Sometimes it might be hard to begin and finish an on-page SEO audit of a website to really find errors that can hurt a site from an SEO perspective.
In this article, I want to show you that an SEO audit doesn’t have to be complicated at all. I’ll walk you through six quick steps on how to quickly look at the page through the eyes of both visitors and search engines, and how to easily complete the audit with four free tools.
Tip: If you want to look at on-page SEO from a broader perspective, be sure to take a look at our ultimate guide to on-page SEO.
The best thing about it is that it will take only 15 minutes of your time — 30 if you decide to have a coffee along the way.
6-step SEO audit process
In this article, I will cover these six steps:
- Checking Google SERP (briefly)
- Detecting a possible penalty from Google
- Finding hidden text
- Running a speed test
- Analyzing on-page factors
- Analyzing a particular issue
Before you start an audit, I recommend choosing at least three different pages of your site. If you check only one single page, you might miss many errors on your site.
Select pages that you think are important in terms of both content and traffic. I recommend going with the category page, product page or a blog post.
You should check these pages for the first three steps of the audit process mentioned above. If you find a problem with one-page type, it’s likely that the problem occurs across the entire site.
Tools required for the SEO audit
For the audit, we will use these free tools:
- Web Developer Toolbar (Chrome add-on)
- Google Search Console
- PageSpeed Insights tool
- On-page SEO audit tool
All of these are essential and free of use.
Step 1: Checking Google SERP (briefly)
Go ahead. Google your brand first.
This step serves to quickly determine if your domain is correctly indexed. Your website should rank first (unless the site is completely new).
The appearance of the result is also important. Do you want to have a high CTR? The heading, URL and meta description should be representative of your site and appear interesting to potential visitors. Do the results look clickable? Would you click through?
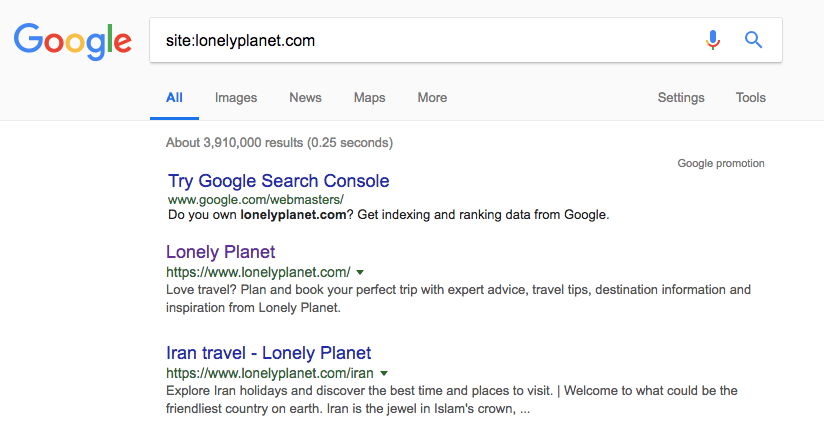
After you search for your brand in Google, you can also check the site’s index rate with “site:” operator.
Write “site:yourdomain.com” into the search box, and you can see how many indexed pages you have. This number is only approximate, as Google will not give you the exact number, but you can take a deeper indexing analysis in the Search Console under the Index Status section.
You probably have an idea how big your site is, so if the number of indexed pages is too low or, on the contrary, it seems to be high, you need to identify the cause.
You can find the most common technical problems with indexations pretty fast. If you think you have some, you can analyze it in an on-page SEO audit tool, as I will show you below in Steps 4 and 5.
Step 2: Detecting a possible penalty from Google
If your site has been hit by a penalty from Google, you’d probably suspect it already. But sometimes it can happen that you don’t know about penalization because you didn’t notice any large drop in organic traffic. That’s why I recommend that you make sure that Google is completely fine with your site.
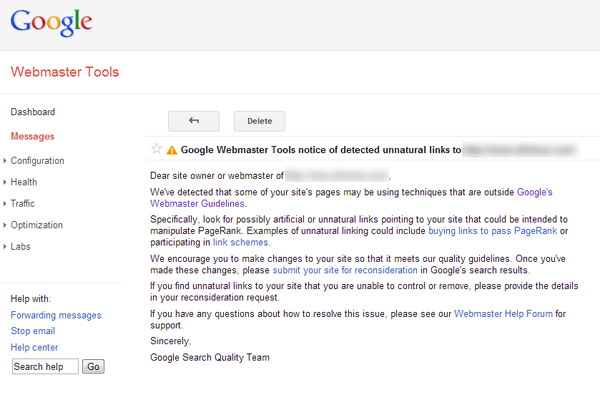
The best way how to find any problems with your site is by visiting Google Search Console. It is a handy tool for developers and marketers as well. If something is not as it should be, you will find it in Search Console messages:
In case you are unlucky and find that you have a penalty from Google because, for example, you hired the wrong SEO person in the past, you can still recover from it. So, don’t worry.
