What is Google algorithm?
Google search algorithm is a complex system that allows Google to find, rank and return the most relevant pages for a certain search query.
To be precise, the whole ranking system consists of multiple algorithms that consider various factors such as quality, relevance or usability of the page.
How does Google search algorithm work?
Here’s a short video that explains how Google Search works:
There are many factors that come into play.
We’ll go through 5 major areas (officially listed by Google) that influence what results will be returned for a certain query:
1. Meaning of the query
To return relevant results, Google must understand what exactly is the user searching for and what’s his search intent.
They must understand and assess various things:
- Meaning of the words – what exactly do the used words mean in the natural language?
- Search intent behind the query – what does the user wants by using the particular query – definition, review, purchase, finding a specific website?
- The need for the freshness of content – is the query time-sensitive and requires fresh information?
Sometimes it’s pretty straightforward. If someone uses the search query “buy new iPhone“, it’s pretty clear in all the aspects – meaning, intent and the need for freshness.
But sometimes, especially with general queries, it’s hard to understand what exactly the user meant. In these cases, Google shows what it considers to be the best results but offers additional choices that help to specify the search results.
For example, look at this disambiguation for the keyword “rock”:
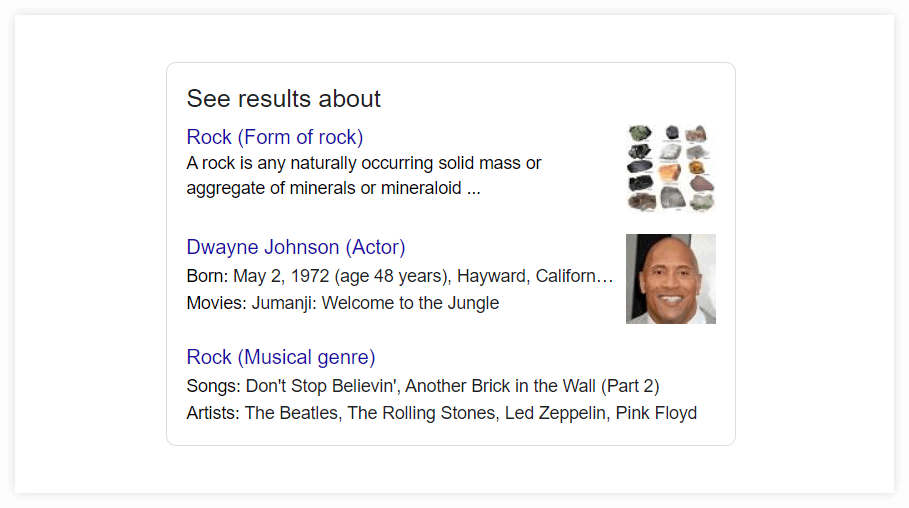
An example of a search results disambiguation.
2. The relevance of pages
Secondly, the search engine has to find what pages are relevant to the search query. In other words – to find the pages that answer the user’s search query in the best way possible.
It does so by regular crawling and indexing of all the websites on the internet and analyzing their content.
The key role is played by keywords. If the search query and the phrases that are related to the search query appear on the page, there’s a high chance the page is relevant for the user.
3. Quality of content
There are likely millions of pages for each search query, so Google has to prioritize the ones that offer quality content and demonstrate:
- Expertise
- Authoritativeness
- Trustworthiness
One of the key elements is the so-called PageRank algorithm that takes into account the quality and quantity of links pointing to a page.
Google PageRank
PageRank algorithm (not to be confused with an obsolete PageRank metric from Google Toolbar) is one of many algorithms that are part of Google’s ranking system.
PageRank is a numeric value assigned to each page to help prioritize the search results.
It is based on an assumption that more important pages are likely to receive more backlinks from other authoritative websites.
