Ever wondered why your website seems stuck on the later pages of Google’s search results, even though you’ve optimized every web page?
Sometimes, slow website performance can be the culprit.
If that rings a bell, then you may want to explore the wonders of a Content Delivery Network, or CDN.
But before you get swamped with thoughts of complex network traffic and bandwidth costs, let’s make it clear: understanding content delivery network services is easier than you think.
So, sit tight, and let’s get into the intricacies of content delivery networks, web traffic, and how they can seriously upgrade your SEO.
What is a CDN?
The term CDN is an acronym for Content Delivery Network. A CDN is not the origin server where your website lives but is instead a geographically distributed network of operational servers designed to speed up the delivery of your web content.
How does a CDN work?
In straightforward terms, a CDN functions as a middleman between your origin server and the end user.
CDNs consist of a network of servers, often referred to as ‘points of presence‘ or POPs, spread out in various global locations.
When user requests come in for your digital content, like media files or web pages, the closest CDN server, or ‘edge server’, to the user takes action.
By connecting users to the nearest edge server, CDNs aim to deliver the best user experience possible, characterized by quicker load times and reduced bandwidth consumption.
These edge servers handle the task of caching both static and dynamic content from your origin servers and delivering it rapidly to website visitors.
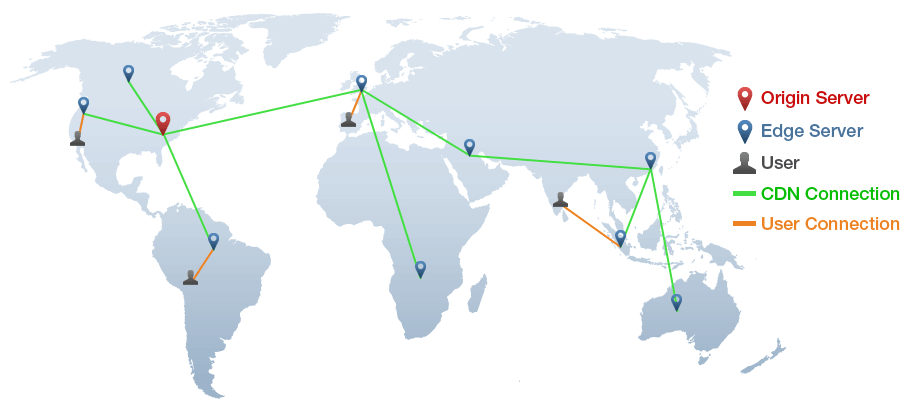
The basic framework: Origin and edge Servers
Before diving into technical details, it’s essential to understand the basic framework of a CDN. A Content Delivery Network (CDN) consists of two main types of servers: origin servers and edge servers.
Your origin server is where your website content originates. This server stores all the files and data that make up your website.
Edge servers, on the other hand, are strategically located at multiple geographical locations and act as intermediaries between the origin server and the end user.
Why is CDN important for SEO?
Content Delivery Networks are a critical tool for website owners looking to optimize various aspects of their site, from speed to security.
It’s no secret that website performance is a significant factor in your SEO rankings.
Search engines like Google have made it clear that user experience is a top priority, and fast load times are a major component of that.
Here are some of the key benefits:
- Improve website performance and load times
- Efficiently deliver web content
- Reduce bandwidth costs
- Enhance user experience
- Help maintain high customer satisfaction rates
- Boost SEO rankings
- Facilitate efficient load balancing
- Reduce network traffic
- Increase website security
- Guard against DDoS attacks
- Serve as a fundamental part of core network infrastructure
- Become increasingly important as web applications grow in complexity and user interaction
These features make CDNs an indispensable part of modern web architecture.
Speed Matters: Loading time and user experience
CDNs specialize in delivering your website content as quickly as possible by leveraging nearby edge servers.
When a user accesses your website, the nearest edge server provides the cached files, slashing the time it would usually take for the request to travel back to the origin server.
The result is dramatically improved website load times, which are a pivotal SEO metric. Faster load times not only elevate user interaction but also improve bounce rates, both of which are monitored by search engines.
Bandwidth Consumption: A hidden SEO factor
While bandwidth costs may not be the first thing that comes to mind when thinking about SEO, they can have a domino effect on your website’s performance.
CDNs optimize bandwidth consumption by compressing media files and utilizing advanced caching techniques.
This includes strategies like caching static content and employing temporary content storage.
Reduced bandwidth consumption not only cuts costs but also contributes to faster website performance, indirectly boosting your SEO.
Localization and global SEO impact
In today’s globalized world, catering to a diverse audience is more important than ever for SEO. If your website has visitors from multiple places in the world, localization of content is imperative.
CDNs make this easy by distributing your web content via data centers strategically located near your target audience.
The result?