Step 3: Finding hidden text
The search engines and visitors can see page content differently because of implemented CSS styles or JavaScript language.
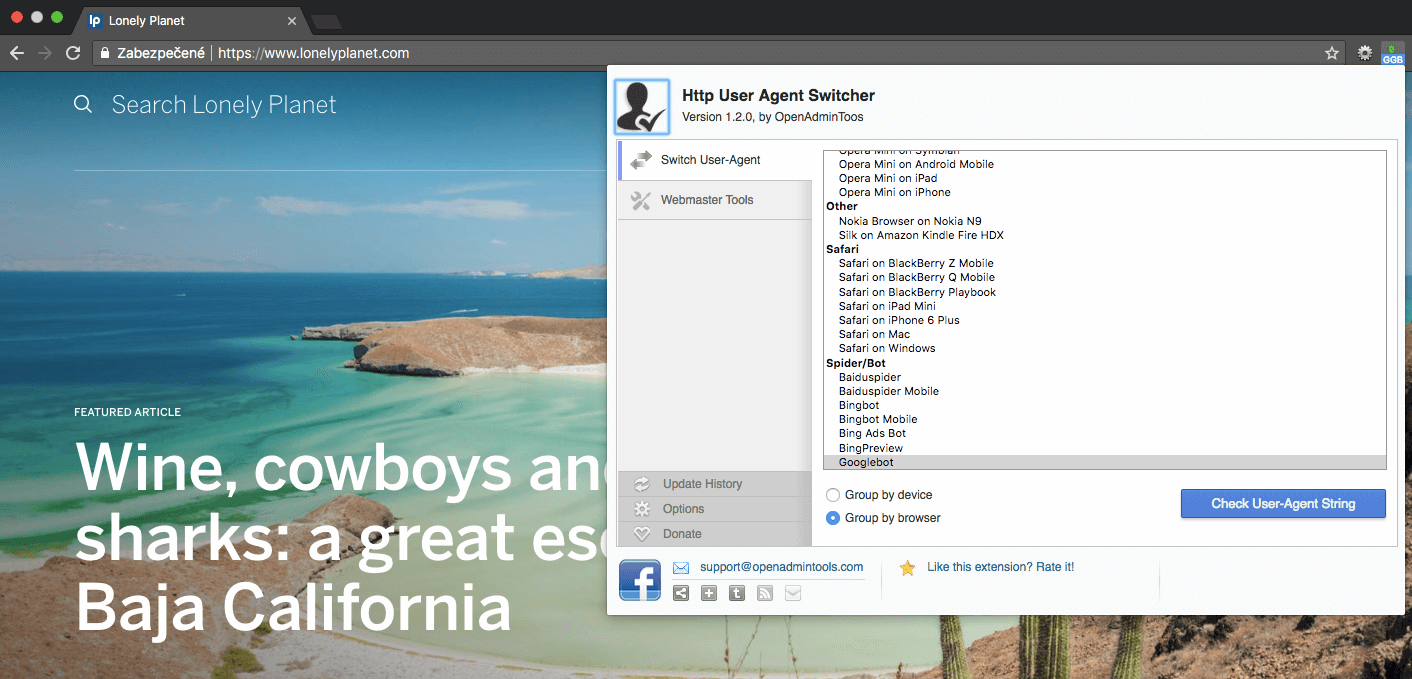
But, you can look at your page through the eyes of Googlebot, as well, and check for hidden text. Or, on the contrary, you can see text that should be seen but is hidden by JS. In order to do that, you can turn off CSS and JS with the Web Developer tool browser add-on.
The biggest problem that can occur is hidden text on the site. Of course, it can be created unwillingly, but Google doesn’t know that, and it can lead to penalization.
The hidden text can be a big problem, also from a different point of view. If there is any text on your site that needs to trigger an action, like click or scroll, that creates a problem for the search engine to render and, at the end, to index.
