- Table – data that can be presented in the form of a table (e.g. prices, dates, percentages, etc.).
- Video – in some cases, Google might use video as an answer for certain queries.
The featured snippet can be obtained only for those pages that rank high within the SERP. They must also provide optimized content that can be used in the snippet.
It’s important to understand that it is up to the search engine to decide which pages will be used as Featured Snippets.
“Google systems determine whether a page would make a good featured snippet for a user’s search request, and if so, elevates it.”
3) Knowledge Panel
Knowledge Panel is a large box that displays important information about the object, person, or brand in the SERP. It usually appears on the side (for desktop devices) or at the top (for mobile devices):
Knowledge Panels play an important role for companies and brands as they are shown at the prominent spots in the SERP.
You cannot directly create or control the Knowledge Panel.
It is automatically generated and the information it contains comes from Google’s database – Knowledge Graph and other sources (e.g. Wikipedia, Wikidata, etc.).
However, you can suggest changes if you are the person (or other entity) displayed in the Knowledge Panel. For more information, check out Google’s official post about How to update your Knowledge Panel.
4) Sitelinks
Sitelinks are links to a website’s subcategories that appear below an organic search result in the SERP.
The purpose of the Sitelinks is to help users better navigate within the website by showing its individual sections:
The main advantage of Sitelinks is that they enhance the basic organic result and occupy more space in the SERP – users are more likely to click on one of those links.
Sitelinks can’t be directly implemented to your website – Google displays them automatically for certain search queries.
However, Sitelinks are more likely to appear for branded queries and mostly for sites that represent those brands.
Google recommends having a good link structure of your site that is logical and helps the users to better navigate between its sections.
Or as Google officially stated:
“We only show sitelinks for results when we think they’ll be useful to the user. If the structure of your site doesn’t allow our algorithms to find good sitelinks, or we don’t think that the sitelinks for your site are relevant for the user’s query, we won’t show them.“
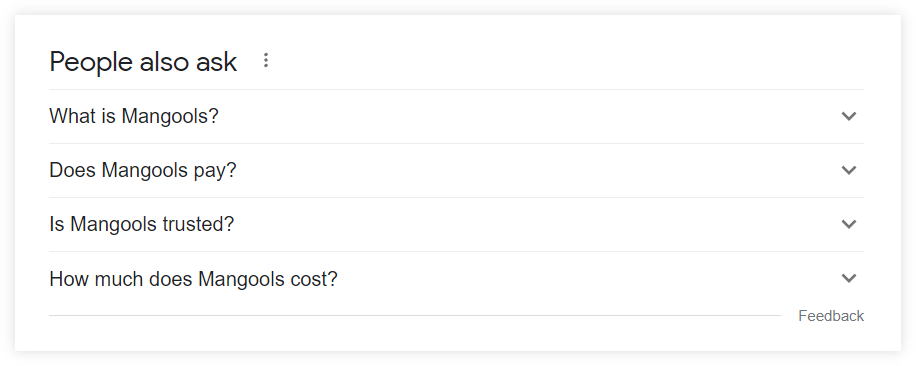
5) People Also Ask
People Also Ask (PAA) is a box that contains questions with answers that are related to the search query.
Whenever a user clicks on one of these questions, the answer will roll out together with a link to the source webpage. Each clicked and rolled-out question will also load more related questions.
Similarly to Featured Snippet, answers in the People Also Ask box can have multiple formats such as:
- paragraphs
- lists
- tables
- videos
The People Also Ask feature provides an opportunity to appear in SERPs in the form of an answer with a clickable link to your page – which can potentially bring more traffic to your website.
From the SEO perspective, People Also Ask boxes are also a great source for content ideas – questions indicate what users might want to know and which content can be produced to satisfy their demand.
You can’t directly control whether the content of your page will appear as an answer for one of the questions in PAA – all you can do is to create content that would answer these questions.
5) Rich Results
Rich Results (also called “Rich Snippets”) are organic results that are visually improved by additional elements (e.g. Breadcrumbs, Review stars, images, etc.).
The main advantage of Rich Results is that they are much more attractive and visually appealing to users as opposed to the traditional search results.
Due to this fact, Rich Results can significantly boost your CTR and bring more organic traffic from the SERP.
Rich Results can be obtained in the SERP by implementing structured data to your pages but only Google will decide which Rich Results will appear in the SERP and which won’t.
Depending on the type of your pages and their content, there are many types of rich results that can be used (e.g. FAQ pages, recipes, articles, etc.).
For more information about individual Rich Result types, check out Google’s official search gallery.
6) Local Packs
Local Packs display results related to the organizations, businesses, or places together with a map for local search queries.
