When Google RankBrain was introduced in October 2015, all we knew was that an artificial intelligence (AI) would learn from search queries and their engagement rate to fit future search queries in a more suitable way.
Nowadays, we know that optimizing for RankBrain is the third most important ranking signal. However, RankBrain itself is not a typical ranking signal when compared to content or backlinks.
Contents:
- How does RankBrain work?
- How can RankBrain update the algorithm?
- RankBrain understands keywords
- Keyword research tactics for RankBrain
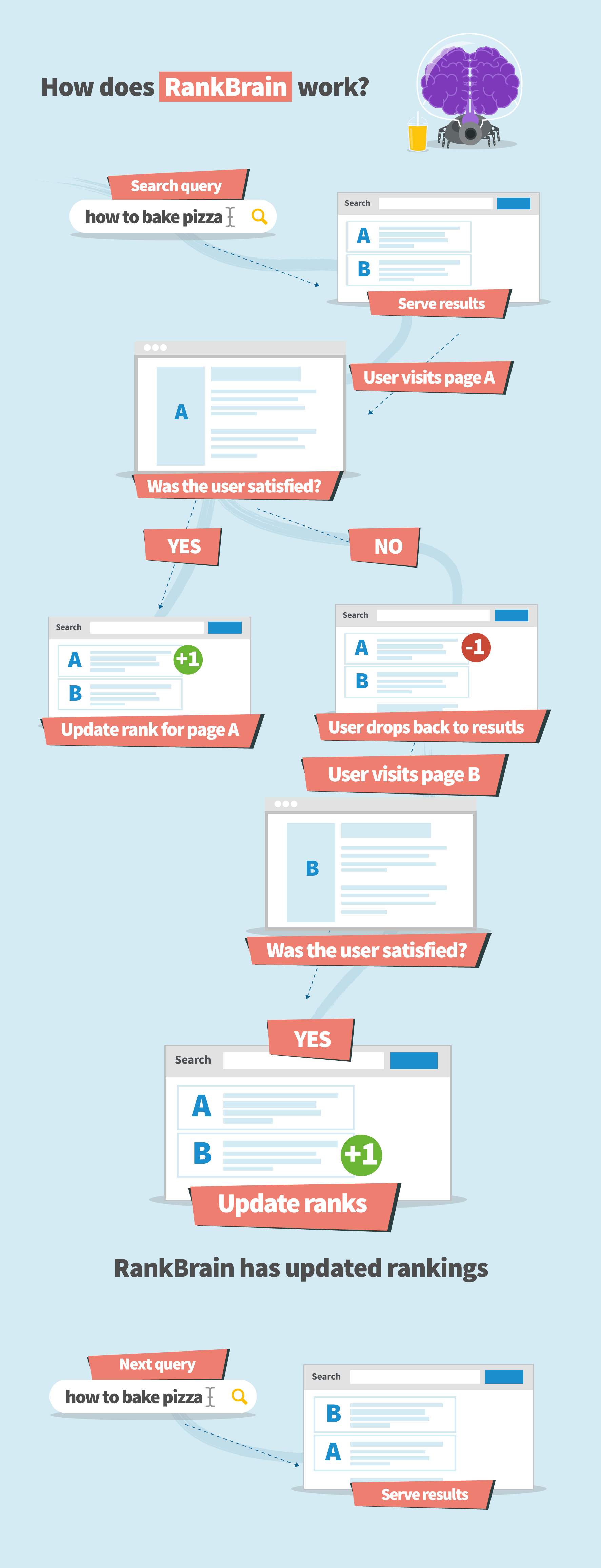
How does RankBrain work?
The machine learning algorithm works something like this:
- It’s not based on the hand-coded algorithm used in the past by Google developers and testers.
- By tracking user’s engagement from searches and learning from it, RankBrain adjusts the algorithm.
- If the updated algorithm leads to results with higher engagement, it’s implemented for future search queries.
According to Google, RankBrain learns offline. It’s given loads of historical data to learn from. Once it generates possible search results, they are tested and launched if proven relevant.
How can RankBrain update the algorithm?