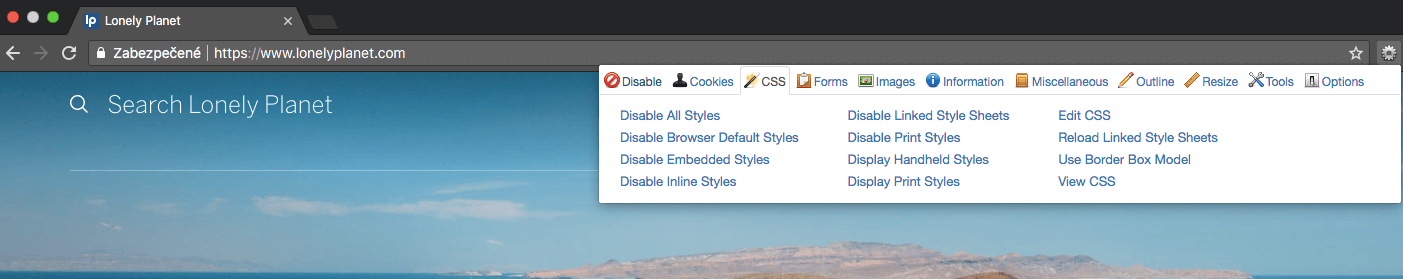
How to proceed when using the add-on:
Change options:
- Disable All Styles in section CSS
- Disable JavaScript in section Disable
Reload the page so you are sure CSS and JS are both disabled. Compare the content with CSS turned off, and then with the CSS turned on. If there is anything different, find out why. In most cases, the best practice is to delete or edit hidden CSS, as it is most likely leading to damaging the site.
If you find differences between having JavaScript on and off, read the guide to Javascript from Tomasz Rudzki, where he recommends developers make sure the JavaScript files can be downloaded and executed in under five seconds. Everything loaded afterwards can be ignored by the majority of search engines and by Google.
You can also double-check with the HTTP User Agent Switcher, where you can switch the user agent to Googlebot (also for the mobile version and other bots).
Step 4: Running a speed test
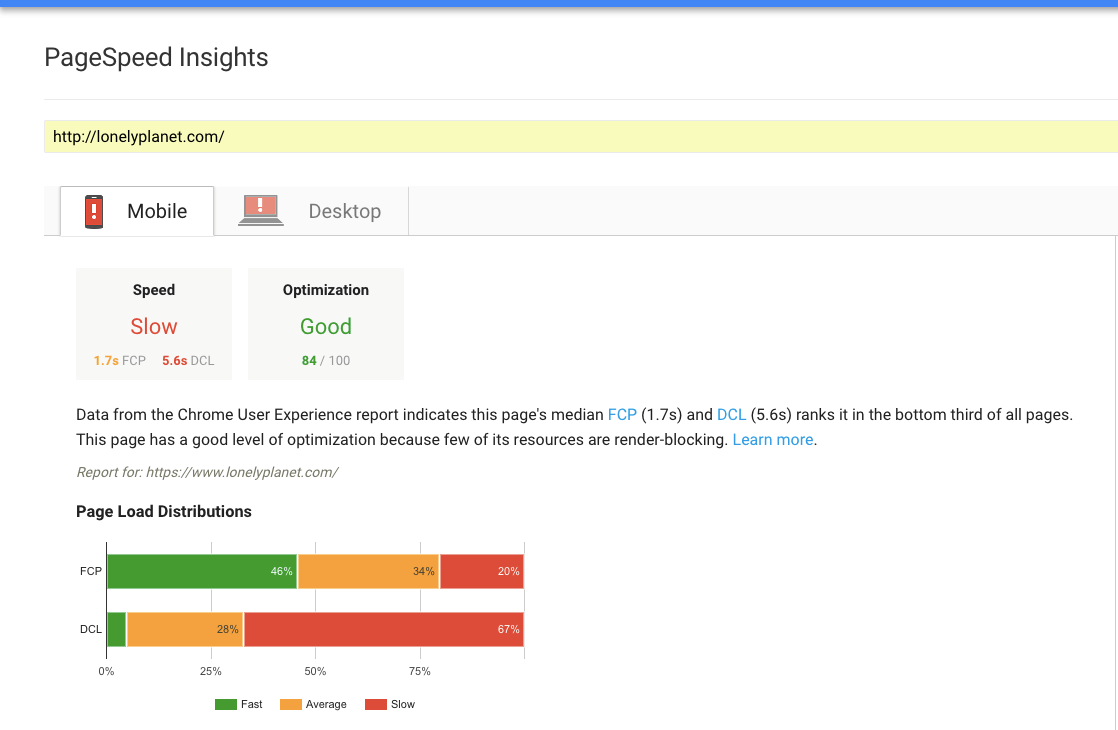
Nobody likes sites that are loading for eternity. Page Speed is one of the most important SEO metrics as it has become a ranking factor for mobile devices in July 2018.