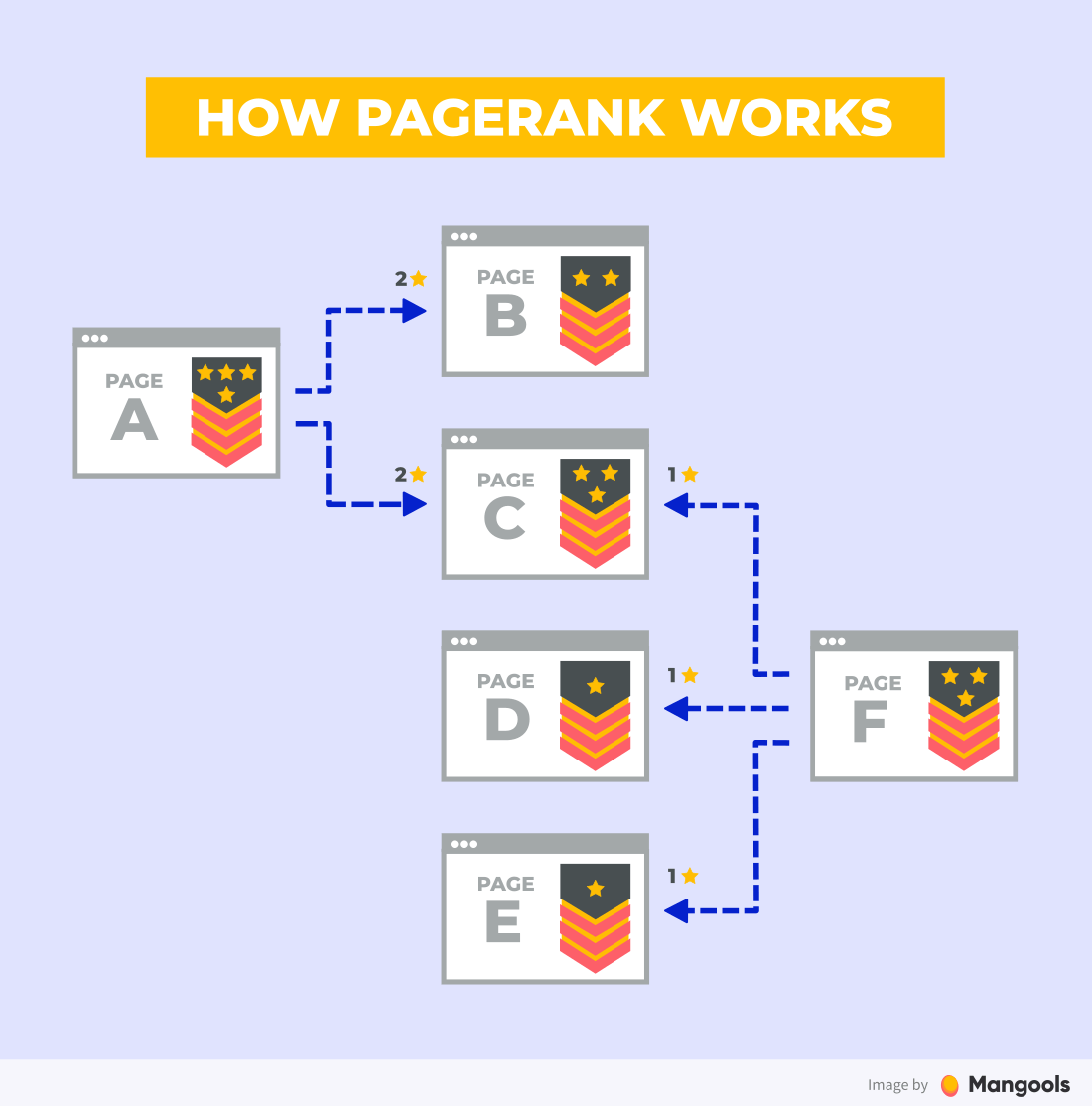
If you look at the image above, you can see that there are 3 main factors that influence the PageRank of a page:
- quantity of backlinks
- quality (PageRank) of the linking page
- number of links on the linking page
To put it simply: The more backlinks from quality pages you get, the higher is the chance that Google will consider you a high-quality page.
If you want to learn more about PageRank, read our post on this topic – Google PageRank: Everything you need to know,
Furthermore, Google uses a number of spam algorithms that detect low-quality pages trying to rank using spammy black-hat SEO techniques.
4. Usability of pages
Now that Google covered the relevance and quality of content, they have to make sure the website has good usability and user-friendliness.
This includes technical aspects such as:
- Page responsiveness
- Correct appearance in all the browsers
- Page speed
- Security of the website
These may not be the most important factors but they are certainly taken into account when other factors (like relevance and quality) are equal.
Note: Google incorporates more and more page experience signals into their ranking algorithms over time.
For example, the so-called Core Web Vitals, “a set of metrics related to speed, responsiveness and visual stability”, were incorporated into the algorithm as ranking signals in 2021.