In many ways. Let’s look at some of the most discussed ranking factors such as content, backlink profile, authority, keyword optimization or content length.
Here’s a very simplified example:
When RankBrain realizes that users aren’t satisfied with a search result with super long content with many backlinks, it may lower the importance of these signals in favor of short content and less backlinks.
In other words, the content freshness and other signals will become more important. Generally speaking, freshness seems to be an important factor for RankBrain. On the other hand, many SERPs are full of outdated content (many times irrelevant) just because those websites have quality backlinks.
RankBrain helps Google algorithm to decide which signals are more important for which search query.
RankBrain understands keywords
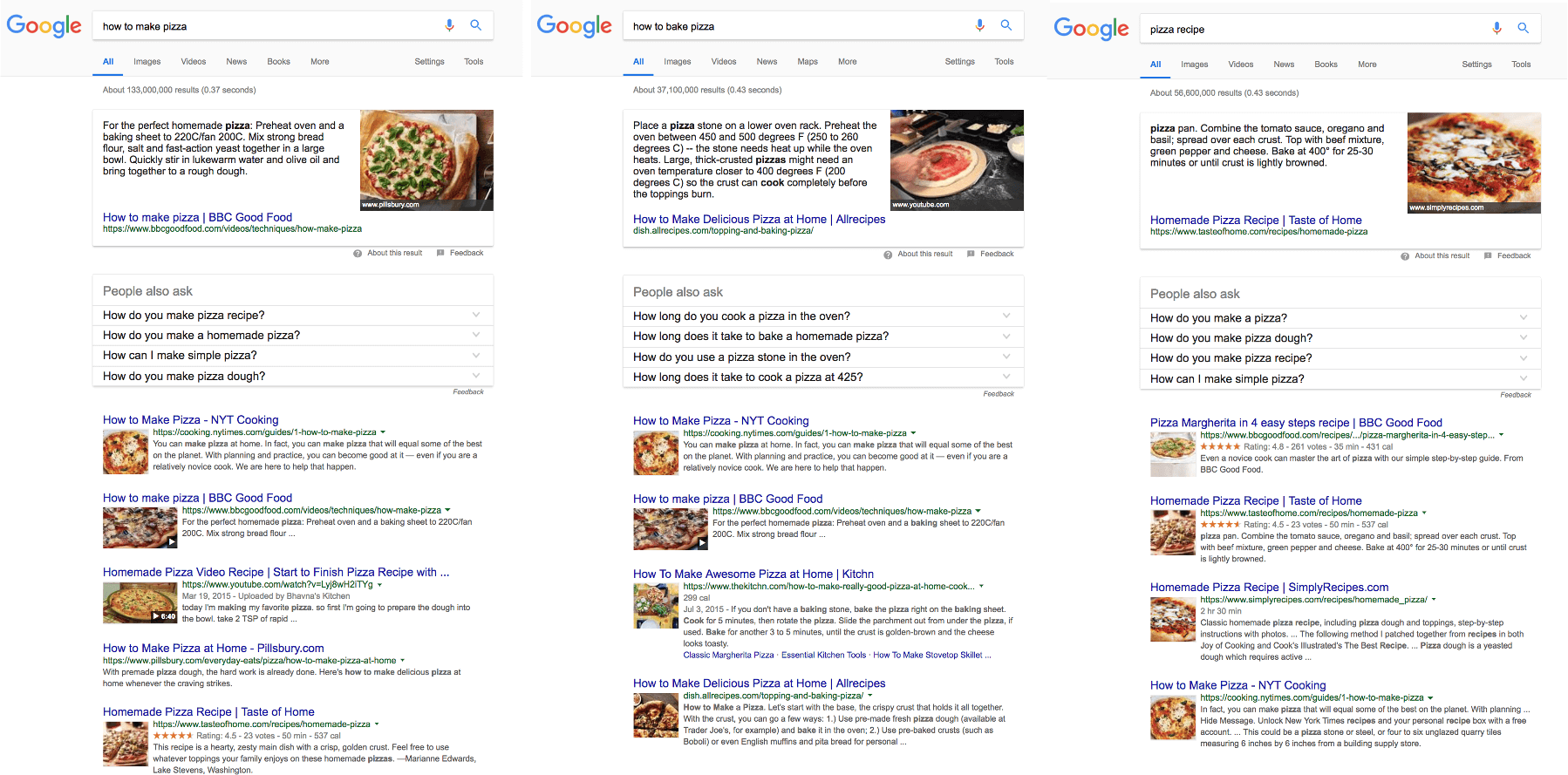
In the past, Google algorithm tried to match the search query with results that contained the exact or at least very similar keyword. Many times it didn’t lead to fitting results.