If you optimize the mobile version, simultaneously, you will also improve the desktop version. A reliable tool that you can use is PageSpeed Insights from Google.
Generally speaking, the better is your page speed the better is the UX.
Step 5: Analyzing on-page factors
As I already mentioned at the beginning of the article, you can find many SEO checklists on the internet. Some of them are probably very useful, but many of them focus on unimportant issues that can’t really harm organic traffic. That is usually because search engines and UI are going forward so fast that many factors are just not important anymore.
Here is my list of issues that are a MUST when you do an SEO audit:
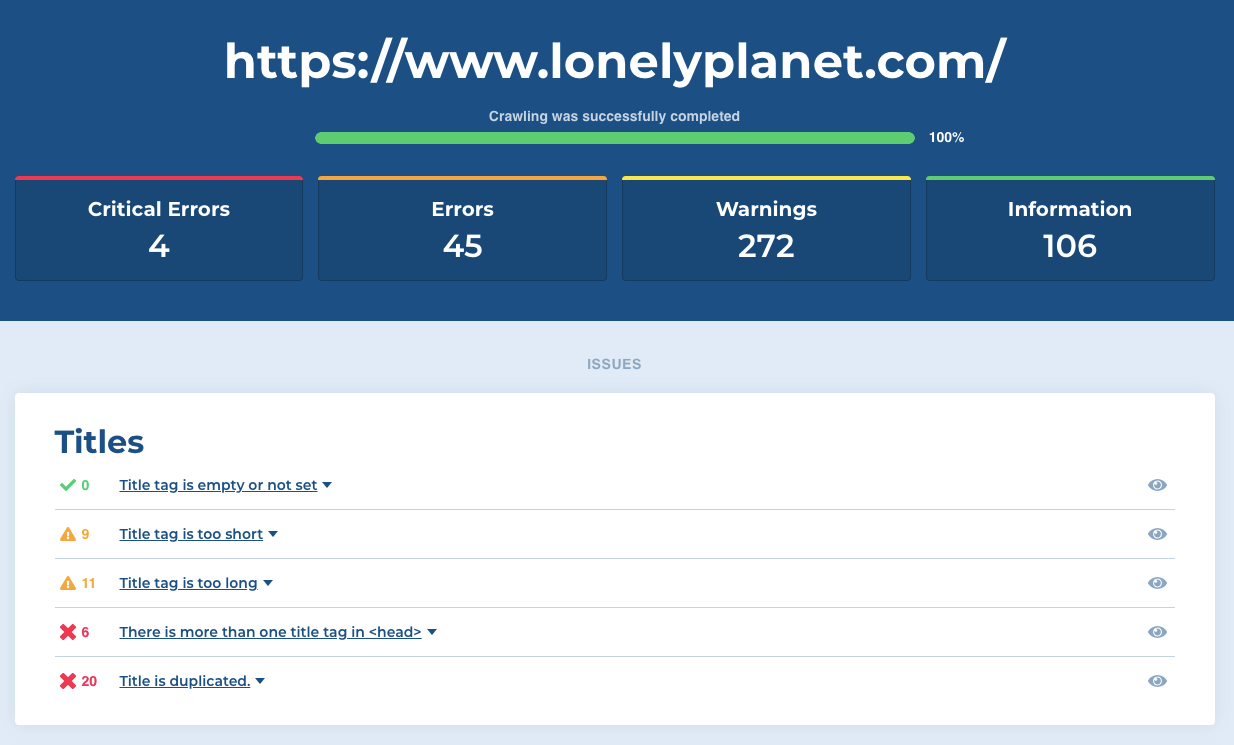
- Titles
- H1 headings
- Meta descriptions
- Images
- Redirections
- Duplicate pages
- Internal links
- Page crawling and indexation
- Not found and server errors
Most of the issues with the worst impact on SEO can be found with the SEO audit tool Spotibo.