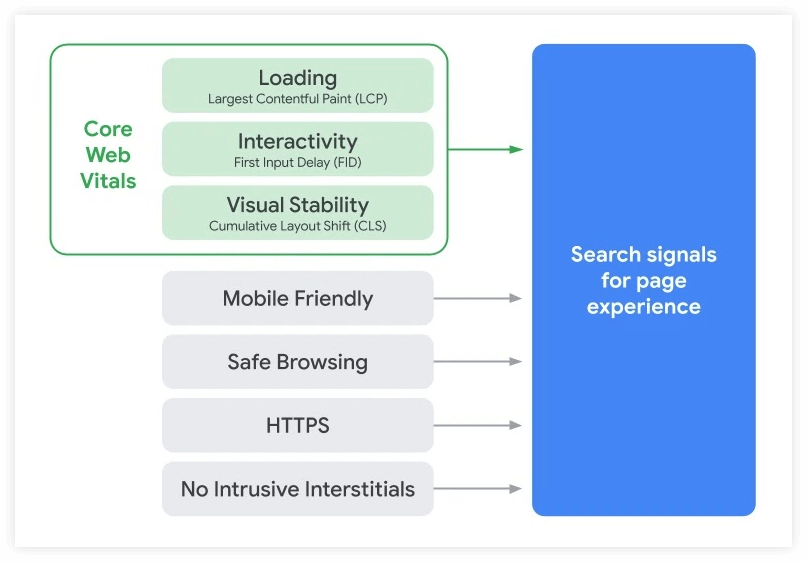
5. Context and settings
Last but not least, the search results are heavily influenced by the individual circumstances and preferences of the user.
These may include things like:
- Location of the user
- History of searches
- Search settings
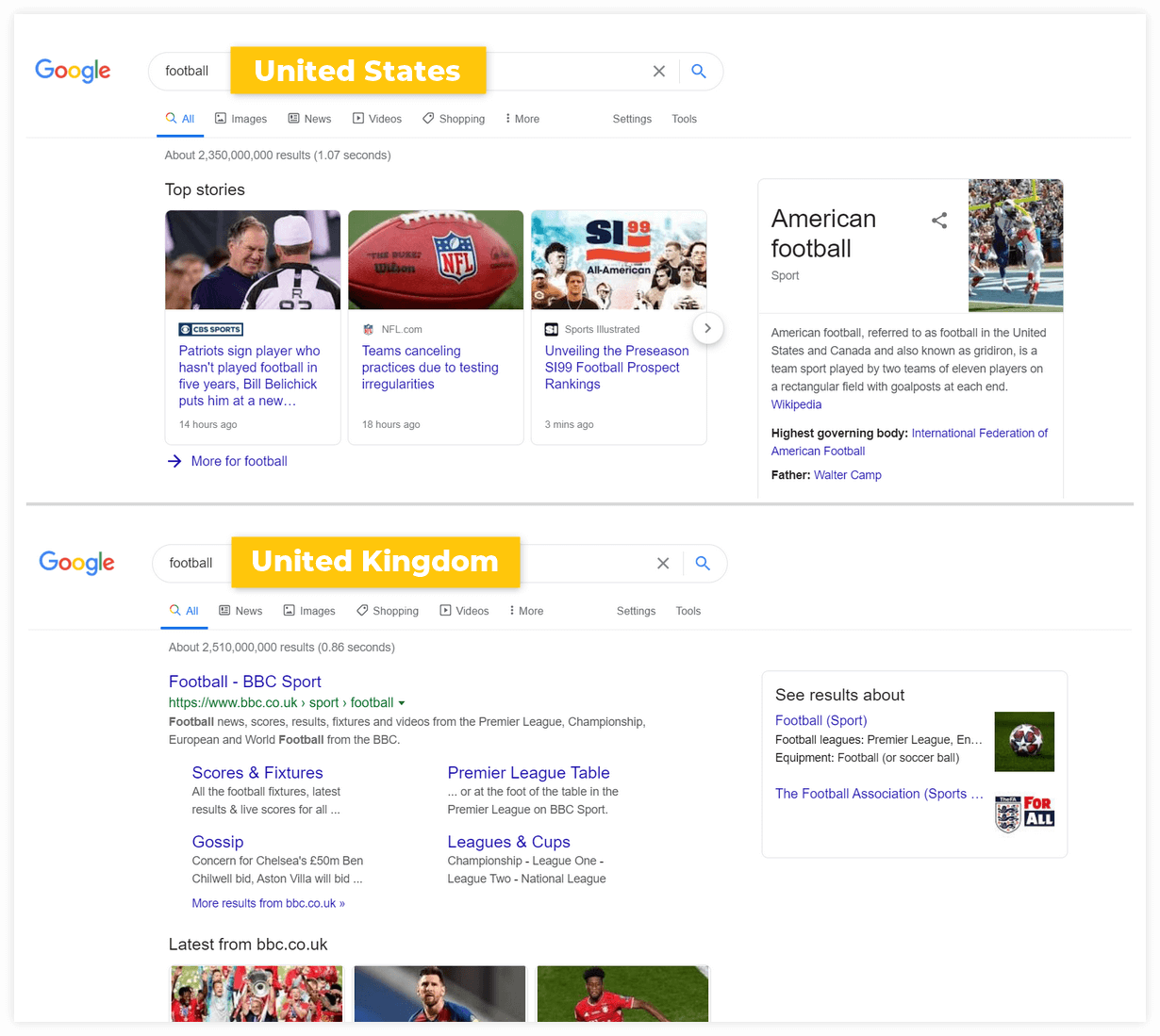
Here’s a typical example of the impact of location on the search results – the results for the keyword “football” in the United States vs. the United Kingdom:
Google Search Quality Raters
Besides the algorithms and machine learning systems (like RankBrain), Google also uses input in the form of feedback from real people.