On top of that, users started submitting more and more unique queries so the algorithm could only guess what they were looking for. RankBrain solves the issue.
All the above mentioned is possible because RankBrain’s AI goes far behind the keywords to understand them, identify search intent and prioritize the ranking signals accordingly.
It understands that similar long tail keywords are about the same topic so it will display basically the same search results for a couple of different long tail queries.
How about non-English keywords?
I guess it works best for English and then for other major languages. On the other hand, results for “smaller” languages are not there yet.
Maybe because there is not enough data that RankBrain can learn from or Google developers just take their time. Who knows.
Keyword research tactics for RankBrain
Keyword research is a complex process, yet it’s only a part of SEO. You will find a lot of tips in many of our blog posts discussing keyword research or KWFinder’s features.
However, this article is dedicated to keyword research for RankBrain so it would be unfair not to include the tactics. But is it even possible to optimize for RankBrain? Well, yes and no.
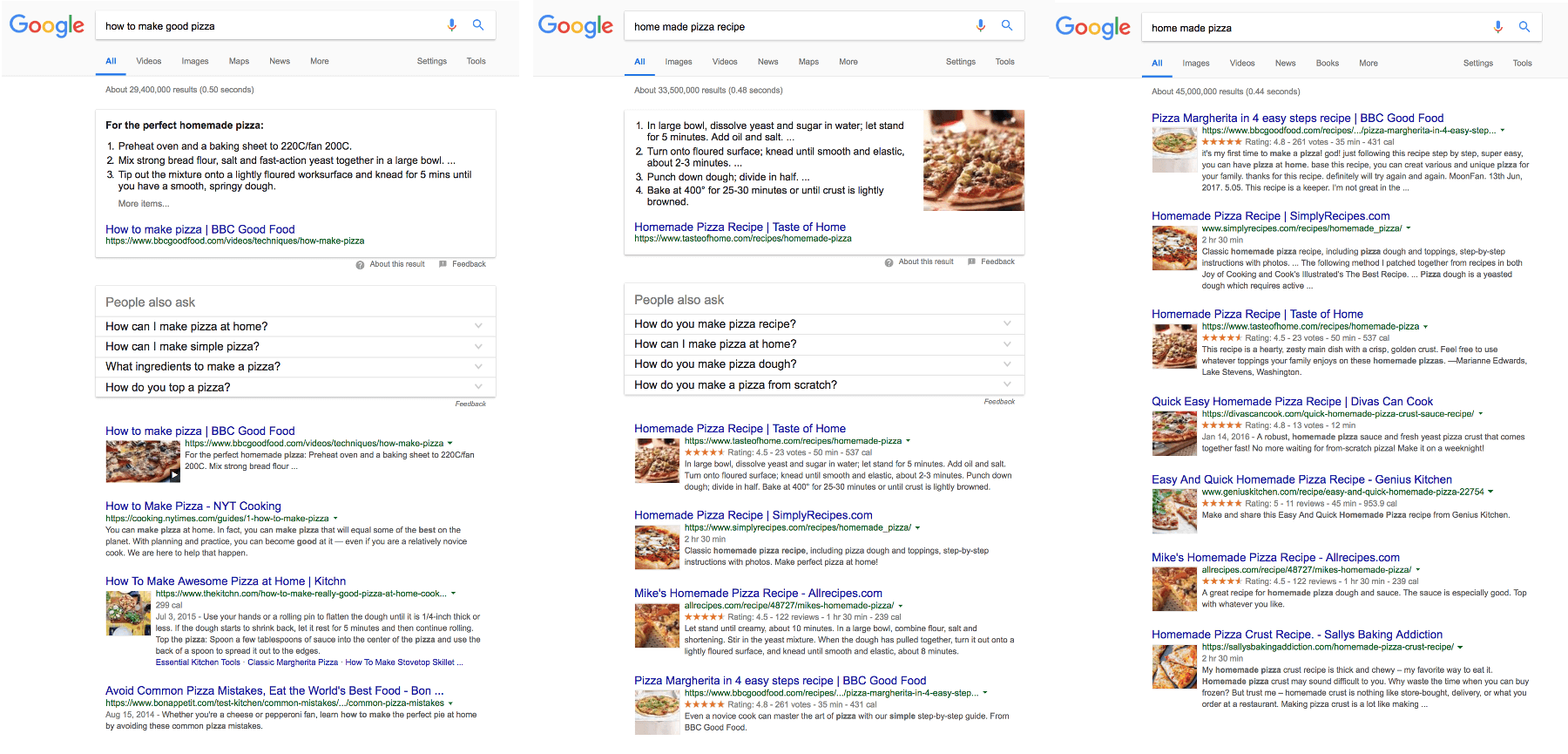
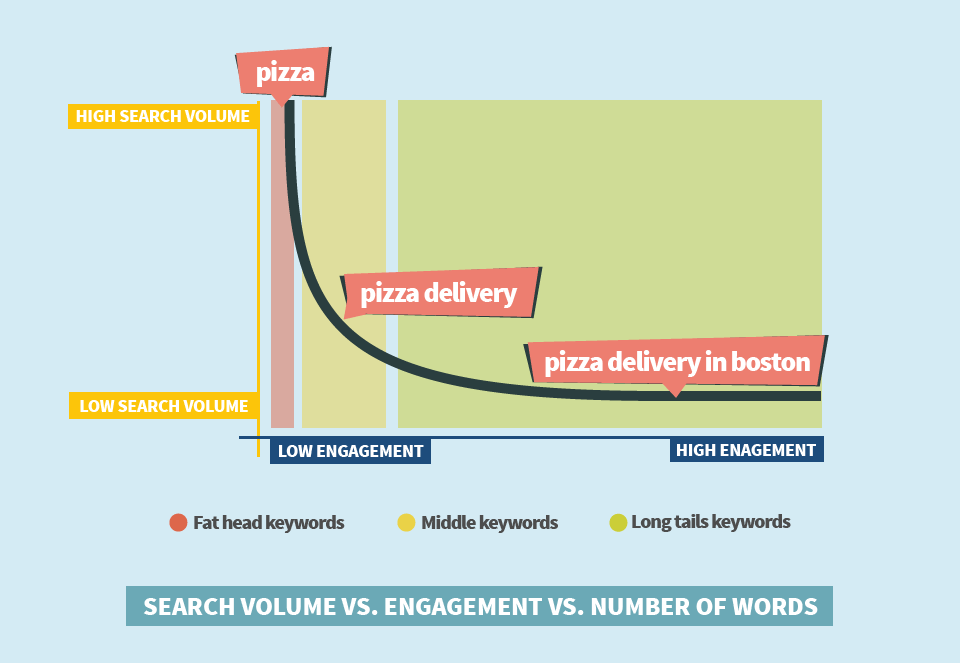
Are long tail keywords dead?
If you think long tail keywords are phrases with 6 or even more words than yes, long tail keywords are dead! For me, long tails are phrases made of 3 or 4 words. Some call them middle keywords.
Tactic 1 (keyword research):
So these shorter long tail or middle tail keywords, whatever we call them, should be the top priority when optimizing (for RankBrain). We can call it “topical keyword research”.
Because RankBrain understands the keywords, we will rank on the same or comparable positions for many similar long tail phrases. I hope I don’t need to say this but it should happen only if the content satisfies users and the website is (naturally) well-optimized.
Having a couple of high-quality backlinks will always help. They remain to be one of the most significant ranking signals.
Keep in mind:
There’s a tendency of the higher SEO difficulty when it comes to middle keywords so it may get a bit more difficult to overcome competitors. On the other hand, there’s a bonus of usually higher average search volume and ranking for many long tail phrases at the same time.