Even if the following steps might seem long or too much work to read, you will go through it very fast.
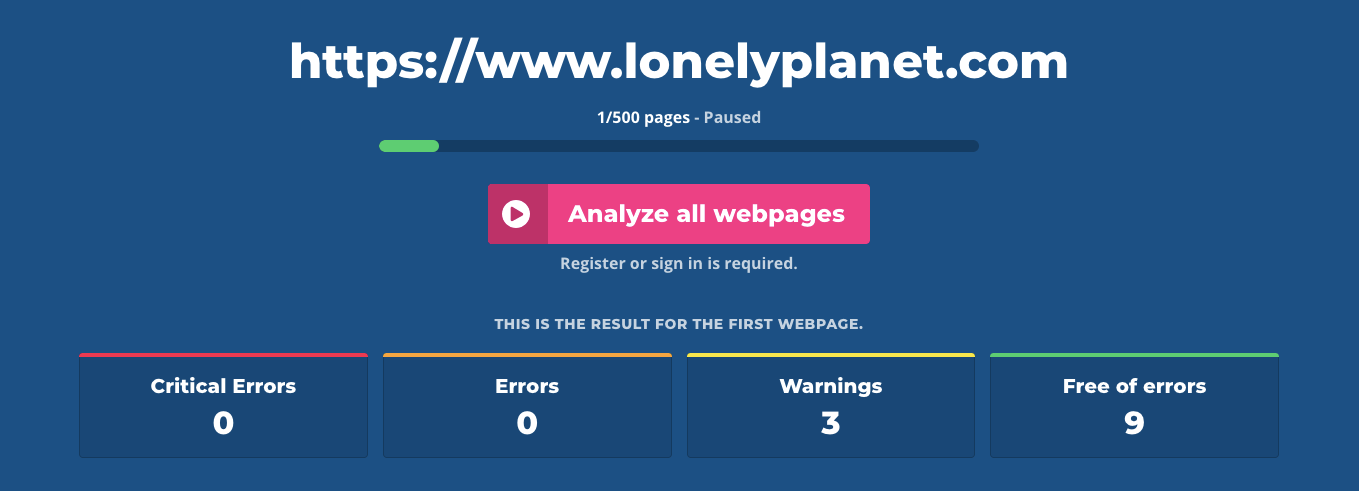
At first, let’s check issues for the homepage. I’ll try it with Lonely Planet.
Only three warnings regarding on-page factors were found for the first page.
But the results of one URL is just not enough. One web page usually generates minimum traffic, so you should also look at the web as a whole. Analyzing hundreds of pages can reveal multiple problems.
On the Lonely Planet website, most issues include empty or unoptimized titles, as well as error pages and problems with indexation and crawling.
Step 6: Analyzing a particular issue
What to do next with identified issues and affected URLs? After you click on the issue, you see its description and possible solution.
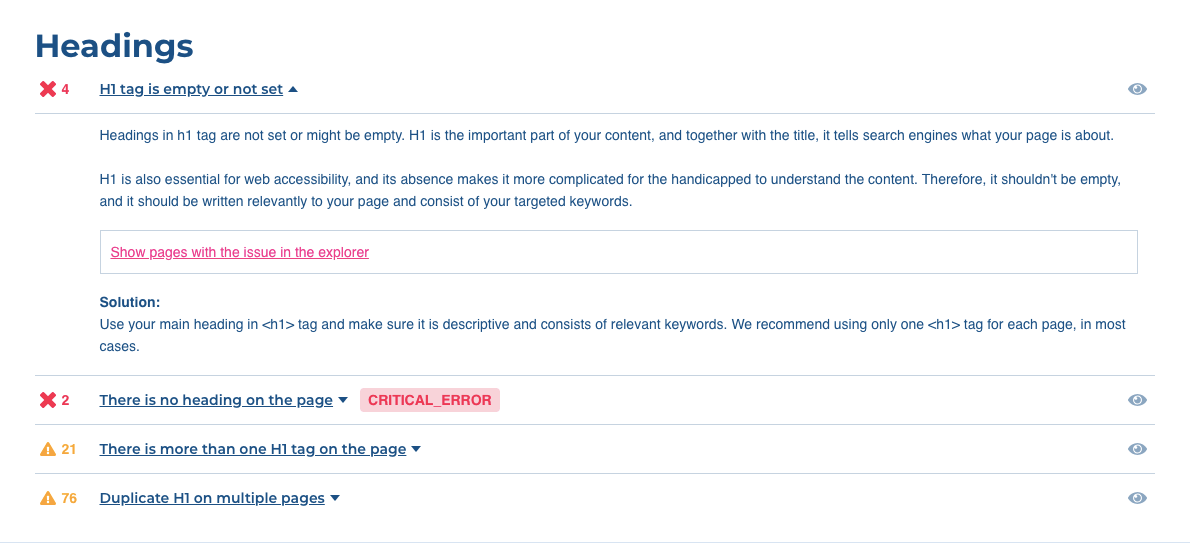
Let’s look at the issue Heading is empty or not set.