They typically appear at the top of the SERP and provide detailed information about the place such as open hours, address, phone number, etc.:
Local Packs are a great opportunity for businesses that are trying to get new customers to their facilities or just increase their awareness for local search queries.
There is no direct way to show Local Packs for your website in the SERP. You can increase the likelihood of appearance by submitting your organization to Google My Business and provide detailed information about your business.
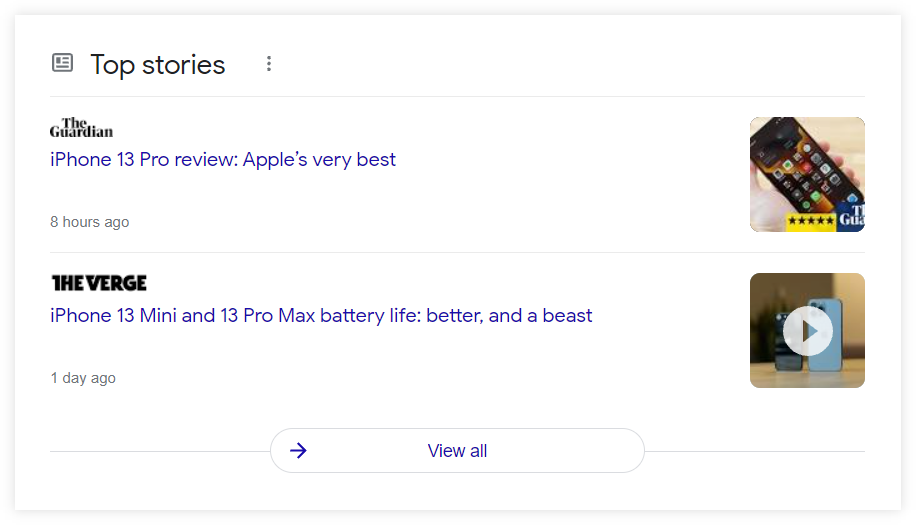
7) Top Stories
Top Stories is a list (or carousel) of pages with titles, authors, release dates, and thumbnails that appear at the top of the SERP for trending search queries.
It usually consists of news, articles, or even recently published videos that can inform users about the time-sensitive topic.
Here’s an example of the Top Stories section for search query “new iPhone“:
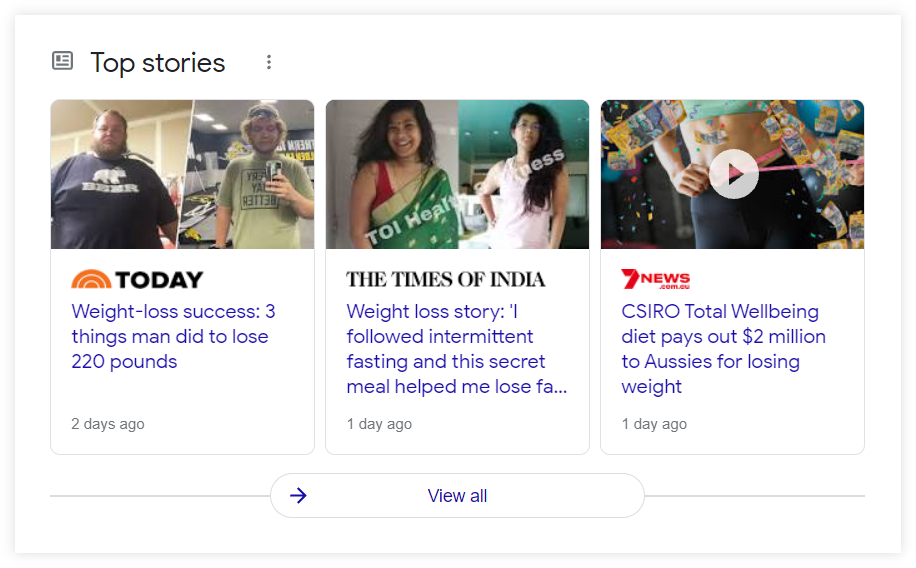
Note: Although the Top Stories section is usually displayed for trending keywords, it can be also displayed for more stable search queries such as “lose weight“:
Google might consider your pages eligible for Top Stories if you provide high-quality content that is suitable for the news-oriented search queries and complies with Google News content policies.
Note: Google also provides many other SERP features that can be displayed such as:
- Direct Answer Box – a short piece of text that provides a direct answer to the question-related search queries or zero-click searches.
- Videos – video boxes with thumbnails, uploaded date, duration, etc.
- Tweet Boxes – new or popular tweets in a carousel displayed for branded queries.
- Image Packs – a group of images that appears at the top of the SERP.