Keyword optimization vs. user satisfaction (engagement)
This is one of those tactics we stress in almost every article on this blog. You need to optimize for both people and search engines. Over-optimized content will influence engagement in a negative way.
Tactic 2 (keyword research, content, engagement):
Create content that is relevant and catchy for users and strategically optimized for search engines. I’m glad that RankBrain pays attention to the engagement. It focuses on content results and not (only) how well it is written, optimized and how many quality backlinks the website has. To put it simply, Rank brain does:
- Understand the keywords (explained above)
- Measure the satisfaction of users with search results
How is the satisfaction measured?
There are many views and misconceptions about this. The fact is that no one knows!
Many bloggers say (and we used to think the same) that the dwell time (the amount of time users spend on a website before they return back to the SERP) or so-called pogo-sticking is one of the factors that the RankBrain takes into account.
The truth is that this metric wouldn’t be enough to determine the quality nor the relevancy of that particular search result.
In many cases, browsing through a website and then immediately going back to the SERP doesn’t mean that the users didn’t find the information they were looking for.
It all begins in SERP
Yep, a very important point! UX starts even before visiting a website. It starts by submitting a search query and may transform into signals for RankBrain.

Tactic 3, 4, 5 … (SEO, UX, content, engagement):
Title tag and description optimization: use numbers, top lists, questions, make a case study, use special characters such as brackets.
Don’t forget to include the main keyword. It doesn’t make sense to write relevant titles and descriptions while not including the keyword. Use emotions to write appealing titles and descriptions. Avoid common title tag mistakes.
Exactly the same applies to content itself. Catchy subheadings, case studies, videos and real-life examples attract a lot of attention. Personalize content for your target audience and make their way super easy to find what they are looking for.
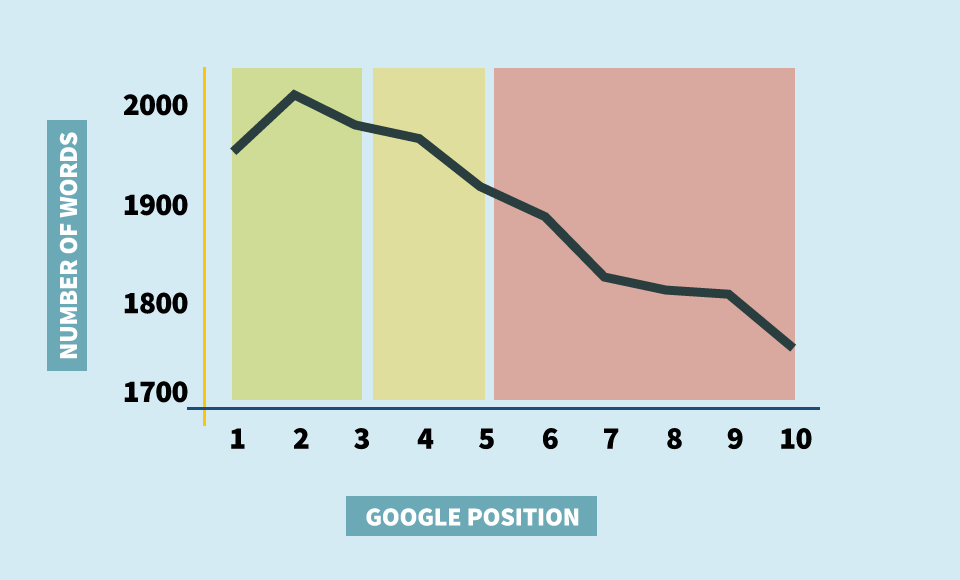
The last tactic I want to mention, though I don’t like it that much, is to write long, in-depth content. There are many studies proving that quality long content leads to higher engagement.
Conclusion
I hope you enjoyed reading this article and learned something new that will help you to optimize for your audience. RankBrain is a deal for users and SEO specialists at the same time.
Becoming successful in today’s SEO means creating a site that satisfies users. It doesn’t matter whether it’s an answer to their question, a product they were exactly looking for, a guide to help them or anything else.