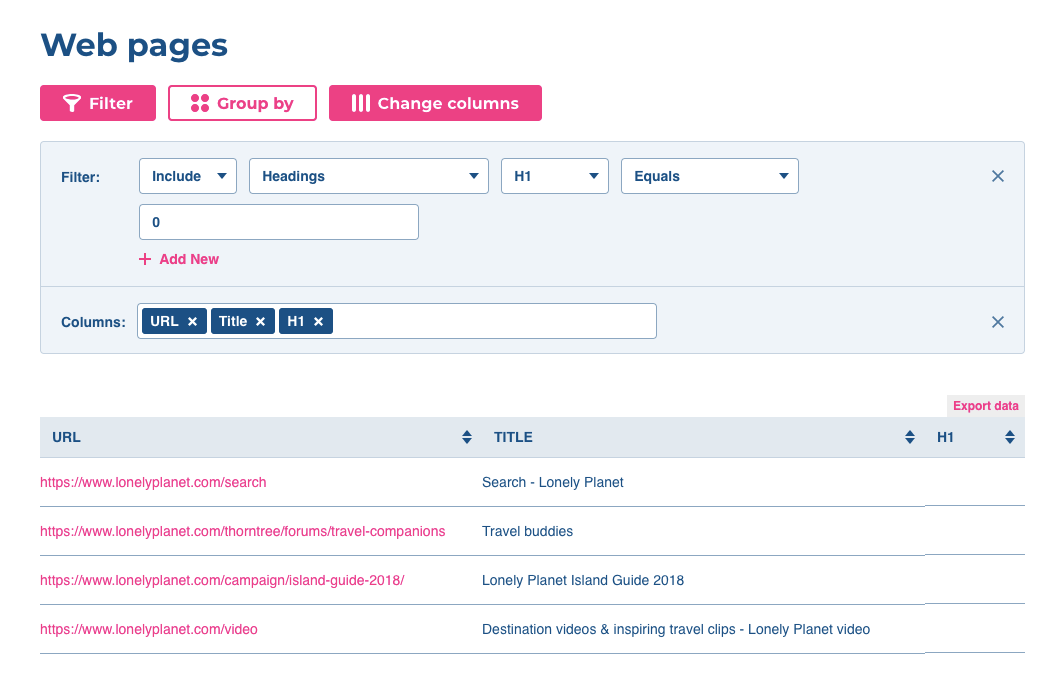
Click on the “eye” symbol and you will get a list of URLs with empty headings in one table.
For small websites, it’s easier to identify problems, because there are usually fewer web pages. For bigger websites, you have to think about the on-page problems from a wider perspective.
- Is the URL important as a landing page for organic traffic?
- Does the URL need an H1 heading?
If the answer to these questions is YES, fix it. Create a main H1 heading for each page. If the answer is NO, you can ask Google to hide the pages.
For instance, look at the Lonely Planet pages listed in the table with empty H1 heading tags. The URL https://www.lonelyplanet.com/campaign/island-guide-2018/ could be a nice landing page for users searching for “Island guide.” The heading is very important and that is a great reason to write H1 on this page.
One by one, you can analyze every issue like this and dig deeper into finding the additional information that is needed.
Conclusion
On-page and technical SEO analysis is not as hard as you may think. With tools that are available nowadays, it can be done very fast and accurately.
However, be careful what checklist and SEO checkers you find on the internet and verify that they are not out of date.
If you want to do a quick on-page SEO analysis for a website you are currently on, make sure check the Mangools SEO extension.
The on-page SEO audit can be done online for smaller websites, but I wouldn’t recommend using it for a website with thousands of pages. Large sites are very complex, and that’s why it is better to hire a professional for that scale of an SEO audit.