Faster and more reliable website performance that not only enhances customer satisfaction but also sends positive signals to search engines regarding content availability.
Core Web Vitals: The new SEO benchmark
Google’s Core Web Vitals have become an essential SEO ranking factor. These metrics measure visual stability, interactivity, and loading performance of web pages.
CDNs contribute positively to Core Web Vitals by efficiently delivering web content and reducing layout shifts, which in turn improves both the user’s experience and your SEO.
How to set up a CDN
1. Picking the Right CDN Provider
Given the plethora of CDN providers out there, how do you make an informed choice?
It comes down to understanding your needs.
Some CDN service providers specialize in video streaming services, while others are more versatile. Popular choices include:
Selecting a CDN provider is a crucial step, and there are several factors to consider:
- Performance: Look for providers that have data centers in locations where your audience is primarily based. This can dramatically improve website performance and reduce load times.
- Security: Security features like DDoS protection and Transport Layer Security (TLS) should be available to protect your website content.
- Scalability: Make sure the CDN can scale with your business. As your web traffic grows, you’ll want a CDN that can handle the increased load.
- Customer support: Good customer support can make all the difference, especially when you encounter issues or need to troubleshoot.
- Price: Compare the pricing models of different CDN providers. Some charge based on the amount of data transferred, while others might have a flat monthly fee.
2. Implementation
The thought of messing with your website server and other operational servers can be a bit scary for some.
Thankfully, most CDN providers offer straightforward guides for setting up their services.
This often involves configuring your DNS settings, so that user requests are directed to nearby CDN servers rather than the origin server.
It sounds complicated, but it’s usually as simple as following a step-by-step guide.
Monitoring and Adjustments
Once your CDN is up and running, it’s vital to track its impact on your SEO and website performance.
Use tools like Google Analytics to monitor user interaction, and GTmetrix to keep an eye on load times and bandwidth consumption.
Make adjustments as needed to continue benefiting from your CDN.
Making the Transition
Once you’ve selected a CDN provider, the next step is to integrate it with your website. Here’s a general step-by-step guide:
- Sign up: Create an account with your chosen CDN provider and navigate to the control panel.
- Add your website: Most CDN services will ask you to enter your website’s URL. Follow the on-screen instructions to do so.
- DNS settings: You’ll need to update your DNS settings so that user requests are routed through the CDN’s caching servers rather than going directly to your origin server. This typically involves changing your website’s CNAME record.
- Configuration: Custom configure your CDN settings, specifying caching rules, setting up SSL certificates, and other preferences.
- Testing: Before fully transitioning, test to make sure everything is working as expected. Use online tools to check website load times and ensure that the CDN is delivering your content correctly.
3. Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Even after successful implementation, ongoing maintenance and occasional troubleshooting are necessary.
Monitor your website performance metrics and make any required adjustments to your CDN settings.
And there you have it: a detailed look at what a CDN is and how it can turbocharge your SEO efforts. From reducing bandwidth costs to delivering content more efficiently, CDNs offer a myriad of benefits that no website owner should overlook.
Final thoughts
In an era where website performance and user experience are crucial for SEO, the role of CDNs will only continue to grow.
With video streaming, cloud computing, and web applications on the rise, expect to see CDNs adapting and offering more sophisticated services to meet these demands.
If you’re serious about improving your SEO and delivering an optimal user experience, investing in a CDN is a logical step.
The advantages far outweigh the limitations, from reduced load times and bandwidth costs to improved content availability and website security.
And that wraps up our comprehensive guide to Content Delivery Networks and their impact on SEO. With this knowledge in hand, you’re well-equipped to make an informed decision for your website’s future!
Frequently asked questions
1. What is the main advantage of using a CDN for my website?
The primary advantage of using a CDN is improved website performance, particularly faster load times. By caching content on edge servers closer to your end users, CDNs help you deliver web content more quickly and efficiently.
2. How do CDNs affect my SEO?
Faster load times and better website performance directly influence SEO rankings. CDNs can also help you reduce bandwidth consumption, which can lead to a better user experience and higher customer satisfaction, factors that search engines consider positively.
3. Are CDNs suitable for all types of websites?
While CDNs are highly beneficial for websites with a global audience and high traffic, they can be an overkill for smaller, localized websites. If your website mostly serves a local audience and doesn’t feature media-heavy content, a CDN might not offer significant benefits.
4. Can using a CDN improve my website’s security?
Yes, many CDN providers offer additional security features like DDoS protection and Transport Layer Security (TLS). These features can help protect your website from various types of cyber attacks, adding an extra layer of security.
5. Is setting up a CDN complicated?
Setting up a CDN is generally straightforward. Most CDN providers offer easy-to-follow guides and customer support to help you integrate their services with your existing website infrastructure. Typically, it involves changing some DNS settings so that user requests go through the CDN’s caching servers rather than directly to your origin server.