Google hires thousands of external employees – Search Quality Raters – to evaluate the actual search results and rate the quality of the ranked pages.
Her’s how Google explains how they use the data:
It’s important to note that this rating does not directly impact how this page or site ranks in Search. Nobody is deciding that any given source is “authoritative” or “trustworthy.” […]
Instead, ratings are a data point that, when taken in aggregate, helps us measure how well our systems are working to deliver great content…
So Quality Raters don’t influence the results and rankings directly but the data gathered from the raters are used to improve the Google algorithm.
Note: Search Quality raters follow strict rating rules summed up in a 200-page PDF called Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines.
It is publicly available and can serve as a useful source of information on how to create quality pages.
A screenshot from the Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines intro.
If you’re interested in this topic, read this interview with a Google Search Quality Rater on Search Engine Land.
Algorithm updates
In general, we can divide Google algorithm updates into two categories:
- Minor updates
- Core updates
Google tweaks its algorithm quite often.
And by quite often we mean several times a day. Most of these changes are very small and people don’t notice them.
Besides these small updates, Google rolls a couple of big core algorithm updates every year. These usually create a lot of buzz in the SEO community and often get catchy names.
Most important core algo updates
Here’s a list of the most well-known algo updates in the last decade that shaped the way Google algorithm works:
Panda (2011)
Google Panda is a filter focused on low-quality pages, thin content, keyword stuffing and duplicate content. It was incorporated into the core algorithm in 2016 and rolls out regularly.
Penguin (2012)
An important algorithm update that focused on any kind of manipulative (low-quality, spammy, irrelevant, over-optimized) links.
Hummingbird (2013)
Hummingbird update improved the way Google understands and interprets search queries; a shift from exact keywords to topics
Pigeon (2014)
Pigeon focused on the improvement of the local results both in terms of quality and accuracy.
Mobile Update (2015)
This update is also known as Mobilegeddon in the SEO community. It favors mobile-friendly pages in mobile search results.
RankBrain (2015)
As mentioned earlier, RankBrain is a machine-learning component of Google’s Hummingbird algorithm that helps provide more relevant search results.
Fred (2017)
Fred is an unconfirmed update that seemed to focus on low-quality, ad-centered content that violates Google Search Quality Guidelines.
Medic (2018)
A broad core algorithm update that heavily affected the so-called YMYL (your money your life) pages, especially health-related content.
Bert (2019)
Another machine learning algorithm focused on a better understanding of the context of a search query. It is based on the natural language processing model called BERT.
Each broad core algorithm update usually leads to a wide variety of speculations and discussions on SEO social media groups and forums.
Since 2020, Google tends to prevent the naming of the big algorithm updates by the SEO community by announcing their names in advance:
Tomorrow, we are releasing a broad core algorithm update, as we do several times per year. It is called the June 2019 Core Update. Our guidance about such updates remains as we’ve covered before. Please see this tweet for more about that:https://t.co/tmfQkhdjPL
— Google SearchLiaison (@searchliaison) June 2, 2019
What to do if you’ve been hit by a Google algorithm update?
- Be patient – Most core updates roll out for several days, so it’s always good to wait till the dust settles down. Rushing into “quick fixes” can do more harm than good.
- Rely on trusted sources – Do not trust every forum “expert” with “100% verified” advice you’ll find (there are many of them). Instead, wait for analyses by trusted experts and publications like Search Engine Journal or Moz.
- Make sure you need a fix – Sometimes, the best thing to do after you’ve been hit by an algo update is doing nothing. Many updates are slightly improved or reverted after a couple of weeks so make sure you don’t fix things that don’t need to be fixed.
- Improve – Last but not least, if you realize that there’s a problem on your website that may have been the reason for your drops in rankings, it’s time to fix it. Or, maybe re-think your whole SEO strategy to focus more on quality rather than quantity.





